编程作业一
我的代码:WordNet.java & SAP.java & Outcast.java
这是第二部分的编程作业,因为第二部分课程开始了,第一部分博客就先放放。
问题简介
WordNet 按字面意思就是单词网,它是一个有向图,点里面是同义的单词,边则指向具有更高层次的抽象含义的点。举例来说,有个点里面含{与电路,与门}表示输入全为 1 输出才为 1 的逻辑门,指向点{门,逻辑门}这更高层的抽象概念。另外需要注意的是,它还是一个具有单根的有向无环图(rooted DAG),贴张样图。
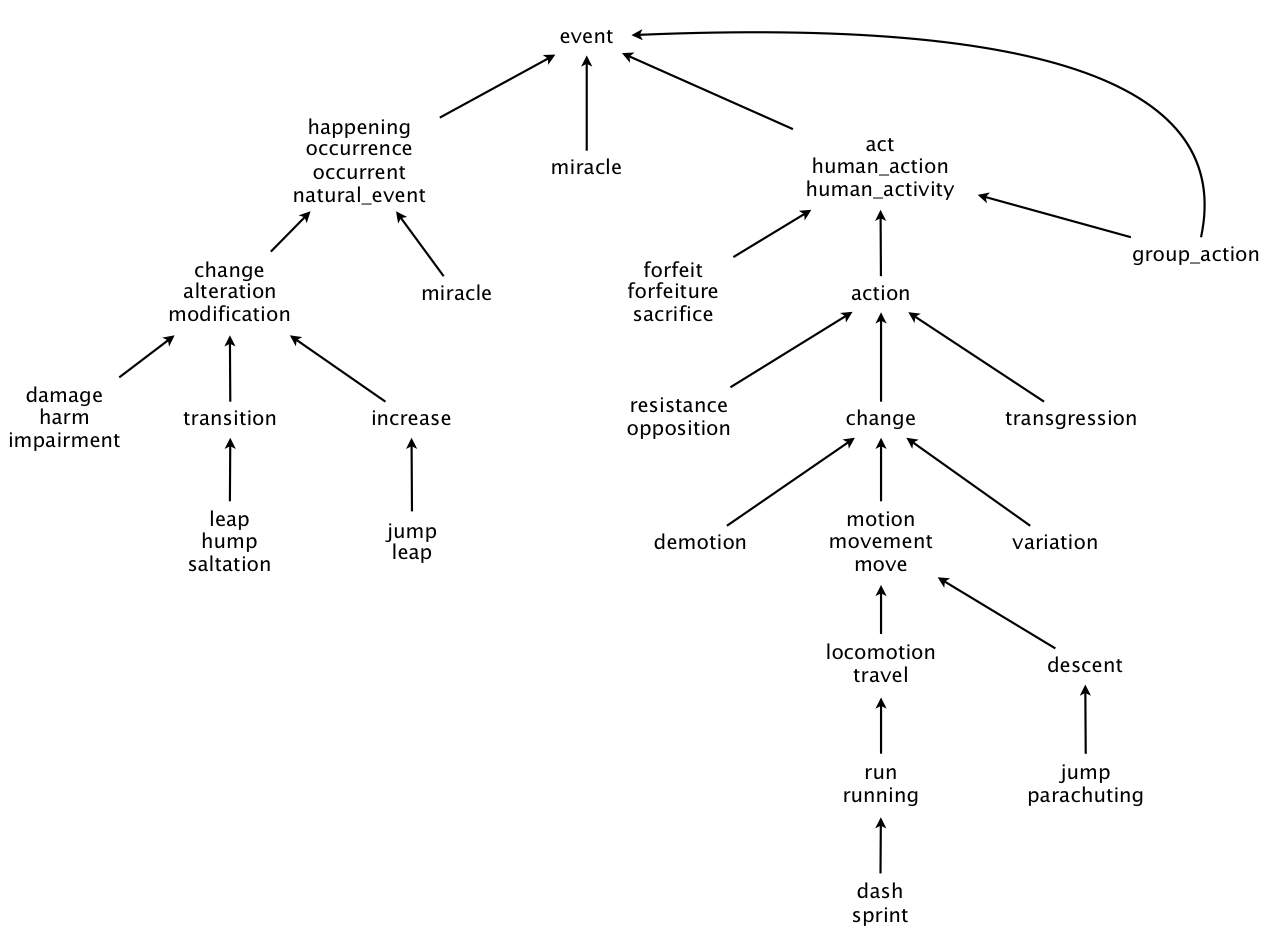
任务摘要
WordNet Data Type
Implement an immutable data type WordNet with the following API:
public class WordNet { // constructor takes the name of the two input files public WordNet(String synsets, String hypernyms) // returns all WordNet nouns public Iterable<String> nouns() // is the word a WordNet noun? public boolean isNoun(String word) // distance between nounA and nounB (defined below) public int distance(String nounA, String nounB) // a synset (second field of synsets.txt) that is the common ancestor of nounA and nounB // in a shortest ancestral path (defined below) public String sap(String nounA, String nounB) // do unit testing of this class public static void main(String[] args) }SAP Data Type
Implement an immutable data type SAP with the following API:
public class SAP { // constructor takes a digraph (not necessarily a DAG) public SAP(Digraph G) // length of shortest ancestral path between v and w; -1 if no such path public int length(int v, int w) // a common ancestor of v and w that participates in a shortest ancestral path; -1 if no such path public int ancestor(int v, int w) // length of shortest ancestral path between any vertex in v and any vertex in w; -1 if no such path public int length(Iterable<Integer> v, Iterable<Integer> w) // a common ancestor that participates in shortest ancestral path; -1 if no such path public int ancestor(Iterable<Integer> v, Iterable<Integer> w) // do unit testing of this class public static void main(String[] args)Outcast Detection
Implement an immutable data type Outcast with the following API:
public class Outcast { public Outcast(WordNet wordnet) // constructor takes a WordNet object public String outcast(String[] nouns) // given an array of WordNet nouns, return an outcast public static void main(String[] args) // see test client below }
详细的要求参见:WordNet。
问题分析
SAP
按照 Checklist 里建议的编程步骤,先实现 SAP 这一数据结构。SAP 即为 Shortest ancestral path,最短的公共祖先路径,像下面的图描述的那样。
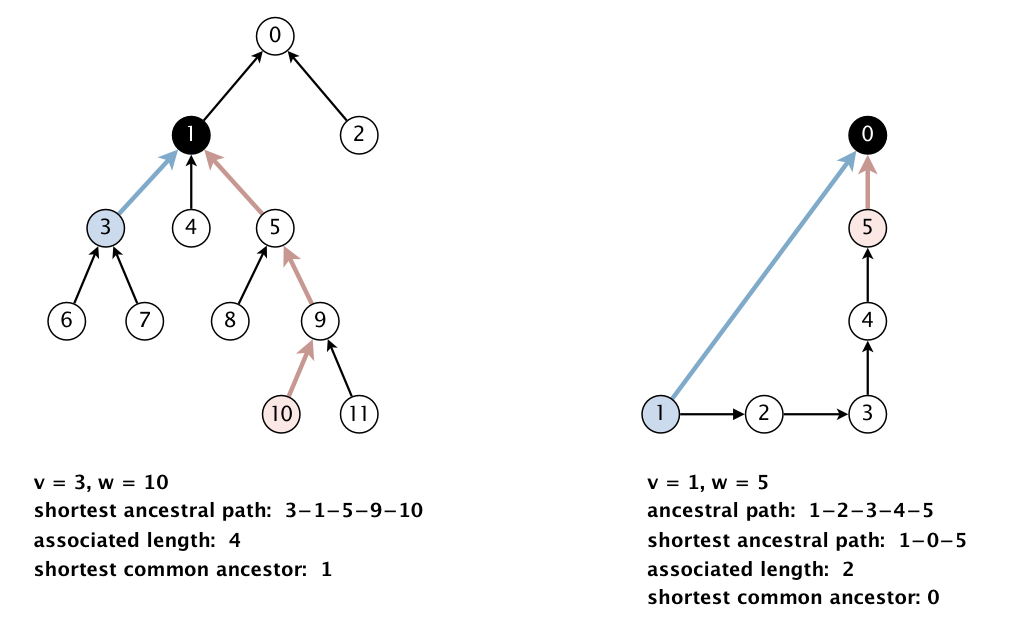
可以看到 SAP 处理的是点已经被映射到 0 到 N-1 的有向图,具体映射的任务需要我们稍后在 WordNet 中实现。有向图即课程中的 Digraph.java,是 SAP 构造函数的参数,不能随便改,下载 algs4.jar,即可 import。
SAP 不但要支持计算单独的两点 v 和 w 的最短公共祖先路径和最近公共祖先,还要支持计算两个点集的。
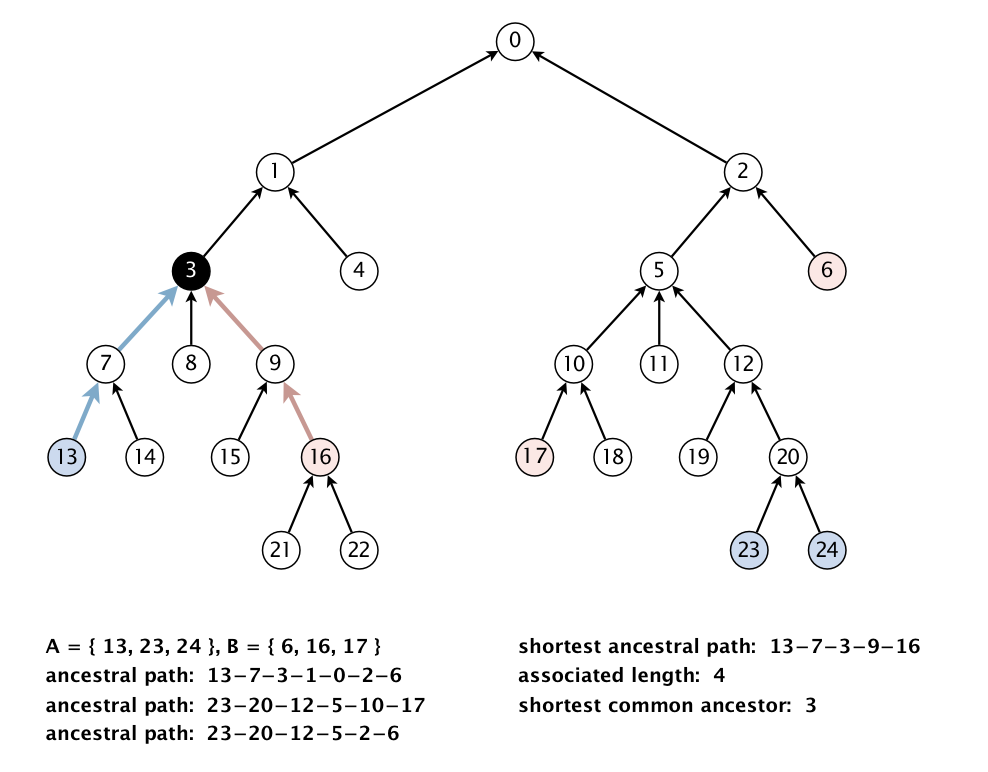
这是因为 SAP 是为 WordNet 提供支持的,而同一个单词可能出现在单词网的多个点,比如多义词,这样计算两个单词在网中的“距离”,要处理的就是点集。
