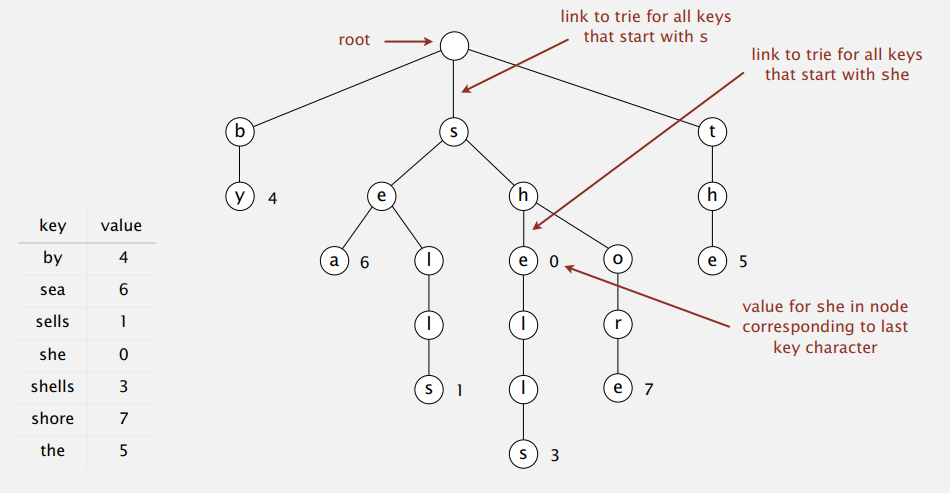
单词查找树
和以字符串为键的排序算法类似,以字符串为键的符号表也有更加高效的实现,可以避免检测整个键。于是乎,先贴下我们要实现的 API:

R-way Tries
单词查找树(Tires),来自 retrieval,为和‘tree’区分,读作‘try’。
- 节点里存储字符而不是键。
- 每个节点有 R(字母表大小,像拓展 ASCII 是 256)个孩子,分别表示可能的下一个字符。
- 为了方便,我们先不画出空链接。
于是乎,来个例图:
Tries: search
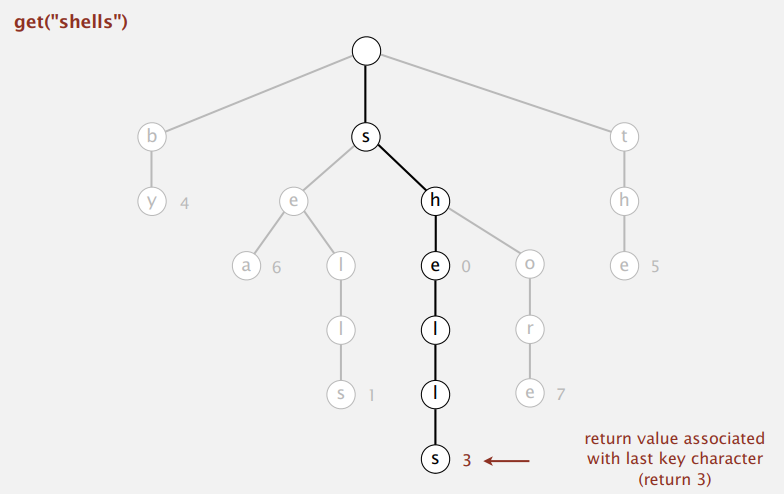
查找自然只有匹配和没有这两种情况:
-
Search hit: 查找时的最后一个字符所在节点有非空值,例如:
-
Search miss: 查找时的遇到空链接或是最后一个字符所在节点没有值,如:
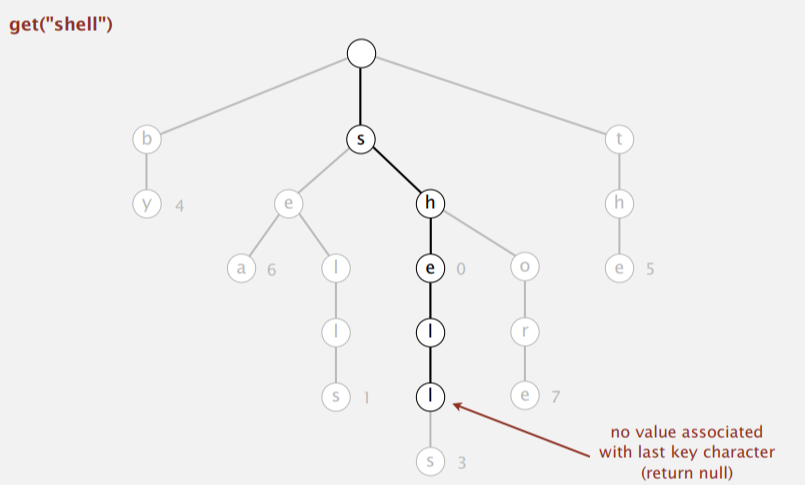
Tries: insertion
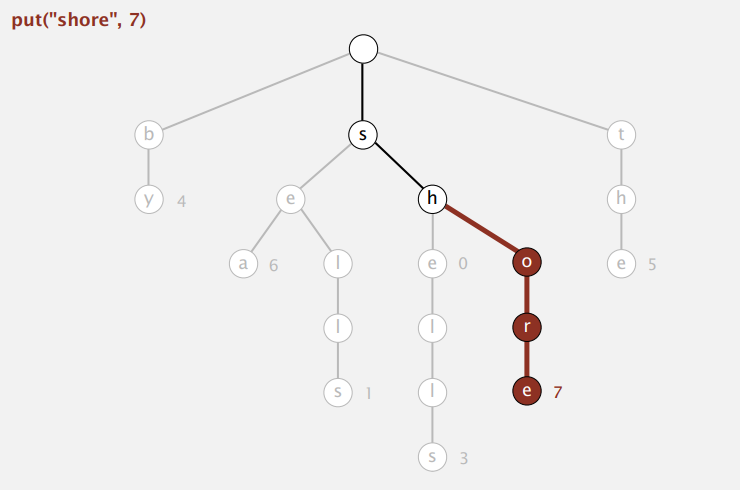
往单词查找树里插入新字符串时,顺着和每个字符匹配的链接走下去,然后:
-
遇到空链接时,创建新的节点。
-
更新字符串最后一个字符所在节点的值。
Tries: Java implementaion
public class TriesST<Value> {
private static final int R = 256; // extended ASCII
private Node root = new Node();
private static class Node {
private Object value;
private Node[] next = new Node[R];
}
public void put(String key, Value val) {
root = put(root, key, val, 0);
}
private Node put(Node x, String key, Value val, int d) {
if (x == null) x = new Node();
if (d == key.length()) {
x.val = val;
return x;
}
char c = key.charAt(d);
// 即用下个字符本身作为数组索引
x.next[c] = put(x.next[c], key, val, d + 1);
return x;
}
public boolean contains(String key) {
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(String key) {
Node x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return (Value) x.val;
}
private Node get(Node x, String key, int d) {
if (x == null) return null;
if (d == key.length()) return x;
char c = key.charAt(d);
return get(x.next[c], key, d + 1);
}
}
Tries: performance
- Search hit: 需要检查字符串的每个字符。
- Search miss: 有可能只要首个字符就能判断没有,典型案例中只需检查一些字符(亚线性级别)。
- Space: 每个叶节点都有 R 个空链接。但如果很多短字符串共享相同前缀,那空间为亚线性级别是可能的。
所以总的来说,可以很快匹配到字符串,判断没有甚至更快,但是浪费空间。
Tries: deletion
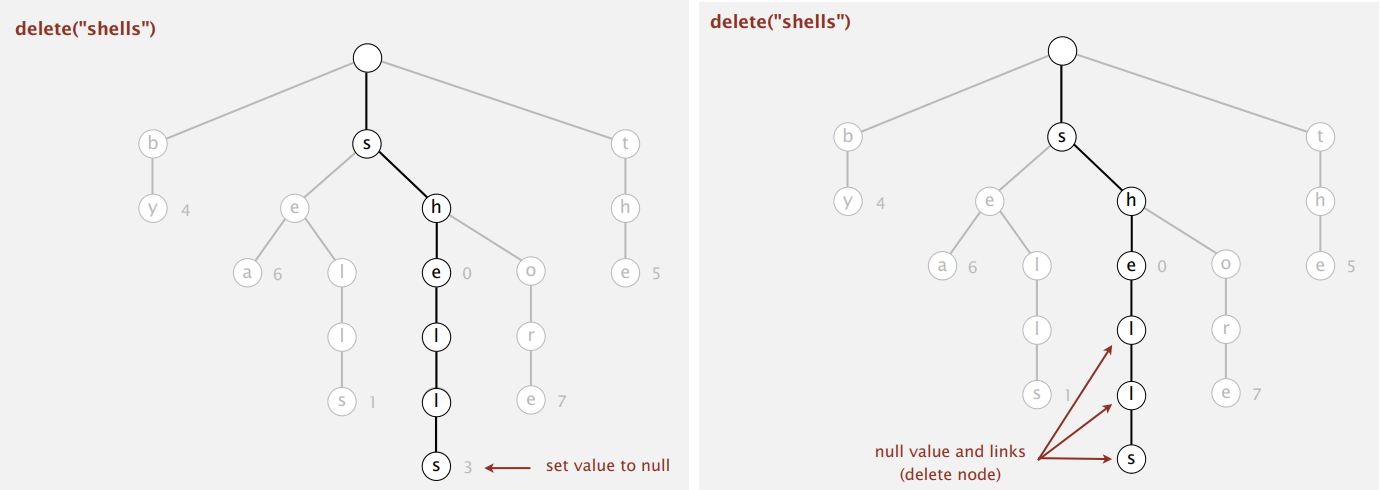
删除单词查找树中的某个字符串时,首先要找到它,然后把最后一个节点的值置空,再递归删除没有非空链接的空值节点。例子:
于是,总的来说,对于 R 比较小的情况,可以考虑使用 R-way trie。但是,当 R 比较大时,它所需要的空间就太大了,16 位的 Unicode 就会是 65536-way trie。
Ternary Search Tries
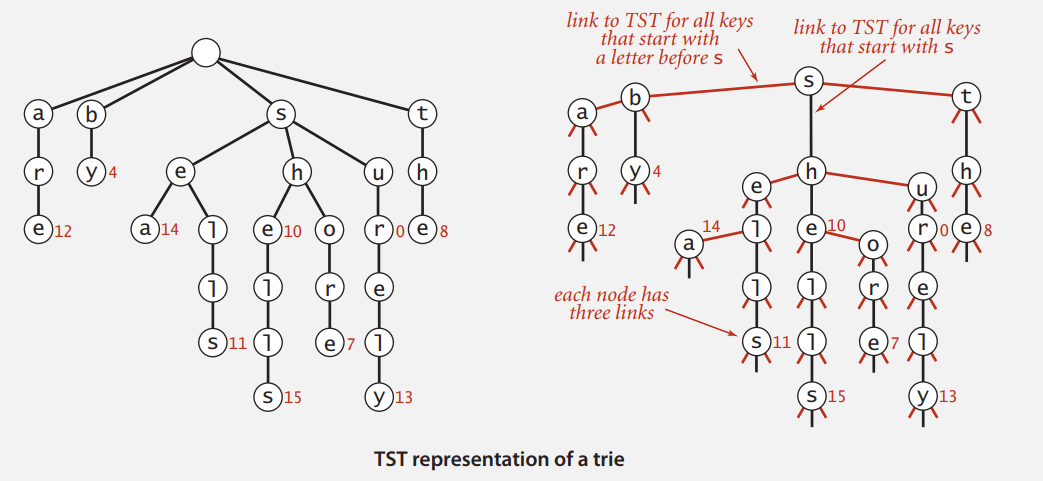
