【yield 详解 协同程序 生成器表达式】
1》 yield
def res ():
for i in range(10):
x = yield i
r = res()
print r.next()
print r.next()
print r.next()
我们来详细的分析下这个程序的执行
r =res() 我们知道 res方法里面有yield关键字 那么这个方法就被认为是一个 generator
那么 yield i 和 x = yield i 的功能上面的区别的就是 x = yield i 可以通过 send 修改表达式的值
yield i 可以理解加了挂起之后的return
而 x = yileld i 这个表达式
则能够挂机的return + 能够在外部修改返回值
def res ():
for i in range(10):
yield i
print '[1]',i
yield i + 1
print '[2]',i
r = res()
print r.next()
print r.next()
如果一个方法里面有两个yield 那么实际上是 这个方法会挂起两次 一次next 只能解除一次挂起
def psychologist():
print 'Please tell me your problems'
while 1:
res=(yield 3)
if res is not None:
if res.endswith('?'):
print ("Don't ask you self too much questions")
elif 'good' in res:
print "A that's good .go on "
elif 'bad' in res:
print "Don't be so negative"
else :
print 'res is None'
free = psychologist()
print '[0]',free.next()
print '[1]',free.next()
print '[2]',free.send("I feel bad")
print '[3]',free.send("Are you OK?")
print '[4]',free.send("I'm a good boy")
然后我们再来看这个代码 就简答很多了
res = yield 3
这里 执行next 或者send 的返回值都是 3 这个是不变的
而 res的值 会随着send 的变化而变化
这里我们可以吧next 看做 send(None)
第一次执行next() 会挂起在 yeild 哪里 所有 输出会是 : [0] 3
第二次执行 next() 就相当于 send(None)此时res = None 则会输出 :[1] res is None 3
最终的全部输出
[0] 3 [1] res is None 3 [2] Don't be so negative 3 [3] Don't ask you self too much questions 3 [4] A that's good .go on 3
然后 和send 相匹配的函数还有两个
throw :允许客户端代码传入要抛出的任何类型 的异常
close:跟throw 类似 但是只会抛出一个特定的异常 GeneratorExit 在这种情况下 生成器必须在抛出GeneratorExit 或Stopteration
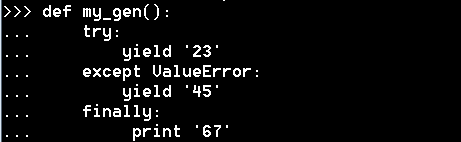
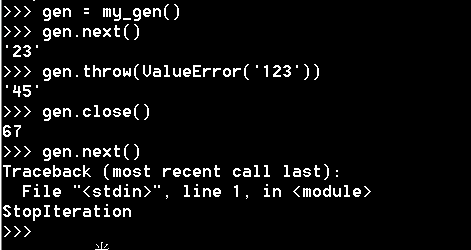
可以在外部 让代码内部抛出异常
那么有了这三个特性我们就能通过生成器来编写协程
2》协程
定义:协同程序是可以挂起,恢复,并且有多个进入点的程序
import multitask
def A1():
for i in range(3):
print 'A1',i
yield i
print 'in A'
def B1():
for i in range(3):
print 'B1',i
yield i
print 'in B'
multitask.add(A1())
multitask.add(B1())
multitask.run()
输出
A1 0 B1 0 in A A1 1 in B B1 1 in A A1 2 in B B1 2 in A in B
multitask这个模块在这里实现了这一模式 一旦执行到yield这个关键字那么久挂起执行另一个函数的代码
我们可以自己写一个类似的程序
def A1():
for i in range(3):
print 'A1',i
yield i
print 'in A'
def B1():
for i in range(3):
print 'B1',i
yield i
print 'in B'
import Queue
class my_task():
def __init__(self):
self._queue = Queue.Queue()
def add(self,res):
self._queue.put(res)
def run(self):
while not self._queue.empty():
for i in xrange(self._queue.qsize()):
try:
gen = self._queue.get()
gen.send(None)
except StopIteration:
pass
else:
self._queue.put(gen)
t = my_task()
t.add(A1())
t.add(B1())
t.run()
这段代码比较复杂了
我们来,了解下 queue 是先进先出的
这样就能很好的理解这个代码了
举个例子 小明和小强在玩游戏机 但是只有一个手柄 他们觉得达成协议 玩超级马里奥 然后一人玩一条命 一直到有一方通关
这里的手柄就是队列 ,通过队列实现这一效果
def a1():
for x in range(4):
print x
yield x
def a2():
for x in range(4,8):
yield x
threads=[]
threads.append(a1())
threads.append(a2())
def run(threads):
while len(threads) != 0 :
for i in threads:
try:
print i.next()
except StopIteration:
pass
else:
threads.append(i)
run(threads)
当然我们也可以通过其他方式来实现这一效果
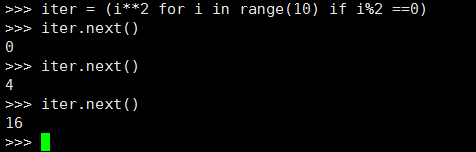
3》生成器表达式
python 里面为了方便写简单的生成器 提供一个方法 类似于列表推导
用(方法 循环 条件)