1脚本语言和编译型语言的区别:编译型的要从源码转换成目标代码,多运行于底层。脚本语言有解释器读入程序代码, 转成内部形式再执行。
2脚本语言,写的时间快,一般有awk,pwel, python Ruby和shell
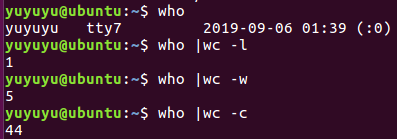
3 使用who 和 wc算登录人数
4 用cat创建文件, 写入程序,修改权限,执行程序
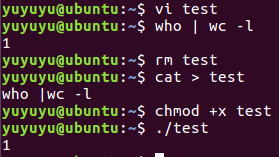
5 创建shell脚本,
#! 用来提示内核扫描其他部分, 是否存在执行程序的解释器的完整路径
#! /bin/csh -f cshell的解释器
shell 脚本通常开头是
#! /bin/sh
6 shell 识别3中基本命令
内建命令:cd read echo 等
shell函数:功能健全的一系列代码
外部命令 :用新进程执行shell的副本
7 变量名定义同c语言变量的语法
8 变量赋值
first=isaac middle=bashevis last=singer
9 变量的值获取,在变量名 前加$
fullname="$first $middle $last"
10 echo , printf输出
echo “enter 有人name”
printf“first program '%s, %s' " hello world

11 重定向和管道
用<改变标准输入 (输入file中数据当做缓存数据, 删除缓存中的 ‘回车’符号)
tr -d ' ' < file.txt
用>改变标准输出 (输入file中数据当做缓存数据, 删除缓存中的 ‘回车’符号, 输出修改后的数据到 dest_file)
tr -d ' ' <file.txt > dest_file.txt
用>>附加到文件中 (输入file中数据当做缓存数据, 删除缓存中的 ‘回车’符号, 输出修改后的数据到 dest_file尾部, 如果dest_file不存在,就创建一个)
tr -d ' ' <file.txt >> dest_file.txt
用 | 建立管道, 能把两个执行程序连接到一起, 程序1的结果作为程序 2的输入
(输入file中数据当做缓存数据, 删除缓存中的 ‘回车’符号, 对数据进行排序, 输出修改后的数据到 dest_file尾部, 如果dest_file不存在,就创建一个)
tr -d ' ' <file.txt > | sort > dest_file.txt
12 位桶,系统的垃圾桶, /dev/null
13 其他控制终端或者串口 /dev/tty
14 自定义的bin目录,添加到$path的方法
.profile 就在home的用户目录下

.profile
# ~/.profile: executed by the command interpreter for login shells.
# This file is not read by bash(1), if ~/.bash_profile or ~/.bash_login
# exists.
# see /usr/share/doc/bash/examples/startup-files for examples.
# the files are located in the bash-doc package.
# the default umask is set in /etc/profile; for setting the umask
# for ssh logins, install and configure the libpam-umask package.
#umask 022
# if running bash
if [ -n "$BASH_VERSION" ]; then
# include .bashrc if it exists
if [ -f "$HOME/.bashrc" ]; then
. "$HOME/.bashrc"
fi
fi
# set PATH so it includes user's private bin directories
PATH="$HOME/bin:$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
永久生效的方法: 在.profile中加入 PATH= $PATH:$HOME/bin
一次性生效的方法: 在shell中 PATH= $PATH:$HOME/bin
15 显示脚本参数,0-9 echo $1
10 以上 echo ${10}
16本地化环境
yuyuyu@ubuntu:/usr/share/locale/zh_CN/LC_MESSAGES$
locale -a 列出所有locale 名称