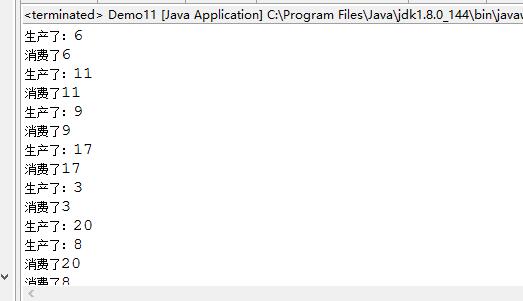
生产者-消费者
轮训机制
//生产者与消费者
class Memory{ //内存
public static ArrayList<Integer> arr=new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
new Thread(new Runnable() { //生产者
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){ //轮训
int temp=r.nextInt(10)+1;
Memory.arr.add(temp);
System.out.println("生产了:"+temp);
//每隔100~900毫秒
int result=(r.nextInt(9)+1)*100;
try {
Thread.sleep(result);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() { //消费者
while(true){ //轮训
try {
Thread.sleep(800); //每隔800毫秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i:Memory.arr){ //一次性全部消费
System.out.println("消费了:"+i);
}
Memory.arr.clear();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
轮训机制也很常用,设计的好也有很多应用场景
线程间的通知机制
wait(),notify()-(notifyAll())
wait和notify是object类的方法,也就是java为所有对象都提供了这两个方法。
wait和notify必须配合syn关键字使用。
wait释放锁,notify不释放锁。
先观察轮训
class ListAdd1 {
private volatile static List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
public void add(){
list.add("oracle");
}
public int size(){
return list.size();
}
}
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ListAdd1 list1=new ListAdd1();
Thread t1=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list1.add();
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"添加了一个元素..");
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if(list1.size()==5){
System.out.println("当前线程收到通知:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" list size=5 线程停止..");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
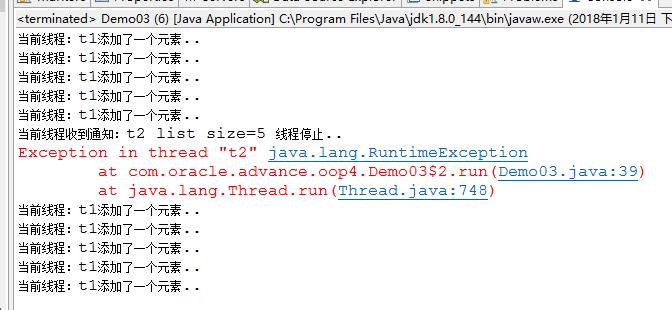
t2线程一直while(true),我们改进代码:
class ListAdd2 {
private volatile static List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
public void add(){
list.add("oracle and java");
}
public int size(){
return list.size();
}
}
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ListAdd2 list2 = new ListAdd2();
//1、 实例化出来一个 lock
//2、当使用wait 和 notify 的时候 , 一定要配合着synchronized关键字去使用
final Object lock = new Object(); //创建锁
Thread t1=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
synchronized (lock) {
for(int i = 0; i <10; i++){
list2.add();
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"添加了一个元素..");
Thread.sleep(500);
if(list2.size()==5){
System.out.println("已经发出通知..");
lock.notify(); //不释放锁,t1执行完之后才会释放锁
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
if(list2.size()!=5){
try {
lock.wait(); //释放锁
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"收到通知线程停止..");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}, "t2");
t2.start(); //先启动t2
t1.start();
}
}

再次写一个生产者与消费者(不要拘泥具体代码)
//wait和notify必须配合synchronized关键字使用
class X{
public static List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public static final Object lock = new Object(); //创建锁
}
class Product implements Runnable{
Random r=new Random();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true){
synchronized (X.lock) {
while(X.list.size()>=100){
X.lock.wait();
}
int number=(r.nextInt(20)+1); //生产一个小余20的随机数
X.list.add(number);
System.out.println("生产了:"+number);
X.lock.notify();
}
int temp=(r.nextInt(11))*100;
Thread.sleep(temp); //每隔100~1000毫秒
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true){
synchronized (X.lock) {
while(X.list.size()==0){
X.lock.wait();
}
for(Integer i:X.list){
System.out.println("消费了"+i);
}
X.list.clear(); //清空
X.lock.notify();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class Demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Product()).start(); //生产者启动
new Thread(new Consumer()).start(); //消费者启动
}
}