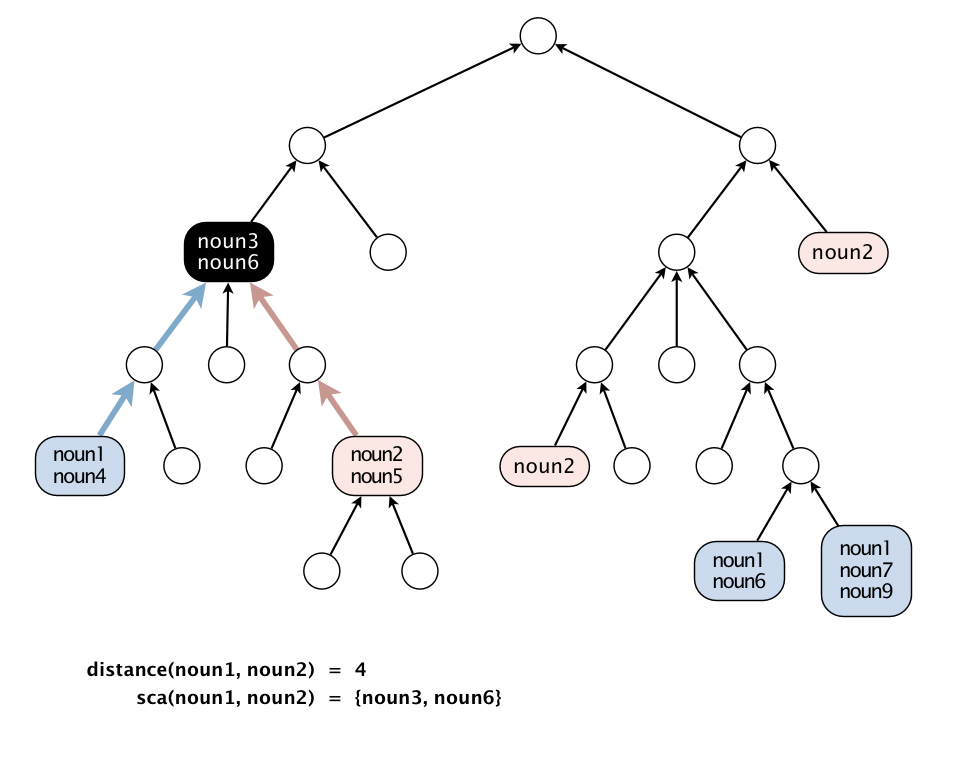
然后是具体的实现,要求最短,结合本周的课程,很自然地想到 BFS 这个图搜索策略。先是计算单独的两个点 v 和 w ,大概思路是来两个队列,交替用 BFS 拓展新的节点,拓展到第一个被两点都访问过的点,应该就是最近公共祖先吧,距离加一下也出来了。
看了 Checklist ,发现有种“暴力”做法是直接调用课程里的 BreadthFirstDirectedPaths.java 分别对 v 和 w 来个整套 BFS ,这样就能知道图的某个点是否能被 v 点访问到,如果能访问到也能知道距离,w 点也是。所以接下来遍历图中所有点,对 v 和 w 都能访问的点,计算距离和并维护最短距离和最近公共祖先。
我最初的想法和 Checklist 的 Optional Optimizations 的第二点契合:
If you run the two breadth-first searches from v and w in lockstep (alternating back and forth between exploring vertices in each of the two searches), then you can terminate the BFS from v (or w) as soon as the distance exceeds the length of the best ancestral path found so far.
最后搜索的伪代码大概长这样:
while(qv 或 qw 不为空) {
if (qv 不为空) {
if (被点 w 访问过) {
计算路径,更优则更新 sap
}
if (与 v 的距离小于 sap) {
继续拓展,往 qv 塞点
}
}
if (qw 不为空) {
类似,略。。。
}
}
当拓展到的点到起点的距离比目前的最短路径还长时,也就没必要继续拓展啦,没必要来整套 BFS ,而且我这个一直都是在同一张图上搜索。
还有可选优化的第一点,说了好长一段,我到实际实现交替 BFS 时才明白在说什么。大概就是建议我们跟踪搜索过程中被访问过的点,好来有针对性地重新初始化一些 BFS 时要的辅助数组,像标记点是否被访问过的布尔数组 marked ,这样就不用浪费大量时间在重新初始化上,因为很多情况下只有一小部分被改变。至于实现的话,我就开个栈,在点被访问到时把它的 id 丢进去,下次交替 BFS 之前,重新初始化弹出的 id 对应的辅助数组。
至于可选优化第三点,它建议实现一个 software cache ,保存最近的 length() 和 ancestor() 。因为最短路径长度和最近公共祖先,其实在一次交替 BFS 中就都可以得到,length(v, w) 和 ancestor(v, w) 完全可以省下一次搜索。我先试了一下单独两个点版本的 length() 和 ancestor() ,搜索前把点和 recentV 及 recentW 比较下,吻合就直接返回上次保存的结果。感觉没问题啊,本地测试也没找到,但交上去 SAP 有个测试就是过不了。