R 路单词查找树每个节点的空链接数太多,会占用大量的空间,于是我们来了解下三向单词查找树。TST 每个节点只有左中右三个链接,例图:
TST: search
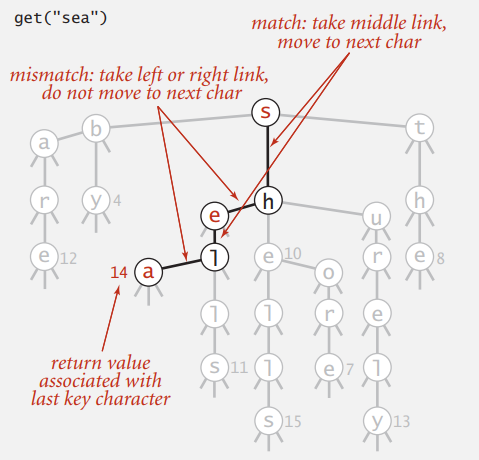
查找时和节点存的字符匹配就走中间,比它大走左边,比它小走右边。这个过程中碰到空链接就说明没有该字符串,或是字符串最后一个字符所在的节点没有值,那就也没有该字符串。
Search Hit
Search Miss
TST: construction
构造(插入新字符串)TST 和查找类似,只是碰到空链接就新建个节点,字符串最后一个字符所到节点给它赋值。
TST: Java implementation
public class TST<Value> {
private Node root;
private class Node {
private Value val;
private char c;
private Node left, mid, right;
}
public void put(String key, Value val) {
root = put(root, key, val, 0);
}
private Node put(Node x, String key, Value val, int d) {
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (x == null) {
x = new Node();
x.c = c;
}
if (c < x.c) x.left = put(x.left, key, val, d);
else if (c > x.c) x.right = put(x.right, key, val, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) x.mid = put(x.mid, key, val, d + 1);
else x.val = val;
return x;
}
public boolean contains(String key) {
return get(key) != null;
}
public Value get(String key) {
