Write a program which reads a sequence A of n elements and an integer M, and outputs "yes" if you can make M by adding elements in A, otherwise "no". You can use an element only once.
You are given the sequence A and q questions where each question contains Mi.
Input
In the first line n is given. In the second line, n integers are given. In the third line q is given. Then, in the fourth line, q integers (Mi) are given.
Output
For each question Mi, print yes or no.
Constraints
- n ≤ 20
- q ≤ 200
- 1 ≤ elements in A ≤ 2000
- 1 ≤ Mi ≤ 2000
Sample Input 1
5 1 5 7 10 21 8 2 4 17 8 22 21 100 35
Sample Output 1
no no yes yes yes yes no no
Notes
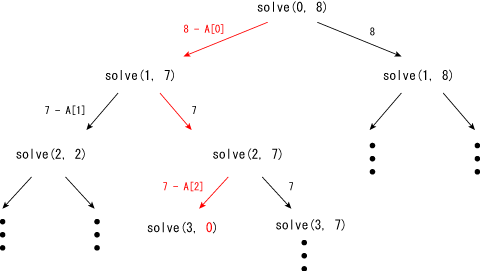
You can solve this problem by a Burte Force approach. Suppose solve(p, t) is a function which checkes whether you can make t by selecting elements after p-th element (inclusive). Then you can recursively call the following functions:
solve(0, M)
solve(1, M-{sum created from elements before 1st element})
solve(2, M-{sum created from elements before 2nd element})
...
The recursive function has two choices: you selected p-th element and not. So, you can check solve(p+1, t-A[p]) and solve(p+1, t) in solve(p, t) to check the all combinations.
For example, the following figure shows that 8 can be made by A[0] + A[2].
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, q;
int A[2010], M[2010];
// 用第i个元素后面的元素能得出m时返回true
// 从输入值M中减去所选元素的递归函数
bool solve(int i, int m)
{
if(m == 0) return true;
if(i >= n) return false;
return solve(i + 1, m) || solve(i + 1, m - A[i]); // 不使用第i个元素 + 使用第i个元素
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
cin >> A[i];
}
cin >> q;
for(int i = 0; i < q; ++ i)
{
cin >> M[i];
if(solve(0, M[i]))
{
cout << "yes" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "no" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
/*
5
1 5 7 10 21
8
2 4 17 8 22 21 100 35
*/