oracle10g以上支持正则表达式的函数主要有下面四个:
1、REGEXP_LIKE :与LIKE的功能相似
2、REGEXP_INSTR :与INSTR的功能相似
3、REGEXP_SUBSTR :与SUBSTR的功能相似
4、REGEXP_REPLACE :与REPLACE的功能相似
POSIX 正则表达式由标准的元字符(metacharacters)所构成:
'^' 匹配输入字符串的开始位置,在方括号表达式中使用,此时它表示不接受该字符集合。
'$' 匹配输入字符串的结尾位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,则 $ 也匹配 '
' 或 '
'。
'.' 匹配除换行符之外的任何单字符。
'?' 匹配前面的子表达式零次或一次。
'+' 匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。
'*' 匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。
'|' 指明两项之间的一个选择。例子'^([a-z]+|[0-9]+)$'表示所有小写字母或数字组合成的字符串。
'( )' 标记一个子表达式的开始和结束位置。
'[]' 标记一个中括号表达式。
'{m,n}' 一个精确地出现次数范围,m=<出现次数<=n,'{m}'表示出现m次,'{m,}'表示至少出现m次。
um 匹配 num,其中 num 是一个正整数。对所获取的匹配的引用。
字符集:
[[:alpha:]] 任何字母。
[[:digit:]] 任何数字。
[[:alnum:]] 任何字母和数字。
[[:space:]] 任何白字符。
[[:upper:]] 任何大写字母。
[[:lower:]] 任何小写字母。
[[:punct:]] 任何标点符号。
[[:xdigit:]] 任何16进制的数字,相当于[0-9a-fA-F]。
各种操作符的运算优先级
转义符
(), (?:), (?=), [] 圆括号和方括号
*, +, ?, {n}, {n,}, {n,m} 限定符
^, $, anymetacharacter 位置和顺序
|
*/
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
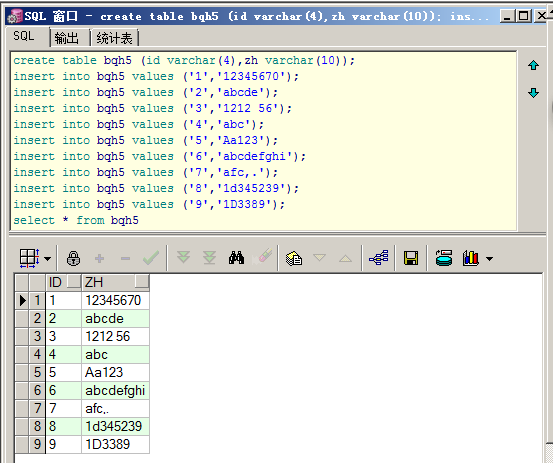
创建测试环境:
create table bqh5 (id varchar(4),zh varchar(10));
insert into bqh5 values ('1','12345670');
insert into bqh5 values ('2','abcde');
insert into bqh5 values ('3','1212 56');
insert into bqh5 values ('4','abc');
insert into bqh5 values ('5','Aa123');
insert into bqh5 values ('6','abcdefghi');
insert into bqh5 values ('7','afc,.');