Node x = get(root, key, 0);
if (x == null) return null;
return x.val;
}
private Node get(Node x, String key, int d) {
if (x == null) return null;
char c = key.charAt(d);
if (c < x.c) return get(x.left, key, d);
else if (c > x.c) return get(x.right, key, d);
else if (d < key.length() - 1) return get(x.mid, key, d + 1);
else return x;
}
}
TST 的复杂度和红黑树相当,查找的效率和哈希实现的符号表差不多。你也可以通过旋转操作保持它的平衡,来保证最坏情况下的性能。还可以把它和 R-way tries 结合起来:
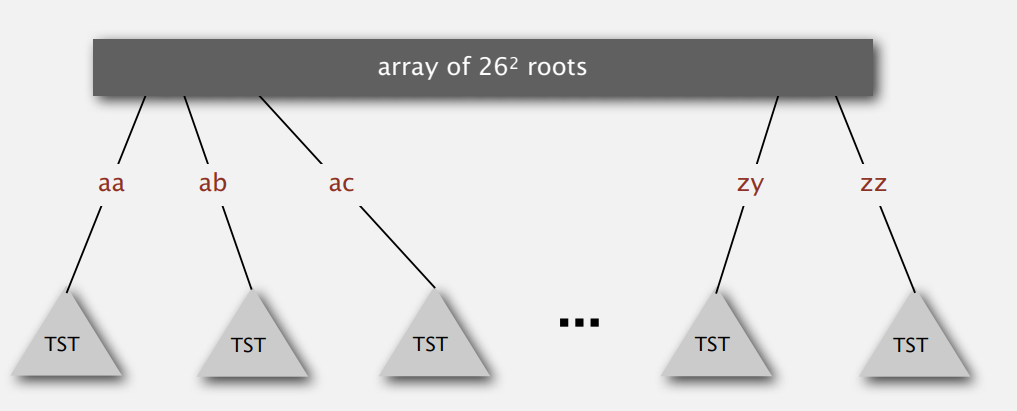
虽然空间上会多花一点,但是实际中会让算法跑得更快一些,因为前面两个字符很快就能判断有没有匹配的,可能直接就是 search miss 的情况。
Character-based Operations
这节的最后介绍了一些基于字符的操作。
Keys
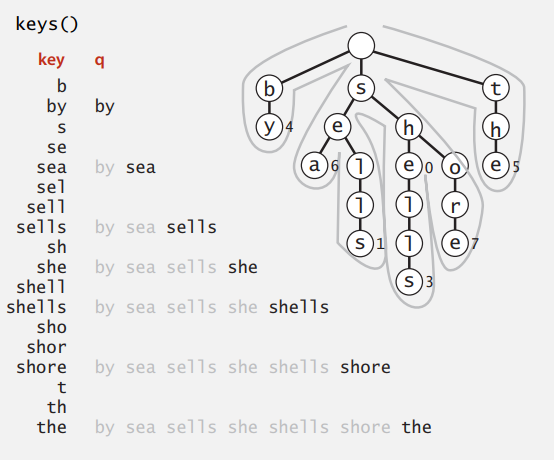
即返回单词查找树中存储的所有字符串(键),这里是中序遍历 Trie。
public Iterable<String> keys() {
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
collect(root, "", queue);
return queue;
}
// prefix: sequence of characters on path from root to x
private void collect(Node x, String prefix, Queue<String> q) {
if (x == null) return;
if (x. val != null) q.enqueue(prefix);
for (char c = 0; c < R; c++)
