异步执行一般用来发送一些消息数据,数据一致性不要求太高的场景,对于spring来说,它把这个异步进行了封装,使用一个注解就可以实现。
Spring中通过在方法上设置@Async注解,可使得方法被异步调用。也就是说该方法会在调用时立即返回,而这个方法的实际执行交给Spring的TaskExecutor去完成。
用法
- 程序启动时开启
@EnableAsync注解 - 建立新的类型,建立
异步方法,为方法添加@Async注解 -
在业务代码中,
@Autowired注入你的类型,使用它即可
我们可以关注到在配置task的时候,是有参数让我们配置线程池的数量的。因为这种实现方法,所以在同一个类中的方法调用,添加@async注解是失效的!,原因是当你在同一个类中的时候,方法调用是在类体内执行的,spring无法截获这个方法调用.
事例
Spring的配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task.xsd"> <!-- 包扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.gdut"/> <!-- 执行异步任务的线程池TaskExecutor --> <task:executor id="myexecutor" pool-size="5" /> <task:annotation-driven executor="myexecutor"/> </beans>
如果是在springboot项目中使用的话,则更加简单。只需要在启动类上面加一个注解:@EnableAsync即可,如:
package com.gdut; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; @SpringBootApplication @EnableAsync //开启异步调用 public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); } }
接下来我们要进入实例部分,我通过一个聊天对话的demo来介绍。
调用方法依次为1,2,3。现在我想实现的是如下场景:
(1)A:你爱我吗?
(3)A:你不回我,肯定不爱我,分手吧!
(2)B:当然爱你!(这里假设有延迟,导致消息不及时,A没有收到)
如果这里不用异步实现的话,在3之前一定会等到2完成,所以最终导致对话是:
(1)A:你爱我吗?
(2)B:当然爱你!(没有延迟的情况下)
(3)A:你不回我,肯定不爱我,分手吧!
不符合我们的要求,所以这里我们必须采用的是异步。
现在我们先什么都不加,相关代码如下:
package com.gdut.conponent; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class ChatTest { public void chat1(){ System.out.println("你爱我吗?"); } public void chat2(){ try { Thread.sleep(2*1000); System.out.println("等了大概2秒...!"); System.out.println("当然爱呀!"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void chat3(){ System.out.println("你回的这么慢,肯定不爱我。分手!"); } }
package com.gdut.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.gdut.conponent.ChatTest; @RestController @RequestMapping("/chat") public class ChatController { @Autowired private ChatTest chatTest; @RequestMapping("/chatTest") public String chatTest(){ chatTest.chat1(); chatTest.chat2(); chatTest.chat3(); return "成功"; } }
console输出:
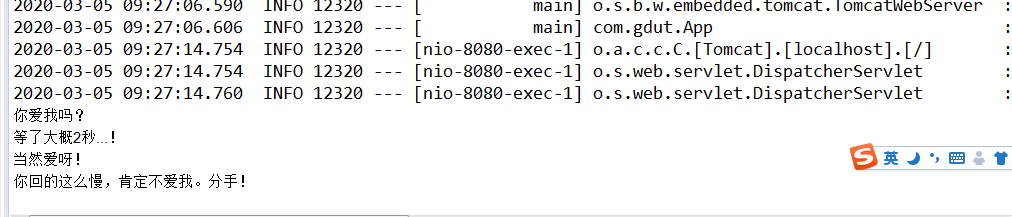
可以看到我们的目的还没有达到,现在我们在chat2方法上面加上@Async注解
package com.gdut.conponent; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class ChatTest { public void chat1(){ System.out.println("你爱我吗?"); } @Async public void chat2(){ try { Thread.sleep(2*1000); System.out.println("等了大概2秒...!"); System.out.println("当然爱呀!"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void chat3(){ System.out.println("你回的这么慢,肯定不爱我。分手!"); } }
console输出:
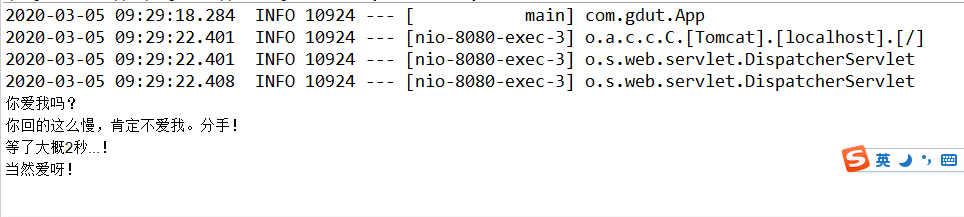
在调用方法3的时候,还没有等到方法2执行结束便执行了3。所以才能达到我们最终的情境。
Async几种方式
1:没有返回值的,不会阻塞主线程,相当于开启新线程在后台执行这个任务
@Async public String sayHello2() throws InterruptedException { Thread.sleep(2 * 1000);//网络连接中 。。。消息发送中。。。 return "我爱你啊!";// 调用方调用后会立即返回,所以返回null }
2:带有返回值的,返回类型必须为Future<>,它会开启新的线程执行任务,并阻塞主线程,执行完成后把结果返回给主线程
@Async public Future<String> asyncFunc() throws InterruptedException { int thinking = 2; Thread.sleep(thinking * 1000); System.out.println("async!"); return new AsyncResult<String>("发送消息用了" + thinking + "秒"); }
调用方法
@GetMapping("/lind-demo/asyncFunc")
public void async() throws Exception {
Future<String> future = null;
future = asyncService.asyncFunc();
System.out.println(future.get());
System.out.println("主线程被阻塞执行完成");
}
执行结果
async!
发送消息用了2秒
主线程执行完成
@Async的使用注意点
- 返回值:不要返回值直接void;需要返回值用AsyncResult或者CompletableFuture
- 所使用的@Async注解方法的类对象应该是Spring容器管理的bean对象
- 调用异步方法类上需要配置上注解@EnableAsync
- 可自定义执行器并指定例如:@Async("otherExecutor")
@Async必须不同类间调用: A类—>B类.C方法()(@Async注释在B类/方法中),如果在同一个类中调用,会变同步执行,例如:A类.B()—>A类.@Async C()。- @Async也可以加到类,表示这个类的所有方法都是异步执行,并且方法上的注解会覆盖类上的注解。但一般不这么用!
总结
其实在我们实际应用中,大多数方法都是用同步的。但是在处理与第三方系统交互的时候,容易造成响应迟缓的情况,之前大部分都是使用多线程来完成此类任务,其实,在spring 3.x之后,就已经内置了@Async来完美解决这个问题。