insert into bqh5 values ('8','1d345239');
insert into bqh5 values ('9','1D3389');
select * from bqh5
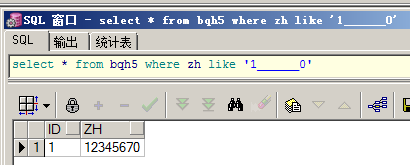
查询zh中以1开头0结束的并且长度是8位的数据:
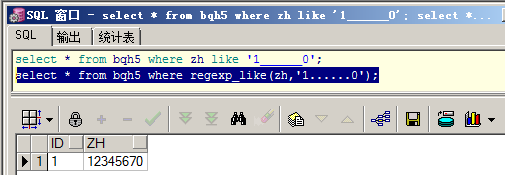
select * from bqh5 where zh like '1______0'
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'1......0');
查询zh中以1开头0结束的并且长度是8位并且全部时数字的数据:
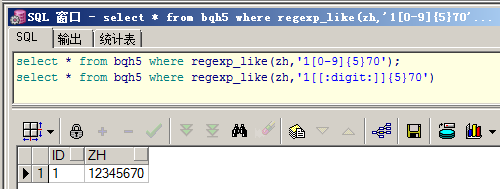
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'1[0-9]{5}70');
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'1[[:digit:]]{5}70')
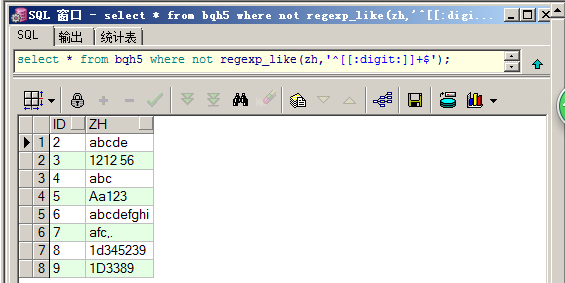
查询zh中不是纯数字的数据:
select * from bqh5 where not regexp_like(zh,'^[[:digit:]]+$');
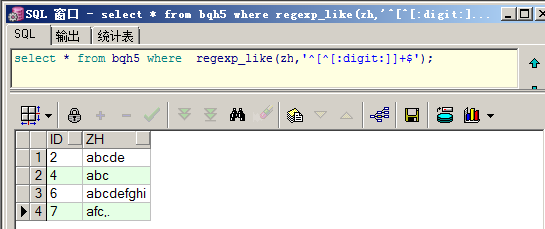
查询zh中不含任何数字的数据:
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'^[^[:digit:]]+$');
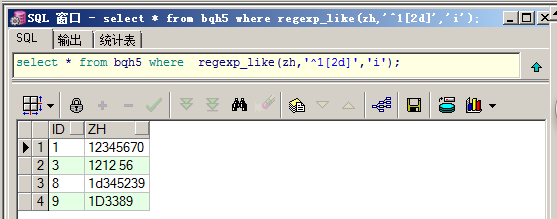
查询以12或者以1d开头的数据,不区分大小写:
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'^1[2d]','i');
查询以12或者以1d开头的数据,区分大小写:
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'^1[2D]');
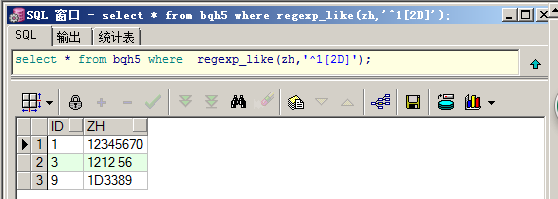
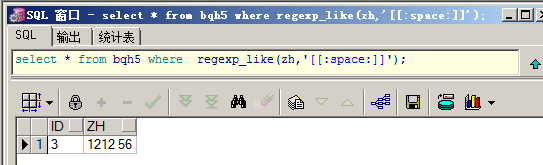
查询包含空格的数据:
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'[[:space:]]');
查询包含标点符号的数据:
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'[[:punct:]]');

查询包含数字或者字母的数据:
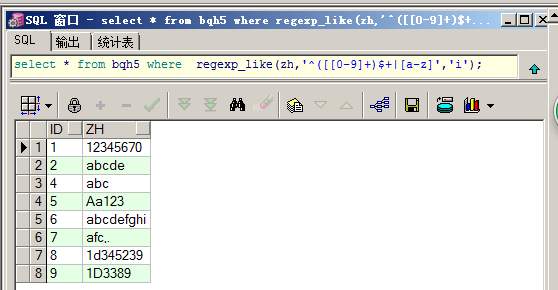
select * from bqh5 where regexp_like(zh,'^([[0-9]+)$+|[a-z]','i');