数组是多个相同数据类型的数据元素的集合,实现对这些数据的统一管理
数组中的数据类型可以是任何数据类型的,包括基本类型和引用类型的
一维数组的声明:
type[] var 或者 type var[]
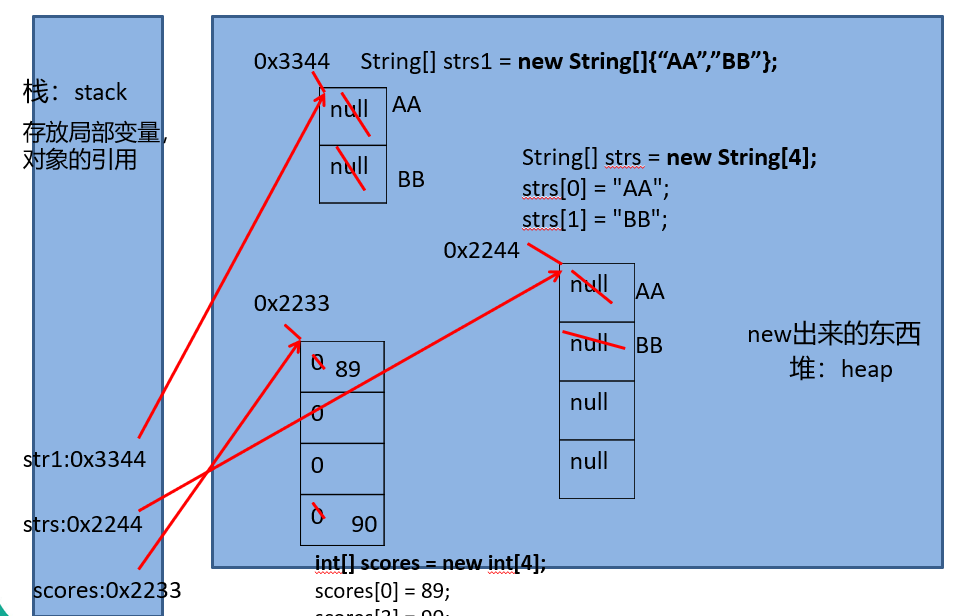
public static void main(String[] args) { //对于基于基本数据类型的变量创建的数组:byte short int long float double char boolean //1.对于byte short int long 而言:创建数组以后,默认值为0 int[] scores = new int[4]; scores[0] = 89; scores[3] = 90; for(int i = 0;i < scores.length;i++){ System.out.println(scores[i]); } byte[] scores1 = new byte[4]; scores1[0] = 89; scores1[3] = 90; for(int i = 0;i < scores1.length;i++){ System.out.println(scores1[i]); } //2.对于float double而言:默认值是0.0 float[] f = new float[3]; f[0] = 1.2F; for(int i = 0;i < f.length;i++){ System.out.println(f[i]); } System.out.println(); //3.对于char而言:默认为空格 char[] c = new char[3]; for(int i = 0;i < c.length;i++){ System.out.println(c[i]); } System.out.println(); //4.对于boolean而言:默认为false boolean[] b = new boolean[3]; for(int i = 0;i < b.length;i++){ System.out.println(b[i]); } //5.对于引用类型的变量构成的数组而言:默认初始化值为null。以String为例 String[] strs = new String[4]; strs[0] = "AA"; strs[1] = "BB"; //strs[2] = "CC"; strs[3] = "DD"; //遍历数组的元素 for(int i = 0;i < strs.length;i++){ System.out.println(strs[i]); } System.out.println(); Person[] pers = new Person[3]; for(int i = 0;i < pers.length;i++){ System.out.println(pers[i]); } int[] myInt = {12,13,14}; int[] myInt1; myInt1 = new int[]{12,1,3,14}; }
java语言中声明数组的时候,不能指定数组长度(数组元素的个数)
如:int arr[5];(非法)
一维数组的初始化
动态初始化:数组声明且为数组元素分配空间与赋值操作分开进行
静态初始化:在定义数组的同时就为数组元素分配空间并赋值
创建基本类型的数组

创建引用类型的数组
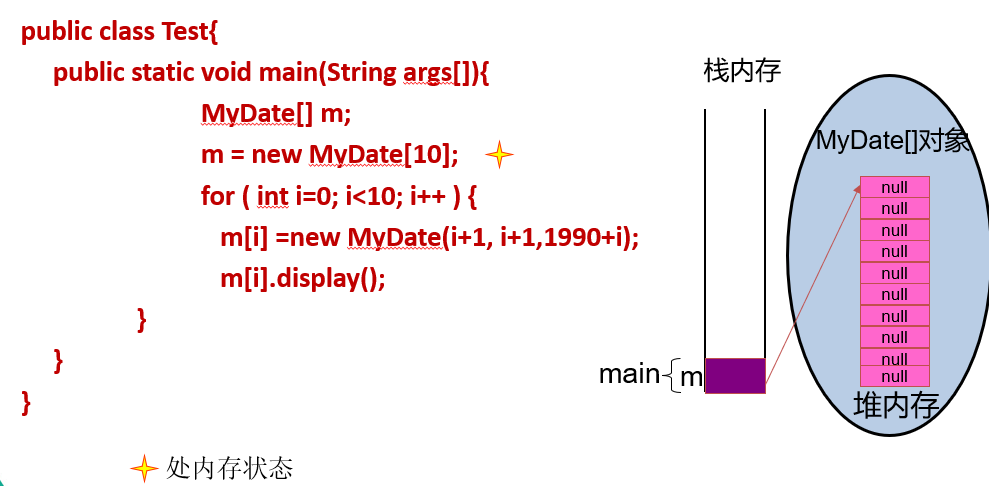
