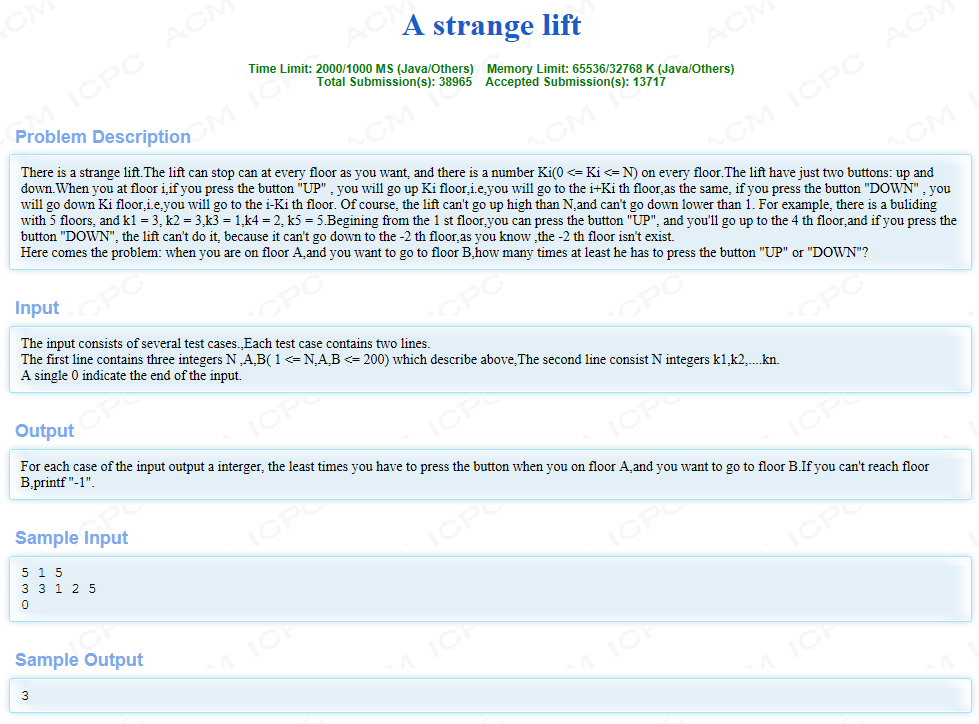
创建一个结构体, 该结构体存储 当前所在楼层 和 当前已走的步数
使用广搜, 将初始节点入队, 并做上已访问的标记, 判断当前节点是否为终点, 若是终点则返回到当前为止走过的步数, 若不是终点, 则将该节点可以访问到的孩子结点入队(同时将孩子结点做上已经访问过的标记)(当前节点出队), 依次判断, 直至队列为空
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct F
{
int floor; // 当前所在楼层
int step; // 当前走的步数
F() {}
F(int x, int y):floor(x), step(y) {}
};
int a, b, n;
int c[210], vis[210];
int bfs()
{
queue<F> q;
F p, m, t;
p = F(a, 0);
vis[p.floor] = 1;
q.push(p);
while(!q.empty())
{
m = q.front();
q.pop();
// 成功返回
if(m.floor == b) return m.step;
if(m.floor + c[m.floor] <= n && !vis[m.floor + c[m.floor]])
{
t.floor = m.floor + c[m.floor];
t.step = m.step + 1;
vis[t.floor] = 1;
q.push(t);
}
if(m.floor - c[m.floor] >= 1 && !vis[m.floor - c[m.floor]])
{
t.floor = m.floor - c[m.floor];
t.step = m.step + 1;
vis[t.floor] = 1;
q.push(t);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> n)
{
if(n == 0) break;
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
cin >> a >> b;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
cin >> c[i];
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
/*
Sample Input:
5 1 5
3 3 1 2 5
0
Sample Output:
3
*/