集合 (唯一性、无序性、可变性)
1、两种定义方法:
>>> set1 = set((1,2,3,4,5)) >>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} >>> set2 = {1,2,3,4,5}
2、三种运算:
>>> set1 = {1,2,3,4,6,5}
>>> set2 = {2,3,4,5,7,8}
>>> set1&set2 #交集
{2, 3, 4, 5}
>>> set1|set2 #并集
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
>>> set1-set2 #差集
{1, 6}
3、集合的增删改查方法
增:
add:增加一个元素
>>> set1.add(8) >>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8}
update:将一个集合的所有元素添加到原来集合中
>>> set1.update({'a','s','d','f'})
>>> set1
{'a', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 8, 's', 'f'}
删:
pop: 删除任意一个元素
{'a', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 8, 's', 'f'}
>>> set1.pop()
'a'
>>> set1
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 8, 's', 'f'}
remove: 删除指定元素
>>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 8, 's', 'f'} >>> set1.remove(8) >>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 's', 'f'}
查:
isdisjoint 有交集返回False
>>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 's', 'f'} >>> set2 {2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8} >>> set1.isdisjoint(set2) False
issubset 判断是否包含于
>>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 's', 'f'} >>> set2 {2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8} >>> set1.issubset(set2) False
issuperset 判断是否包含
>>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 's', 'f'} >>> set2 {2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8} >>> set1.issuperset(set2) False
字典 key键唯一性、无序性、可变性
一、两种定义方法
>>> dict1 = {'name':'炎志','age':'18'}
>>> dict2 = dict(name = '炎志',age = '18')
>>> dict1
{'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'}
>>> dict2
{'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'}
二、修改和添加
>>> dict1 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'} >>> dict2 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'} >>> dict1['name'] = '刘阳' #修改 >>> dict2['post'] = '老师' #添加 >>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18'} >>> dict2 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18', 'post': '老师'}
三、字典的增删改查
删:
pop:通过keyj键删除对应value键值,并返回
>>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18'} >>> dict2 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18', 'post': '老师'} >>> dict2.pop('post') '老师' >>> dict2 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'}
popitem : 删除一个键值对,并返回
>>> dict2 {'name': '炎志', 'age': '18'} >>> dict2.popitem() ('name', '炎志') >>> dict2 {'age': '18'}
clear :清空列表
>>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18'} >>> dict1.clear() >>> dict1 {}
查:
get :通过key查找对应的value值
>>>dict1 = {'name':'刘阳','age':'18'}
>>> dict1.get('name')
'刘阳'
keys : 查找出列表内所有的key
>>> dict1 = {'name':'刘阳','age':'18'}
>>> dict1.keys()
dict_keys(['name', 'age'])
values :查询所有的value
>>> dict1 = {'name':'刘阳','age':'18'}
>>> dict1.values()
dict_values(['刘阳', '18'])
items: 显示所有的键值对
>>> dict1 = {'name':'刘阳','age':'18'}
>>> dict1.items()
dict_items([('name', '刘阳'), ('age', '18')])
增 :
update:把一个字典里的键值对添加的原来的字典里
>>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18'} >>> dict1.update({'from':'沈阳'}) >>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'from': '沈阳'}
setdefault 有则查,无则增
>>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'from': '沈阳'} >>> dict1.setdefault('from') #查 '沈阳' >>> dict1.setdefault('school') #增 >>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'school': None, 'from': '沈阳'}
其他方法:
copy:复制
>>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'school': None, 'from': '沈阳'} >>> dict2 = dict1.copy() >>> dict2 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'school': None, 'from': '沈阳'}
fromkeys : 返回一个新的字典(创建字典)
>>> dict.fromkeys(['aa','bb'],[1,2]) {'bb': [1, 2], 'aa': [1, 2]} >>> dict.fromkeys(['aa','bb']) {'bb': None, 'aa': None} >>> dict.fromkeys(['aa','bb'],{1,2}) {'bb': {1, 2}, 'aa': {1, 2}}
运算符优先级
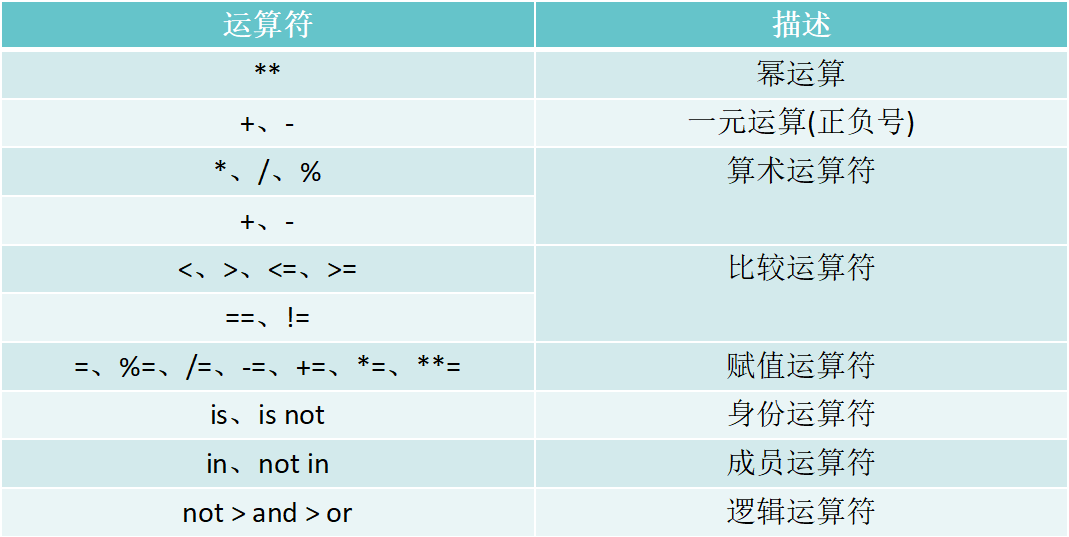
逻辑运算
1、查看对象类型:type
>>> set1 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'd', 's', 'f'} >>> dict1 {'name': '刘阳', 'age': '18', 'school': None, 'from': '沈阳'} >>> type(set1) <class 'set'> >>> type(dict) <class 'type'> >>> type(dict1) <class 'dict'>
判断对象类型:isinstance
>>> isinstance(set1,dict) False >>> isinstance(set1,set) True
2、比较运算符:
== (等于)
>>> 1 == 1 True >>> 2 == 1 False
!=(不等于)
>>> 1 != 1 False >>> 2 != 1 True
3、如果有多个条件:
判断语句1 and 判断语句
>>> True and False False >>> True and True True >>> False and False False
2 判断语句1 or 判断语句2
>>> False or False False >>> True or False True >>> True or True True
not 判断语句1
>>> not True False >>> not False True