嘟嘟嘟
旋转卡壳模板题。
首先求出凸包。
然后(O(n ^ 2))的算法很好想,但那就不叫旋转卡壳了。
考虑优化:直观的想是在枚举点的时候,对于第二层循环用二分或者三分优化,但实际上两点距离是不满足单调性的,见下图:
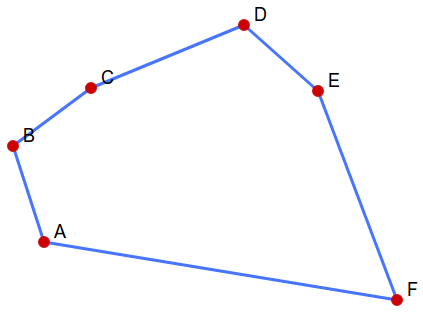
对于(A)点,(AB < AC < AD > AE < AF)。
那怎么办呢?
转换一下思路,如果枚举边,会发现每一个不在这条边上的顶点到边的距离是一个单峰函数!因此就能想到三分这个点,复杂度变成(O(nlogn))。
不过实际上还可以优化,如果逆时针枚举的话,对于边(e_i)的下一条边(e_{i + 1}),会发现到(e_{i + 1})的最远点一定在(e _ i)的最远点的逆时针方向。换句话说,如果边是逆时针枚举的,那么最远点也是逆时针方向的。
因此维护两个指针,一个代表边,一个代表最远点。因为这两个指针最多转一圈,所以复杂度为(O(n))。
一个优化就是判断距离的时候,因为底边是固定的,所以比较距离就是在比较三角形面积。(还能防止掉精度)
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cctype>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define enter puts("")
#define space putchar(' ')
#define Mem(a, x) memset(a, x, sizeof(a))
#define rg register
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const db eps = 1e-8;
const int maxn = 5e4 + 5;
inline ll read()
{
ll ans = 0;
char ch = getchar(), last = ' ';
while(!isdigit(ch)) last = ch, ch = getchar();
while(isdigit(ch)) ans = (ans << 1) + (ans << 3) + ch - '0', ch = getchar();
if(last == '-') ans = -ans;
return ans;
}
inline void write(ll x)
{
if(x < 0) x = -x, putchar('-');
if(x >= 10) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
int n;
struct Point
{
int x, y;
Point operator - (const Point& oth)const
{
return (Point){x - oth.x, y - oth.y};
}
int operator * (const Point& oth)const
{
return x * oth.y - oth.x * y;
}
friend inline int dis(const Point& A)
{
return A.x * A.x + A.y * A.y;
}
inline friend void swap(Point& A, Point& B)
{
swap(A.x, B.x); swap(A.y, B.y);
}
}p[maxn], S;
bool cmp(Point A, Point B)
{
int s = (A - S) * (B - S);
if(s != 0) return s > 0;
return dis(A - S) < dis(B - S);
}
int st[maxn], top = 0;
void Graham()
{
int id = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
if(p[i].x < p[id].x || (p[i].x == p[id].x && p[i].y < p[id].y)) id = i;
if(id != 1) swap(p[id], p[1]);
S.x = p[1].x, S.y = p[1].y;
sort(p + 2, p + n + 1, cmp);
st[++top] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
{
while(top > 1 && (p[st[top]] - p[st[top - 1]]) * (p[i] - p[st[top - 1]]) < 0) top--;
st[++top] = i;
}
}
int area(Point A, Point B, Point C)
{
return abs((A - B) * (A - C));
}
int nxt(int x)
{
if(++x > top) x = 1;
return x;
}
int rota()
{
if(top == 2) return dis(p[st[1]] - p[st[2]]);
int ret = 0;
st[top + 1] = 1;
for(int i = 1, j = 3; i <= top; ++i)
{
while(nxt(j) != i && area(p[st[i]], p[st[i + 1]], p[st[j]]) <= area(p[st[i]], p[st[i + 1]], p[st[j + 1]])) j = nxt(j);
ret = max(ret, dis(p[st[i]] - p[st[j]]));
ret = max(ret, dis(p[st[i + 1]] - p[st[j]]));
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
n = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) p[i].x = read(), p[i].y = read();
Graham();
write(rota()), enter;
return 0;
}