嘟嘟嘟
一开始就觉得这道题很恶心,但还是硬这头皮做了。
因为(n leqslant 1000),所以可以有(O(n ^ 2))的做法。刚开始我想统计每一个圆盘能覆盖其他圆盘的长度,最后减去。但是这样会有重复统计。后来反过来想,每一个圆盘被覆盖的面积是多少。虽然一个个算也会重复统计,但是如果把每一次覆盖的角度算出来,然后转换成极坐标,不就变成线段覆盖了吗!
这样的话整个算法基本就出来了,复杂度(O(n ^ 2logn))。
不过这要具备一定的计算几何知识。也就是怎么把两圆相交的部分转换成极坐标的区间。
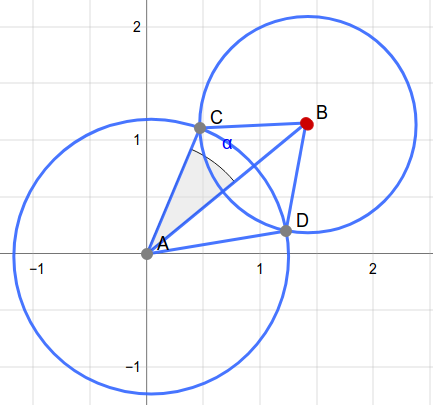
对于这张图,假设已经判断完两圆相交。
首先求出(AB, AC, BC),这样利用余弦定理就能求出(angle alpha)。然后因为(overrightarrow{AB})的极坐标已知,就能通过(+ alpha)和(- alpha)求出(overrightarrow{AC}, overrightarrow{AD})的极坐标。
代码到不长,坑点就是(pi)的精度得高一点……别像我刚开始只弄(8)位……
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cctype>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define enter puts("")
#define space putchar(' ')
#define Mem(a, x) memset(a, x, sizeof(a))
#define rg register
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const db eps = 1e-8;
const db PI = 3.1415926535897932;
const db PI2 = PI * 2;
const int maxn = 1e3 + 5;
inline ll read()
{
ll ans = 0;
char ch = getchar(), last = ' ';
while(!isdigit(ch)) last = ch, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) ans = (ans << 1) + (ans << 3) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
if(last == '-') ans = -ans;
return ans;
}
inline void write(ll x)
{
if(x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if(x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int n;
struct Cir
{
db r, x, y;
friend inline db dis(const Cir& A, const Cir& B)
{
return sqrt((A.x - B.x) * (A.x - B.x) + (A.y - B.y) * (A.y - B.y));
}
}c[maxn];
struct Seg
{
db L, R;
bool operator < (const Seg& oth)const
{
return L < oth.L - eps || (fabs(L - oth.L) < eps && R < oth.R - eps);
}
}a[maxn];
int cnt = 0;
bool flg = 1;
void add(db l, db r) {a[++cnt] = (Seg){l, r};}
void solve(Cir A, Cir B)
{
db d = dis(A, B);
if(B.r + d < A.r - eps || A.r + B.r < d - eps) return;
if(A.r + d < B.r - eps) {flg = 0; return;}
db alp = acos((A.r * A.r + d * d - B.r * B.r) / (2 * A.r * d));
db bet = atan2(B.y - A.y, B.x - A.x);
db l = bet - alp, r = bet + alp;
if(l < 0 && r < 0) l += PI2, r += PI2;
if(l > -eps && r < PI2 - eps) add(l, r);
else
{
if(l < -eps) add(l + PI2, PI2), add(0, r);
else add(l, PI2), add(0, r - PI2);
}
}
db calc()
{
sort(a + 1, a + cnt + 1);
db ret = 0, l = 0, r = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; ++i)
{
if(a[i].L > r + eps) ret += r - l, l = a[i].L, r = a[i].R;
else if(a[i].R > r) r = a[i].R;
}
return ret + r - l;
}
int main()
{
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &c[i].r, &c[i].x, &c[i].y);
db ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
cnt = 0; flg = 1;
for(int j = i + 1; j <= n && flg; ++j) solve(c[i], c[j]);
if(!flg) continue;
ans += (PI2 - calc()) * c[i].r;
}
printf("%.3lf
", ans + PI2 * c[n].r);
return 0;
}