栈(stack)是简单的数据结构,但在计算机中使用广泛。它是有序的元素集合。栈最显著的特征是LIFO (Last In, First Out, 后进先出)。当我们往箱子里存放一叠书时,先存放的书在箱子下面,我们必须将后存放的书取出来,才能看到和拿出早先存放的书。

栈中的每个元素称为一个frame。而最上层元素称为top frame。栈只支持三个操作, pop, top, push。
pop取出栈中最上层元素(8),栈的最上层元素变为早先进入的元素(9)。
top查看栈的最上层元素(8)。
push将一个新的元素(5)放在栈的最上层。
栈不支持其他操作。如果想取出元素12, 必须进行3次pop操作。
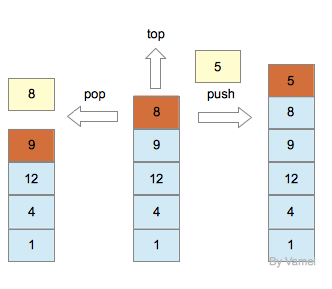
栈以及pop, push, top操作
栈最经典的计算机应用是函数调用。每个进程都会有一个栈,每个frame中记录了调用函数的参数,自动变量和返回地址。当该函数调用一个新的函数时,栈中会 push一个frame。当函数执行完毕返回时,该frame会pop,从而进入调用该函数的原函数,继续执行。详细请参阅Linux从程序到进程
实际使用的栈并不一定符合数据结构的栈。比如说,有的语言允许被调用函数查看非top frame的记录。这样的栈更类似于下面的经典游戏

栈的C实现 (基于表)
由于栈是限定了操作的有序的元素集合,所以我们既可以在数组的基础上来实现栈,也可以在表的基础上来实现栈。如果使用数组来实现栈,我们需要预留充足的空间供栈使用,并需要一个下标来记录最上层元素的位置。
我们这里使用单向链表来实现栈。我们可以利用介绍表(list)的文章中已经定义的操作来实现三个操作,但这里相对独立的重写了代码。
/* By Vamei */
/* use single-linked list to implement stack */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node *position;
typedef int ElementTP;
// point to the head node of the list
typedef struct node *STACK;
struct node {
ElementTP element;
position next;
};
STACK init_stack(void);
void delete_stack(STACK);
ElementTP top(STACK);
void push(STACK, ElementTP);
ElementTP pop(STACK);
int is_null(STACK);
void main(void)
{
ElementTP a;
int i;
STACK sk;
sk = init_stack();
push(sk, 1);
push(sk, 2);
push(sk, 8);
printf("Stack is null? %d
", is_null(sk));
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
a = pop(sk);
printf("pop: %d
", a);
}
printf("Stack is null? %d
", is_null(sk));
delete_stack(sk);
}
/*
* initiate the stack
* malloc the head node.
* Head node doesn't store valid data
* head->next is the top node
*/
STACK init_stack(void)
{
position np;
STACK sk;
np = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
np->next = NULL; // sk->next is the top node
sk = np;
return sk;
}
/* pop out all elements
* and then delete head node
*/
void delete_stack(STACK sk)
{
while(!is_null(sk)) {
pop(sk);
}
free(sk);
}
/*
* View the top frame
*/
ElementTP top(STACK sk)
{
return (sk->next->element);
}
/*
* push a value into the stack
*/
void push(STACK sk, ElementTP value)
{
position np, oldTop;
oldTop = sk->next;
np = (position) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
np->element = value;
np->next = sk->next;
sk->next = np;
}
/*
* pop out the top value
*/
ElementTP pop(STACK sk)
{
ElementTP element;
position top, newTop;
if (is_null(sk)) {
printf("pop() on an empty stack");
exit(1);
}
else {
top = sk->next;
element = top->element;
newTop = top->next;
sk->next = newTop;
free(top);
return element;
}
}
/* check whether a stack is empty*/
int is_null(STACK sk)
{
return (sk->next == NULL);
}
输出结果:
Stack is null? 0
pop: 8
pop: 2
pop: 1
Stack is null? 1
总结
栈, LIFO
pop, push, top
欢迎继续阅读“纸上谈兵: 算法与数据结构”系列。
Update:
我之前是用双向循环链表实现的栈,后来发现这样没有必要。它不能给栈带来额外的好处,还会增加所需的内存空间。
