字节输出流OutputStream
OutputStream此抽象类,是表示输出字节流的所有类的超类。操作的数据都是字节
基本方法:
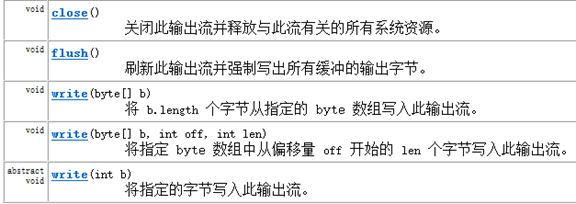
子类可继承调用以上方法
FileOutputStream类
构造方法:

FileOutputStream类写入数据到文件中
例子:
package com.oracle.FileoutStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class OutPUTsteam { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("e:\test\bi.txt");//此构造方法,如果文件存在,则覆盖 //没有,则创建 // f.write(100);//字节流,结果为d,想输出100,就写三个字节,49,48,48 byte[] bytes={-65,-66,-67,-68};//烤郊 // byte[] bytes={65,66,67,68};//ABCD // f.write(bytes); f.write(bytes,1,2);//窘 /* FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("e:\test\bi.txt",true);//在后面续写,加true // f.write(bytes,1,2);//窘 String str="abcd ";// 换行 f.write(str.getBytes()); // new String(bytes); */ f.close(); } }
IO异常的处理
package com.oracle.FileoutStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class IoEXCEPTION { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义FileOutputStream的引用 FileOutputStream f=null; try{ //创建FileOutputStream对象 f=new FileOutputStream("e:\test\bi.txt"); //写数据 f.write(100); }catch(IOException e){ throw new RuntimeException("文件写入失败");//一旦发生io异常,直接终止关闭 }finally{ try { //一定要判断fos是否为null,只有不为null时,才可以关闭资源 if(f!=null){ f.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("关闭资源失败"); } } } }
字节输入流InputStream

int read():读取一个字节并返回,没有字节返回-1.
int read(byte[]): 读取一定量的字节数,并存储到字节数组中,返回读取到的字节数。
FileInputStream类

FileInputStream类读取数据read方法

public class FileInputStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File file = new File("c:\file.txt"); //创建一个字节输入流对象,必须明确数据源,其实就是创建字节读取流和数据源相关联。 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); //读取数据。使用 read();一次读一个字节。 int ch = 0; while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.println("ch="+(char)ch); } // 关闭资源。 fis.close(); } }
读取数据read(byte[])方法

public class FileInputStreamDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* * 演示第二个读取方法, read(byte[]); */ File file = new File("c:\file.txt"); // 创建一个字节输入流对象,必须明确数据源,其实就是创建字节读取流和数据源相关联。 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); //创建一个字节数组。 byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//长度可以定义成1024的整数倍。 int len = 0; while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len)); } fis.close(); } }
字节流复制文件
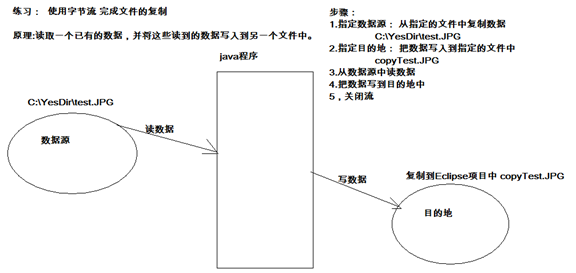
public class CopyFileTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1,明确源和目的。 File srcFile = new File("c:\YesDir est.JPG"); File destFile = new File("copyTest.JPG"); //2,明确字节流 输入流和源相关联,输出流和目的关联。 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //3, 使用输入流的读取方法读取字节,并将字节写入到目的中。 int ch = 0; while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){ fos.write(ch); } //4,关闭资源。 fos.close(); fis.close(); } }
缓冲数组方式复制文件
public class CopyFileByBufferTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { File srcFile = new File("c:\YesDir est.JPG"); File destFile = new File("copyTest.JPG"); // 明确字节流 输入流和源相关联,输出流和目的关联。 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //定义一个缓冲区。 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1) { fos.write(buf, 0, len);// 将数组中的指定长度的数据写入到输出流中。 } // 关闭资源。 fos.close(); fis.close(); } }
这样执行速度比一个一个读写要快
字符流
FileReader读取包含中文的文件
public class CharStreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //给文件中写中文 writeCNText(); //读取文件中的中文 readCNText(); } //读取中文 public static void readCNText() throws IOException { FileReader fr = new FileReader("D:\test\cn.txt"); int ch = 0; while((ch = fr.read())!=-1){ //输出的字符对应的编码值 System.out.println(ch); //输出字符本身 System.out.println((char)ch); } } //写中文 public static void writeCNText() throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\test\cn.txt"); fos.write("欢迎你".getBytes()); fos.close(); } }
FileWriter写入中文到文件中
public class FileWriterDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //演示FileWriter 用于操作文件的便捷类。 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\text\fw.txt"); fw.write("你好谢谢再见");//这些文字都要先编码。都写入到了流的缓冲区中。 fw.flush(); fw.close(); } }
flush和close的区别

flush():将流中的缓冲区缓冲的数据刷新到目的地中,刷新后,流还可以继续使用。
close():关闭资源,但在关闭前会将缓冲区中的数据先刷新到目的地,否则丢失数据,然后在关闭流。流不可以使用。如果写入数据多,一定要一边写一边刷新,最后一次可以不刷新,由close完成刷新并关闭。
字符流复制文本文件
public class CopyTextFileTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { copyTextFile(); } public static void copyTextFile() throws IOException { //1,明确源和目的。 FileReader fr = new FileReader("c:\cn.txt"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("c:\copy.txt"); //2,为了提高效率。自定义缓冲区数组。字符数组。 char[] buf = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while((len=fr.read(buf))!=-1){ fw.write(buf,0,len); } /*2,循环读写操作。效率低。 int ch = 0; while((ch=fr.read())!=-1){ fw.write(ch); } */ //3,关闭资源。 fw.close(); fr.close(); } }