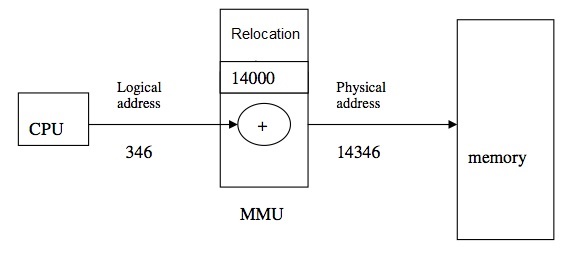
Logical vs physical address
1) An address generated by the CPU is a logical address. Whereas, an address seen by the memory unit, that is, the one loaded into the memory-address register of the memory, is a physical address.
2) The user program never sees the physical addresses. The program creates a pointer to a logical address, say 346, stores it in memory, manipulate it, compares it to other logical addresses- all as the number 346.
Only when a logical address is used as memory address, it is relocated relative to the base/relocation register. The memory-mapping hardware device called the memory- management unit(MMU) converts logical addresses into physical addresses.
3) Logical addresses range from 0 to max. User program that generates logical address thinks that the process runs in locations 0 to max. Logical addresses must be mapped to physical addresses before they are used. Physical addresses range from (R+0) to (R + max) for a base/relocation register value R.
4) Example: