刘 勇 Email:lyssym@sina.com
简介
鉴于基于划分的文本聚类方法只能识别球形的聚类,因此本文对基于密度的文本聚类算法展开研究。DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise)是一种典型的基于密度的聚类方法,可以找出形状不规则的聚类,而且聚类时无需事先知道聚类的个数。
基本概念
DBSCAN算法中有两个核心参数:Eps和MinPts(文献与程序中经常使用)。前者定义为邻域半径,后者定义为核心对象的阈值。本文为了描述方便,下文将Eps和MinPts分别简记为E和M。
(1) E 邻域:给定对象半径E内的区域成为该对象的E邻域。该E邻域为球形,其半径的界定可以采用距离(欧式距离)、余弦相似度、Word2Vec等表征,本文实现采用余弦相似度来表征。
(2) 核心对象:若给定对象E 邻域内的对象(样本点)个数大于等于M,则称该对象为核心对象。
(3) 直接密度可达:给定一个对象集合D,若对象p在q的E 邻域内,且q是一个核心对象,则称对象p从对象q出发是直接密度可达的(directly density-reachable)。
(4) 密度可达:给定一个对象集合D,若存在一个对象链p1,p2,p3,...,pn,p1=q,pn=p,对于pi属于D,i属于1~n,p(i+1)是从pi关于E和M直接密度可达的,则称对象p从对象q关于E和M密度可达的。
(5) 密度相连:给定一个对象集合D,若存在对象o属于D,使对象p和q均从o关于E和M密度可达的,那么对于对象p到q是关于E和M密度相连的。
(6) 边界对象:给定一个对象集合D,若核心对象p中存在对象q,但是q对象自身并非核心对象,则称q为边界对象。
(7) 噪声对象:给定一个对象集合D,若对象o既不是核心对象,也不是边界对象,则称o为噪声对象。
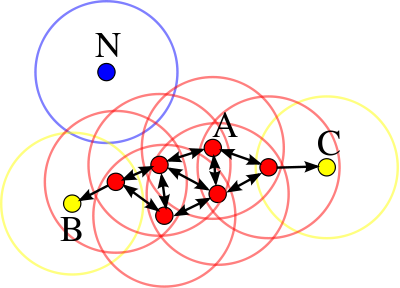
图1 集合对象
如图1所示,其设定M=3,红色节点为核心对象,黄色节点为边界节点,蓝色为噪声节点。
DBSCAN算法不仅能对对象进行聚类,同时还能识别噪声对象,即不属于任何一个聚类。需要指出:密度可达是直接密度可达的传递闭包,这种关系是非对称的,只有核心对象之间相互密度可达;但是,密度相连是一种对称的关系。
DBSCAN的核心思想:寻找密度相连的最大集合,即从某个选定的核心对象(核心点)出发,不断向密度可达的区域扩张,从而得到一个包含核心对象和边界对象的最大化区域,区域中任意两点密度相连。
算法伪代码(参考维基百科):
1 DBSCAN(D, eps, MinPts) {
2 C = 0
3 for each point P in dataset D {
4 if P is visited
5 continue next point
6 mark P as visited
7 NeighborPts = regionQuery(P, eps)
8 if sizeof(NeighborPts) < MinPts
9 mark P as NOISE
10 else {
11 C = next cluster
12 expandCluster(P, NeighborPts, C, eps, MinPts)
13 }
14 }
15 }
16
17 expandCluster(P, NeighborPts, C, eps, MinPts) {
18 add P to cluster C
19 for each point P' in NeighborPts {
20 if P' is not visited {
21 mark P' as visited
22 NeighborPts' = regionQuery(P', eps)
23 if sizeof(NeighborPts') >= MinPts
24 NeighborPts = NeighborPts joined with NeighborPts'
25 }
26 if P' is not yet member of any cluster
27 add P' to cluster C
28 }
29 }
30
31 regionQuery(P, eps)
32 return all points within P's eps-neighborhood (including P)
程序源代码如下:
1 import java.util.List;
2
3 import com.gta.cosine.ElementDict;
4
5 public class DataNode {
6 private List<ElementDict> terms;
7 private boolean isVisited;
8 private int category;
9
10 public DataNode(List<ElementDict> terms)
11 {
12 this.terms = terms;
13 this.isVisited = false;
14 this.category = 0;
15 }
16
17
18 public void setVisitLabel(boolean isVisited)
19 {
20 this.isVisited = isVisited;
21 }
22
23
24 public void setCatagory(int category)
25 {
26 this.category = category;
27 }
28
29
30 public boolean getVisitLabel()
31 {
32 return isVisited;
33 }
34
35
36 public int getCategory()
37 {
38 return category;
39 }
40
41
42 public List<ElementDict> getAllElements()
43 {
44 return terms;
45 }
46
47 }
1 import java.util.List;
2 import java.util.ArrayList;
3
4 import com.gta.cosine.TextCosine;
5 import com.gta.cosine.ElementDict;
6
7 public class DBScan {
8 private double eps;
9 private int minPts;
10 private TextCosine cosine;
11 private int threshold;
12 private List<DataNode> dataNodes;
13 private int delta;
14
15 public DBScan()
16 {
17 this.eps = 0.20;
18 this.minPts = 3;
19 this.threshold = 10000;
20 this.cosine = new TextCosine();
21 this.delta = 0;
22 dataNodes = new ArrayList<DataNode>();
