---恢复内容开始---
1.代码的基本使用
// 1.创建UIButton对象 // UIButton *btn = [[UIButton alloc] init]; // 通常情况下使用按钮都是设置custom类型 UIButton *btn = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeCustom]; // 2.设置类型 // 注意:如果想要设置btn的类型,必须在初始化的时候设置 // btn.buttonType = UIButtonTypeContactAdd; // 3.设置frame(位置和尺寸) btn.frame = CGRectMake(100, 100, 175, 50); // 4.设置背景颜色 // btn.backgroundColor = [UIColor yellowColor]; // btn setBackgroundColor:<#(UIColor * _Nullable)#> // 5.设置显示的文字 // 注意:如果设置按钮的文字,必须告诉系统该文字在什么状态下显示 // btn.titleLabel.text = @"普通按钮"; [btn setTitle:@"普通按钮" forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [btn setTitle:@"高亮按钮" forState:UIControlStateHighlighted]; // 6.设置文字的颜色 [btn setTitleColor:[UIColor redColor] forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [btn setTitleColor:[UIColor blueColor] forState:UIControlStateHighlighted]; // 7.设置按钮的图片 // 注意:如果设置按钮的图片,必须告知系统该图片在什么状态下显示 // btn.imageView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:@"player_btn_pause_normal"]; [btn setImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"player_btn_pause_normal"] forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [btn setImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"player_btn_pause_highlight"] forState:UIControlStateHighlighted]; // 设置imageView的背景 设置button的背景颜色 // btn.imageView.backgroundColor = [UIColor purpleColor]; btn.imageView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeScaleAspectFit; // 8.设置背景图片 [btn setBackgroundImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"buttongreen"] forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [btn setBackgroundImage:[UIImage imageNamed:@"buttongreen_highlighted"] forState:UIControlStateHighlighted]; // 将button对象添加到控制器的View中 [self.view addSubview:btn]; // 重要:代码创建的按钮,监听点击 // Target : 目标,谁想做事情. // action : 要执行的方法(发送消息) // Events : touchUpInside // SEL sel = ; UIButton通过代码设置监听 [btn addTarget:self action:@selector(btn1Click:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; }
总结:设置背景图片 设置图片
1.设置背景图片,如果图片的尺寸比按钮的尺寸要大,则图片尺寸变成Button的尺寸
2.设置button中imageView的image的时,如果图片的尺寸比按钮大,这按钮的尺寸会谁图片的尺寸而变大 在stordBoard中中测试过
跟 /* 监听的方法 - (IBAction)btnClick { self.btn.enabled = NO; } */ - (IBAction)btnClick:(UIButton *)sender { sender.enabled = NO; } - (void)btn1Click:(UIButton *)btn { NSLog(@"%@", btn); } - (void)demo { NSLog(@"%s", __func__); }
2.九宫格案例推倒出懒加载
@interface ViewController () // 购物车的View @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIView *shopCartView; // 添加商品和移除商品的按钮 @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *removeProductBtn; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *addProductBtn; // 商品的数据 定义一个数组保存数据 @property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *products; @end @implementation ViewController //- (void)loadView //{ // //} - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; // 加载数据 /* self.products = @[ 如果放在这里加载数据的话,虽然数据只会加载一次,但是不管程序在启动的时候都会加载一次 @{@"icon" : @"liantiaobao", @"title" : @"链条包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shoutibao", @"title" : @"手提包"}, @{@"icon" : @"danjianbao", @"title" : @"单肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shuangjianbao", @"title" : @"双肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"xiekuabao", @"title" : @"斜挎包"}, @{@"icon" : @"qianbao", @"title" : @"钱包"} ]; */ } /* - (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated { } - (void)viewWillLayoutSubviews { } - (void)viewDidLayoutSubviews { } - (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated { } */ #pragma mark - 添加和移除商品 #pragma mark 添加商品 - (IBAction)addProduct:(UIButton *)sender { /********************** 1.常亮 *****************************/ // 1.1.定义一些常亮 CGFloat width = 70; CGFloat height = 100; // 1.2.