Test 19: random calls to both version of length() and ancestor(), with probabilities p1 and p2, respectively * random calls in a random rooted DAG (20 vertices, 100 edges) (p1 = 0.5, p2 = 0.5) - no path from v or w to ancestor - failed on call 34 to ancestor() - v = 1, w = 6 - reference length = 1 - student ancestor = 8 - reference ancestor = 1 * random calls in a random digraph (20 vertices, 100 edges) (p1 = 0.5, p2 = 0.5) - ancestor() is not ancestor on shortest ancestral path - failed on call 67 to ancestor() - v = 8, w = 5 - student ancestor = 0 - distance from 8 to 0 = 2 - distance from 5 to 0 = 1 - reference ancestor = 5 - reference length = 2 ==> FAILED
我把 cache 去掉,这个测试就过了,无法理解哪里不对。而且讲道理,最短距离是 0 说明参数是同一个点,那 recentV 和 recentW 该是一样,那对现在不同点的查询,怎么会直接返回上次结果啊。
不过,大概是因为实现了另外两个优化,最后还是拿到了额外的分数的。
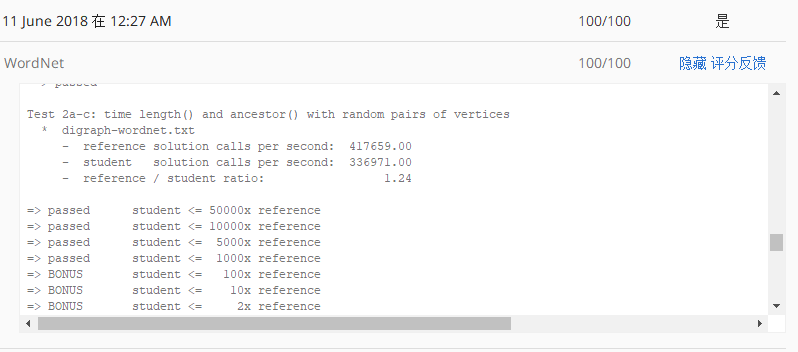
最后还有,那个处理点集的版本,一开始把点分别全部丢到队列里就好。完整代码:SAP.java 。
WordNet
接着 Checklist 建议先搞清楚怎么正确从 CSV 文件读入数据,用到了 [In](file:///C:/Users/Archeroc/AppData/Local/Temp/360zip$Temp/360$0/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/In.java.html).readLine() 和 String.split() ,前者在课程的 algs4.jar 里,后者给了示例 Domain.java ,总得来说问题不大。
于是该用文件里读来的数据构造 WordNet ,建议至少分成两个子任务。我将其分成了 readSynsets(synsets) 和 readHypernyms(hypernyms) ,前者完成对单词和所在点的 id 映射关系的存储,后者则构建要传给 SAP 实例的有向图。
我用 ST<String, SET<Integer>> synsets ([ST](file:///C:/Users/Archeroc/AppData/Local/Temp/360zip$Temp/360(1/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/ST.java.html) 和 [SET](file:///C:/Users/Archeroc/AppData/Local/Temp/360zip)Temp/360$2/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/SET.java.html) 同样在 algs4.jar 中)来存储单词和它所在点的 id ,因为一个单词可能出现在多个点。查询两个单词距离就方便,把 synsets.get(nounA) 和 synsets.get(nounB) 丢给 SAP 实例相应的方法就好。而且其他方法也很简单,用 ST.keys() 和 ST.contains() 就能实现。
我一路实现下来,直到最后一个 "String sap(String nounA, String nounB)" ,发现有点不对劲。SAP 里面的最近公共祖先方法返回的是点的 id ,这边要的是点里面有哪些单词。我只好遍历所有单词,用 SET.contains(id) 判断,如果包含 id 则把这个单词加到最后返回的字符串上。啊对,我一开始还用了 String 对象,测评系统提醒我该用 StringBuilder 才对,但是最后交上去 WordNet 有些测试还是超时啦。
于是我又加了个 ST<Integer, String> id_nouns 保存点及其含有的所有单词,这样用 id 找单词就快多了。交上去,成功解决了超时问题,而且没有超出内存限制。
第二个任务,从文件构建有向图。构建本身问题不大,但是题目要求我们检测它是不是 rooted DAG ,这就不知道怎么做了。去题目讨论页面找了下,发现又可以直接调用课程实现过的啊。讲拓扑排序时说到 DAG 才有可能有,于是 Topological.java 就有用来检测图有没有环的,它基于的 DirectedCycle.java 也可以。至于只有一个根,我是在构建的时候记录出度为零的点的个数,最后只有一个就说明是单根。完整代码:WordNet.java。
Outcase
这个没什么问题,给一组单词,要求挑出和其它最不相关的单词。具体做法就是计算每个单词和其它单词的距离,调用 WordNet ,最后距离总和最大的即为所求。完整代码:Outcast.java。
测试结果
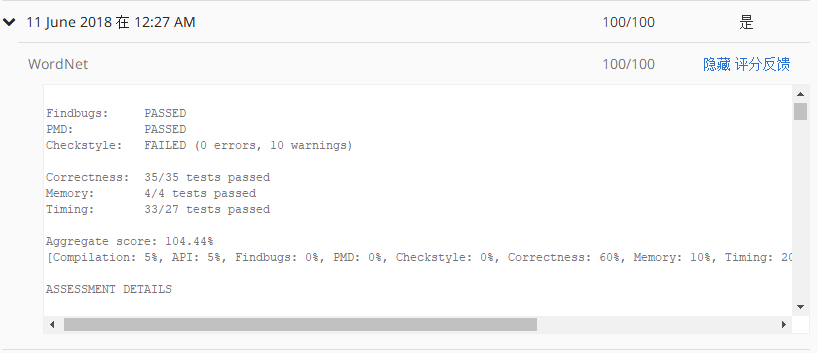
完成两个可选优化,时间测试上额外通过了 6 个附加测试。