Properties类:
Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
特点:
1、Hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用,实现了map接口。不可以使用普通for遍历,没有下标。
2、该集合没有泛型。键值都是字符串。
3、它是一个可以持久化的属性集。键值可以存储到集合中,也可以存储到持久化的设备(硬盘、U盘、光盘)上。键值的来源也可以是持久化的设备。
4、有和流技术相结合的方法

将数据存到集合中:
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建Properties集合 Properties pro=new Properties(); //存值 pro.put("url","jdbc:mysql://loacathost:8080..."); pro.put("user","root"); pro.put("pwd", "13456"); //取值 System.out.println(pro.getProperty("url")); System.out.println(pro.getProperty("user")); System.out.println(pro.getProperty("pwd")); } }

方法应用:
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建Properties集合 Properties pro=new Properties(); //明确数据源 FileInputStream frs=new FileInputStream("src/com/oracle/demo04/pro.properties"); //将文件中的键值对读取到集合中 pro.load(frs); System.out.println(pro); } }
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建Properties集合 Properties pro=new Properties(); pro.put("name", "tom"); pro.put("age", "20"); //明确目的地 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("src/com/oracle/demo04/pro.properties",true); //将集合中的数据存储到文件中 pro.store(fw,"This is a person");//只能是英文 } }
driver=com.mysql.jdba.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:8080 user=root pwd=123456# #Mon Nov 02 19:18:56 CST 2020 age=20 name=tom #This is a person #Mon Nov 02 19:19:58 CST 2020 age=20 name=tom
只能存入以properties结尾的文件,其他文件都不行,并且properties文件不能有空格,分号,只能存键值对。
Properties的通常用法:
解决硬编码问题。
public class JDBCUtils {
//获取连接对象
public static Connection getConn(){
Connection conn=null;
try {
// 2:获取连接对象
Properties pro=new Properties();
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src/com/oracle/tools/db.properties");
pro.load(fis);
Class.forName(pro.getProperty("driver"));
String url = pro.getProperty("url");
String user =pro.getProperty("user");
String pwd =pro.getProperty("pwd");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
#driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo0803?characterEncoding=utf8 #user=root #pwd=123456 #driver=com.oracle.jdbc.Driver #url=jdbc:oracle://localhost:3306/demo0803?characterEncoding=utf8 #user=root #pwd=123456
可以注释,只需要改动部分代码。
序列化流与反序列化流:
将一个对象存到文件中,将文件取出来用反序列化流。
ObjectOutputStream 将 Java 对象的基本数据类型和图形写入 OutputStream。可以使用 ObjectInputStream 读取(重构)对象。通过在流中使用文件可以实现对象的持久存储。
需要明确目的地:依旧是功能流。
代码:
public class Person implements Serializable{ //瞬态关键字 private transient String name; private static int age; private static final long serialVersionUID=123l; public Person() { super(); } //构造方法倒数第三行 public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() {
return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Person p=new Person("张三",18); //明确目的地 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("D:\io0803\person.txt"); //创建一个序列化流 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos); //将对象写入文件中 oos.writeObject(p); //释放资源 oos.close(); } }
类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。
反序列化流:
ObjectInputStream 对以前使用 ObjectOutputStream 写入的基本数据和对象进行反序列化。支持 java.io.Serializable接口的对象才能从流读取。

