分为三种情况:
第一种情况: 一个链表有环,一个链表没有环,那这两个链表不可能相交
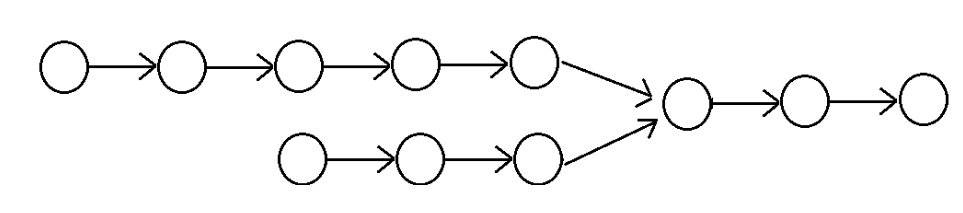
第二种情况: 两个链表都没有环
第三种情况: 两个链表都有环
public class FindFirstIntersectNode { public static class Node { public int value; public Node next; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } /** * 分为三种情况: * 第一种情况: 一个链表有环,一个链表没有环,那这两个链表不可能相交。 * 第二种情况: 两个链表都没有环, * 第三种情况: 两个链表都有环, */ public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { return null; } Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); //两个无环链表是否相交 if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) { return noLoop(head1, head2); } //两个有环链表是否相交 if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) { return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); } return null; } /** * 判断链表是否有环,链表有环返回第一个入环的节点,没有环返回null * @param head * @return */ public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) { //先求出快慢指针的相遇点cross Node fast = head; Node slow = head; Node cross = null; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (slow == fast) { cross = fast; break; } } //从链表头部和相遇点开始,每次移动一个节点,他们相遇点就是环的入口 Node start = head; while (start != null && cross != null) { if (start == cross) { return cross; } start = start.next; cross = cross.next; } return null; } /** * 两个无环链表是否相交,相交返回第一个相交节点,不相交返回null * @param head1 * @param head2 * @return */ public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { return null; } Node cur1 = head1; int len1 = 1; Node cur2 = head2; int len2 = 1; while(cur1.next != null) { len1++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while(cur2.next != null) { len2++; cur2 = cur2.next; } //最后一个节点不相同,两个链表不相交 if(cur1 != cur2) { return null; } //first 始终指向长链表的开始,second始终指向短链表的开始,diff表示两个链表的长度差 Node first = null; Node second = null; int diff = 0; if(len1 > len2) {//链表1比链表2要长, first = head1; second = head2; diff = len1 -len2; }else { first = head2; second = head1; diff = len2 - len1; } //在diff不为零的前提下,长链表先走diff while(diff > 0) { first = first.next; diff--; } //first和second同时走,如果相同了,表示相加了 while(first != second) { first =first.next; second = second.next; } return first; } /** * 两个有环链表是否相交,相交返回第一个相交节点,不相交返回null * @param head1 第一个链表的头节点 * @param loop1 第一个链表的入环节点 * @param head2 第二个链表的头节点 * @param loop2 第二个链表的入环节点 * @return */ public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) { Node cur1 = null; Node cur2 = null; if (loop1 == loop2) { //对应情况一和情况二,与判断两个无环的链表是否相交是同样的步骤,只是结束节点变成了loop1 cur1 = head1; cur2 = head2; int n = 0; while (cur1 != loop1) { n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2 != loop2) { n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0) { n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2) { cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; } else { //对应情况三和情况四,其中情况三相交的,情况四不相交 cur1 = loop1.next; while (cur1 != loop1) { if (cur1 == loop2) { return loop1; } cur1 = cur1.next; } return null; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null Node head1 = new Node(1); head1.next = new Node(2); head1.next.next = new Node(3); head1.next.next.next = new Node(4); head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); // 0->9->8->6->7->null Node head2 = new Node(0); head2.next = new Node(9); head2.next.next = new Node(8); head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); // 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4... head1 = new Node(1); head1.next = new Node(2); head1.next.next = new Node(3); head1.next.next.next = new Node(4); head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); head1.next.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4 // 0->9->8->2... head2 = new Node(0); head2.next = new Node(9); head2.next.next = new Node(8); head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); // 0->9->8->6->4->5->6.. head2 = new Node(0); head2.next = new Node(9); head2.next.next = new Node(8); head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); } }
两个有环单向链表相交示例图

两个无环单向链表相交示例图