collect(x.next[c], prefix + c, q);
}
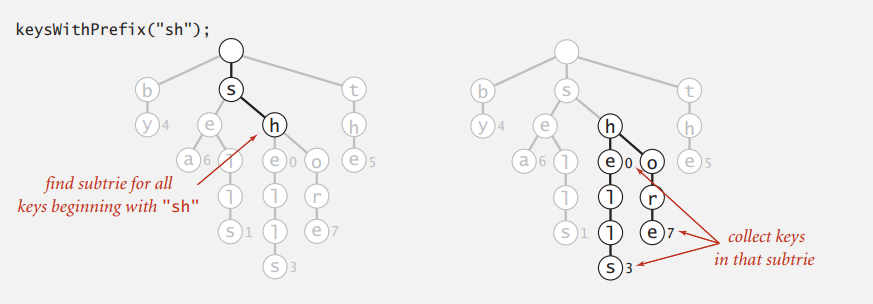
Prefix
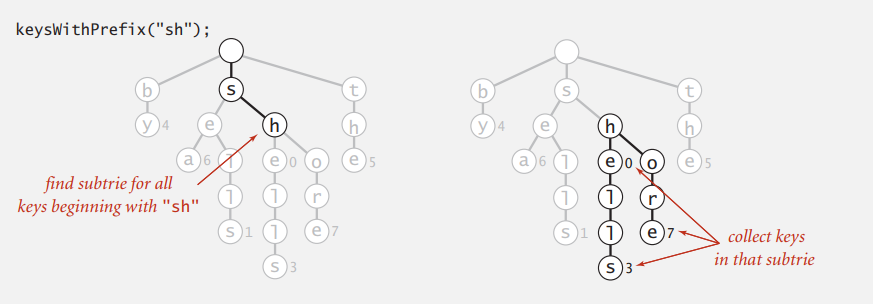
即找出以输入字符串为前缀的字符串,像浏览器搜索时出现的提示框那样。
public Iterable<String> keyWithPrefix(String prefix) {
Queue<String> queue = new Queue<String>();
// x: root of subtrie for all strings
// beginning with given prefix
Node x = get(root, prefix, 0);
collect(x, prefix, queue);
return queue;
}
Longest Prefix
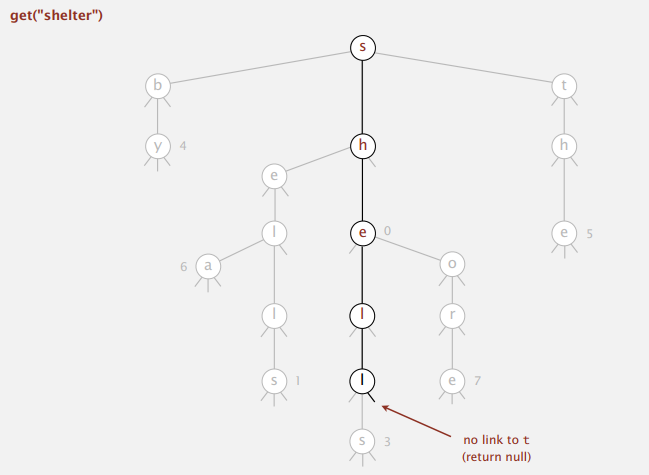
例子:

再来张图:

即找出 Trie 中为输入字符串前缀的最长字符串。
public String longestPrefixOf(String query) {
int length = search(root, query, 0, 0);
return query.substring(0, length);
}
private int search(Node x, String query, int d, int length) {
if (x == null) return length;
if (x.val != null) length = d;
if ( d == query.length()) return length;
char c = query.charAt(d);
return search(x.next[c], query, d + 1, length);
}
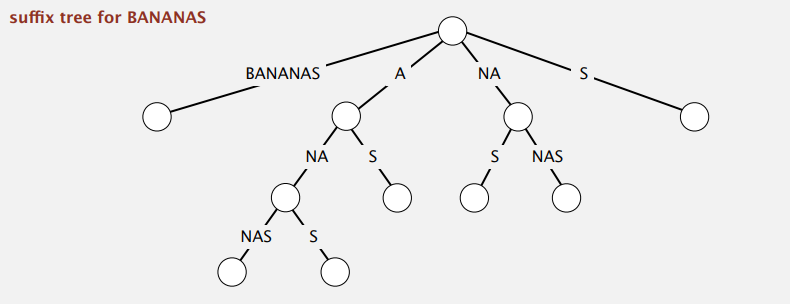
最后稍微提了下前缀树(patricia trie)和后缀树(suffix tree),贴图感受下。
Patricia Trie
Suffix Tree