public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException { //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\io0803\person.txt"); //创建反序列化流对象 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis); //读出一个对象 Person p=(Person)ois.readObject();//将Object转为Person,强转 System.out.println(p); //释放资源 ois.close(); //创建对象的方式,反序列化 } //不能用字符流 }
注意事项:
程序序列化过程:
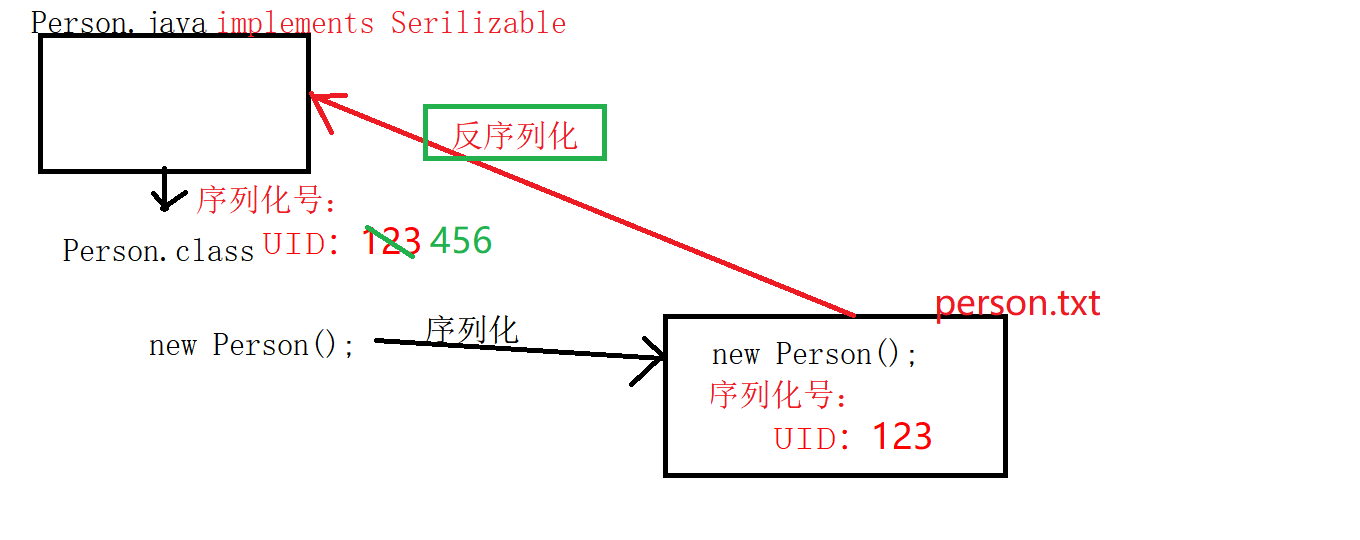 person.java编译时,只要实现此接口,就会形成序列化号,对象存入文件中的时候,会将类的序列化号存入文件中,当反序列化时,2个号会对比,一样就成功,不一样会报错。
person.java编译时,只要实现此接口,就会形成序列化号,对象存入文件中的时候,会将类的序列化号存入文件中,当反序列化时,2个号会对比,一样就成功,不一样会报错。
Serializable标记接口。该接口给需要序列化的类,提供了一个序列版本号。serialVersionUID. 该版本号的目的在于验证序列化的对象和对应类是否版本匹配。private static final long serialVersionUID=123L;
瞬态关键字:
当一个类的对象需要被序列化时,某些属性不需要被序列化,这时不需要序列化的属性可以使用关键字transient修饰。只要被transient修饰了,序列化时这个属性就不会序列化了。
同时静态修饰也不会被序列化,因为序列化是把对象数据进行持久化存储,而静态的属于类加载时的数据,不会被序列化。
private transient String name;
打印流:
打印流添加输出数据的功能,使它们能够方便地打印各种数据值表示形式.
打印流根据流的分类:
字节打印流 PrintStream
字符打印流 PrintWriter
方法:
void print(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,
void println(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,自动写入换行操作
字节与字符的方法打印流都可以使用
PrintWriter:

可以通过构造方法,完成文件数据的自动刷新功能
构造方法:
开启文件自动刷新写入功能
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush)
public PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush)
代码:
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 明确数据源 FileReader fr=new FileReader("D:\io0803\demo01.txt"); //添加创建缓冲字符输入流加速 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr); //明确目的地 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("D:\demo01.txt"); //创建打印流,开启自动刷新功能 PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw,true); //开始复制 String line=null; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ //写一行 pw.println(line); } //释放资源 br.close(); pw.close(); }
工具类:commons-IO
1:导入classpsth
加入classpath的第三方jar包内的class文件才能在项目中使用
创建lib文件夹
将commons-io.jar拷贝到lib文件夹
右键点击commons-io.jar,Build Path→Add to Build Path
2:FilenameUtils
这个工具类是用来处理文件名(译者注:包含文件路径)的,他可以轻松解决不同操作系统文件名称规范不同的问题
常用方法:
getExtension(String path):获取文件的扩展名;
getName(String filename):获取文件名;
isExtension(String fileName,String ext):判断fileName是否是ext后缀名;
3:FileUtils
提供文件操作(移动文件,读取文件,检查文件是否存在等等)的方法。
常用方法:
readFileToString(File file):读取文件内容,并返回一个String;
writeStringToFile(File file,String content):将内容content写入到file中;
copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir,File destDir);文件夹复制
copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile);文件复制
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取文件扩展名 String ext=FilenameUtils.getExtension("D:\io0803\demo01.txt"); System.out.println(ext); //获取文件名 String name=FilenameUtils.getName("D:\io0803\demo01.txt"); System.out.println(name); //判断文件是否以某后缀结尾 boolean flag=FilenameUtils.isExtension(name,"java"); System.out.println(flag); //读取文件内容,并返回下一个String } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 复制文件夹 //明确数据源 //File file1=new File("D:\io0803"); //明确目的地 //File file2=new File("D:\io0804"); //复制 //FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(file1, file2); //读取文件内容,并返回一个String /*File file3=new File("D:\io0803\demo01.txt"); String aa1=FileUtils.readFileToString(file3); System.out.println(aa1);*/ //File file=new File("D:\io0803\demo02.txt"); //FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file,"将字符内容写入文件中"); File file1=new File("D:\io0803\demo02.txt"); File file2=new File("D:\io0803\demo000.txt"); FileUtils.copyFile(file1, file2); } }