计算常亮 九宫格的计算方式 CGFloat hMargin = (self.shopCartView.frame.size.width - 3 * width) / 2; CGFloat vMargin = (self.shopCartView.frame.size.height - 2 * height) / 1; NSInteger index = self.shopCartView.subviews.count; CGFloat x = index % 3 * (hMargin + width); X方向上取余 CGFloat y = index / 3 * (vMargin + height); Y方向上相除 /********************** 2.添加商品的View *****************************/ // 2.1.创建商品的View UIView *productView = [[UIView alloc] init]; // 2.2.设置frame productView.frame = CGRectMake(x, y, width, height); // 2.3.添加到购物车的View中 [self.shopCartView addSubview:productView]; // 2.4.添加UIImageView对象用于显示商品的图片 UIImageView *iconView = [[UIImageView alloc] init]; iconView.frame = CGRectMake(0, 0, width, width); [productView addSubview:iconView]; // 2.5.添加UILabel对象用于显示商品的名字 UILabel *titleLabel = [[UILabel alloc] init]; titleLabel.frame = CGRectMake(0, width, width, height - width); titleLabel.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter; [productView addSubview:titleLabel]; // 2.6.设置展示的数据 /* NSArray *products; if (self.products == nil) { 这种方法做到了用到时加载,并且通过判断只加载一次,但是代码阅读性非常差
// 实际开发中,不要将数据和代码混在一起
// 从资源包中加载products.plist文件
// 1.获取plist文件的路径
products = @[ @{@"icon" : @"liantiaobao", @"title" : @"链条包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shoutibao", @"title" : @"手提包"}, @{@"icon" : @"danjianbao", @"title" : @"单肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shuangjianbao", @"title" : @"双肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"xiekuabao", @"title" : @"斜挎包"}, @{@"icon" : @"qianbao", @"title" : @"钱包"} ]; } self.products = products; */ /* if (self.products == nil) { self.products = @[ @{@"icon" : @"liantiaobao", @"title" : @"链条包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shoutibao", @"title" : @"手提包"}, @{@"icon" : @"danjianbao", @"title" : @"单肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shuangjianbao", @"title" : @"双肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"xiekuabao", @"title" : @"斜挎包"}, @{@"icon" : @"qianbao", @"title" : @"钱包"} ]; } */ NSDictionary *productDict = self.products[index]; iconView.image = [UIImage imageNamed:productDict[@"icon"]]; titleLabel.text = productDict[@"title"]; /********************** 3.判断按钮的状态 *****************************/ // 3.1.判断添加商品的按钮状态 判断按钮的状态 sender.enabled = self.shopCartView.subviews.count != 6; // 3.2.让移除按钮可以点击 self.removeProductBtn.enabled = YES; } #pragma mark 移除商品 - (IBAction)removeProduct:(UIButton *)sender { // 1.取出最后一个商品,并且移除掉 UIView *lastProduct = [self.shopCartView.subviews lastObject]; [lastProduct removeFromSuperview]; // 2.判断按钮的状态 // 2.1.判断移除按钮的状态 sender.enabled = self.shopCartView.subviews.count; // 2.2.判断添加按钮的状态 self.addProductBtn.enabled = YES; } - (void)demo { NSDictionary *productDict = self.products[2]; } #pragma mark - 懒加载代码 /* 懒加载的步骤 1.定义成员变量 2.重写get方法 3.在get方法中判断,变量是否有值,如果没有值,则加载数据,如果有值,直接返回 */ - (NSArray *)products { if (_products == nil) { _products = @[ @{@"icon" : @"liantiaobao", @"title" : @"链条包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shoutibao", @"title" : @"手提包"}, @{@"icon" : @"danjianbao", @"title" : @"单肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"shuangjianbao", @"title" : @"双肩包"}, @{@"icon" : @"xiekuabao", @"title" : @"斜挎包"}, @{@"icon" : @"qianbao", @"title" : @"钱包"} ]; } return _products; }
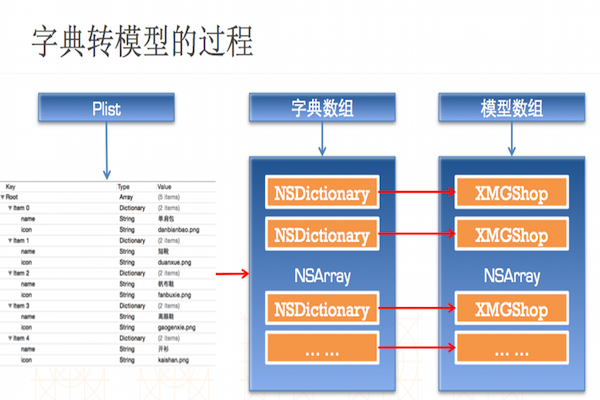
3.字典转模型(推导)
使用字典的坏处 一般情况下,设置数据和取出数据都使用“字符串类型的key”,编写这些key时,编辑器没有智能提示,需要手敲 dict[@"name"] = @"Jack"; NSString *name = dict[@"name"]; 手敲字符串key,key容易写错 Key如果写错了,编译器不会有任何警告和报错,造成设错数据或者取错数据 使用模型的好处 什么是模型 所谓模型,其实就是数据模型,专门用来存放数据的对象,用它来表示数据会更加专业 模型设置数据和取出数据都是通过它的属性,属性名如果写错了,编译器会马上报错,因此,保证了数据的正确性 使用模型访问属性时,编译器会提供一系列的提示,提高编码效率 app.name = @"Jack"; NSString *name = app.name;
字典转模型的注意事项
l字典转模型的过程最好封装在模型内部
l
l模型应该提供一个可以传入字典参数的构造方法
Ø- (instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict;
Ø+ (instancetype)xxxWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict;
2。模型创建基本都是继承与NSObject的对象,定义根字典中key相同的属性
---恢复内容结束---