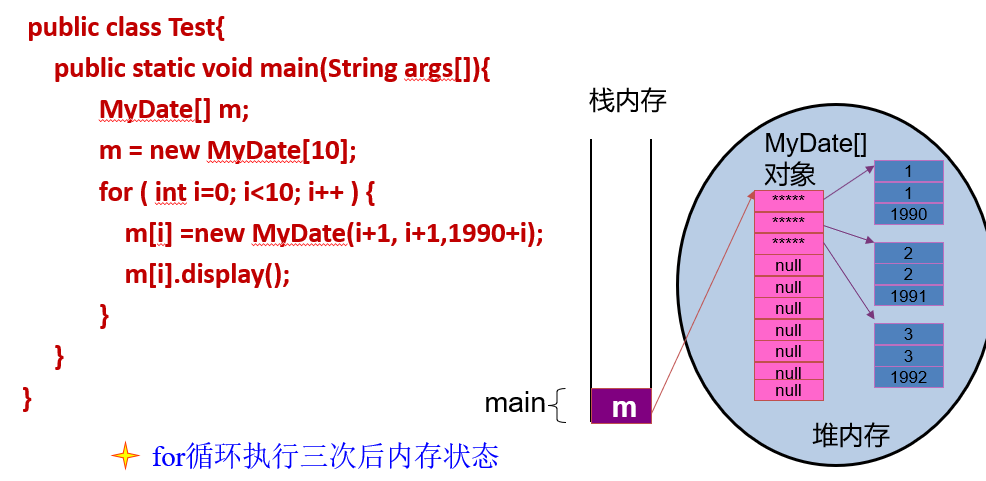
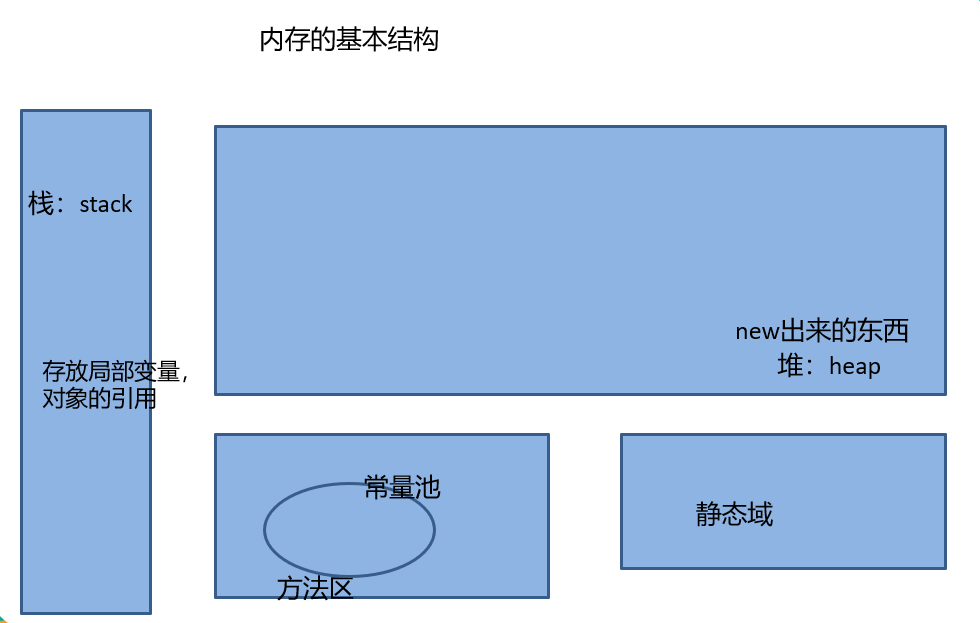
数组元素的默认初始化:
数组是引用类型,他的元素相当于类的成员变量,因此数组一经分配内存空间,其中的每个元素也被按照成员变量同样的方式被隐式的初始化
对于基本数据类型,默认初始化各不相同
对于引用类型,默认初始化值为null
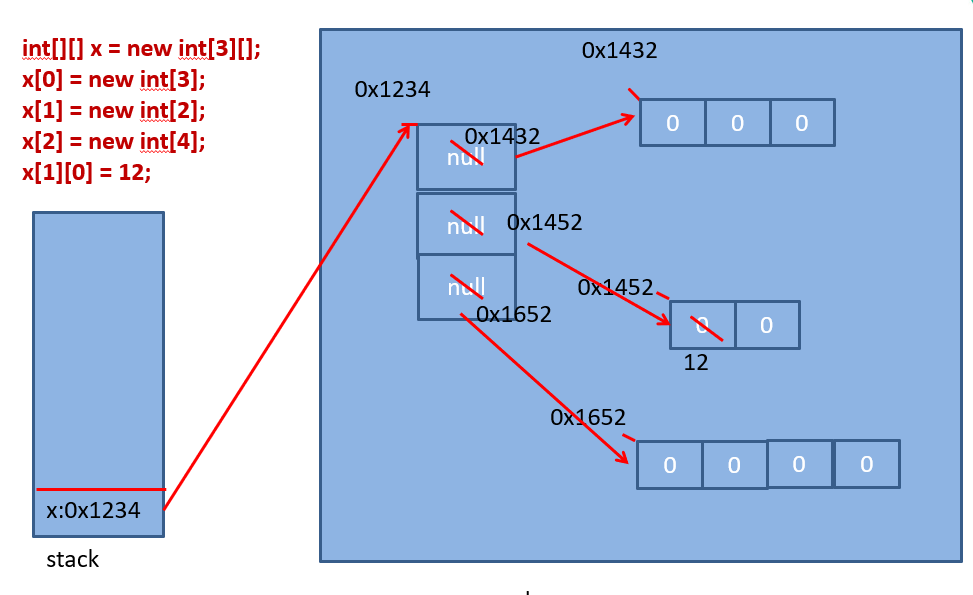
二维数组:
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] scores1 = new int[10]; int[][] scores2; String[][] names; //1.二维数组的初始化 scores2 = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{3,4,5},{6}};//静态初始化 names = new String[6][5];//动态初始化的方式一 names = new String[6][];//动态初始化的方式二 names[0] = new String[5]; names[1] = new String[4]; names[2] = new String[7]; names[3] = new String[5]; names[4] = new String[8]; names[5] = new String[5]; //错误的初始化方式 //names = new String[][]; //names = new String[][5]; //2.如何来引用具体的某一个元素 int[][] i = new int[3][2];//int[] i[] = new int[3][2]; i[1][0] = 90; i[2][1] = 100; //3.数组的长度 //二维数组的长度:length属性 System.out.println(i.length);//3 //二维数组中元素的长度 System.out.println(i[0].length);//2 System.out.println(names.length);//6 System.out.println(names[4].length);//8 System.out.println(); //4.如何遍历二维数组 for(int m = 0;m < scores2.length;m++){//控制行数 for(int n = 0;n < scores2[m].length;n++){ System.out.print(scores2[m][n] + " "); } System.out.println(); } //5.内存结构 int[] x,y[]; //int[] x;//一维 //int[] y[];//二维 y = new int[3][2]; x = y[0]; x[0] = y[1][2]; }
数组中的常见异常