23 }
24
25
26 public DBScan(double eps, int minPts, int threshold)
27 {
28 this.eps = eps;
29 this.minPts = minPts;
30 this.threshold = threshold;
31 this.cosine = new TextCosine();
32 this.delta = 0;
33 dataNodes = new ArrayList<DataNode>();
34 }
35
36
37 public void setThreshold(int threshold)
38 {
39 this.threshold = threshold;
40 }
41
42
43 public int getThreshold()
44 {
45 return threshold;
46 }
47
48
49 public double getEps()
50 {
51 return eps;
52 }
53
54
55 public int getMinPts()
56 {
57 return minPts;
58 }
59
60
61 public List<DataNode> getNeighbors(DataNode p, List<DataNode> nodes)
62 {
63 List<DataNode> neighbors = new ArrayList<DataNode>();
64 List<ElementDict> vec1 = p.getAllElements();
65 List<ElementDict> vec2 = null;
66 double countDistance = 0;
67 for (DataNode node : nodes)
68 {
69 vec2 = node.getAllElements();
70 countDistance = cosine.analysisText(vec1, vec2);
71 if (countDistance >= eps)
72 {
73 neighbors.add(node);
74 }
75 }
76 return neighbors;
77 }
78
79
80 public List<DataNode> cluster(List<DataNode> nodes)
81 {
82 int category = 1;
83 for (DataNode node : nodes)
84 {
85 if (!node.getVisitLabel())
86 {
87 node.setVisitLabel(true);
88 List<DataNode> neighbors = getNeighbors(node, nodes);
89 if (neighbors.size() < minPts)
90 {
91 node.setCatagory(-1);
92 }
93 else
94 {
95 node.setCatagory(category);
96 expandCluster(neighbors, category, nodes);
97 }
98 }
99 category ++;
100 }
101
102 return nodes;
103 }
104
105
106 public void expandCluster(List<DataNode> neighbors, int category, List<DataNode> nodes)
107 {
108 for (DataNode node : neighbors)
109 {
110 if (!node.getVisitLabel())
111 {
112 node.setVisitLabel(true);
113 List<DataNode> newNeighbors = getNeighbors(node, nodes);
114 if (newNeighbors.size() >= minPts)
115 {
116 expandCluster(newNeighbors, category, nodes);
117 }
118 }
119
120 if (node.getCategory() <= 0) // not be any of category
121 {
122 node.setCatagory(category);
123 }
124 }
125 }
126
127
128 public void showCluster(List<DataNode> nodes)
129 {
130 for (DataNode node : nodes)
131 {
132 List<ElementDict> ed = node.getAllElements();
133 for (ElementDict e: ed)
134 {
135 System.out.print(e.getTerm() + " ");
136 }
137 System.out.println();
138 System.out.println("所属类别: "+ node.getCategory());
139 }
140 }
141
142
143 public void addDataNode(String s)
144 {
145 List<ElementDict> ed = cosine.tokenizer(s);
146 DataNode dataNode = new DataNode(ed);
147 dataNodes.add(dataNode);
148 delta ++;
149 }
150
151
152 public void analysis()
153 {
154 if (delta >= threshold)
155 {
156 showCluster(cluster(dataNodes));
157 delta = 0;
158 }
159 }
160 }
关于计算余弦相似度及其源代码,见本系列之文本挖掘之文本相似度判定。本文考虑到随着文本数量的递增,文本聚类结果会分化,即刚开始聚类的文本与后面文本数据相差甚远,本文非常粗略地采用门限值进行限定,本文后续系列联合KMeans和DBSCAN进行解决,若有更好的方法,请联系我。
需要指出:DBSCAN算法对输入参数E和M非常敏感,即参数稍有变化,其聚类结果则会有明显变化。此外,对E和M的选择在实际应用中,需要大规模数据集调优选择(小数据集另当别论),同时对该算法进行改进也是重要研究方向。
作者:志青云集
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/lyssym
如果,您认为阅读这篇博客让您有些收获,不妨点击一下右下角的【推荐】。
如果,您希望更容易地发现我的新博客,不妨点击一下左下角的【关注我】。
如果,您对我的博客所讲述的内容有兴趣,请继续关注我的后续博客,我是【志青云集】。
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。