public static void main(String[] args) { //1.数组下标越界的异常:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException int[] i = new int[10]; // i[0] = 90; // i[10] = 99; // for(int m = 0;m <= i.length;m++){ // System.out.println(i[m]); // } //2.空指针的异常:NullPointerException //第一种: // boolean[] b = new boolean[3]; // b = null; // System.out.println(b[0]); //第二种: // String[] str = new String[4]; // //str[3] = new String("AA");//str[3] = "AA"; // System.out.println(str[3].toString()); //第三种: int[][] j = new int[3][]; j[2][0] = 12; }
获取二维数组的所有元素的值
public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] m = new int[][]{{3,8,2},{2,7},{9,0,1,6}}; int sum = 0; for(int i = 0;i < m.length;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < m[i].length;j++){ System.out.print(m[i][j] + " "); sum += m[i][j]; } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("总和为:" + sum); }
杨辉三角:
/* * 使用二维数组打印一个 10 行杨辉三角. 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 5 10 10 5 1 .... 【提示】 1. 第一行有 1 个元素, 第 n 行有 n 个元素 2. 每一行的第一个元素和最后一个元素都是 1 3. 从第三行开始, 对于非第一个元素和最后一个元素的元素. yanghui[i][j] = yanghui[i-1][j-1] + yanghui[i-1][j]; */ public class TestApp { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] yangHui = new int[10][]; //1.初始化二维数组 for(int i = 0;i < yangHui.length;i++){ yangHui[i] = new int[i + 1]; } //2.显式的为二维数组的每个元素赋值 for(int i = 0;i < yangHui.length;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < yangHui[i].length;j++){ yangHui[i][0] = yangHui[i][i] = 1; if(i > 1 && j > 0 && j < i){ yangHui[i][j] = yangHui[i-1][j] + yangHui[i-1][j-1]; } } } //遍历二维数组 for(int i = 0;i < yangHui.length;i++){ for(int j = 0;j < yangHui[i].length;j++){ System.out.print(yangHui[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }