Preface
我们今天来把第三本书从开局到现在讲的一大堆理论运用到我们的框架中,那么今天我们首先将原始的材质改为基于重要性采样原理的材质
这一篇是代码工程中进行MC理论应用的初步尝试篇
Ready
我们需要这几个重要的文件,我担心大家手上的文件可能不太对,所以再贴一下

/// rectangle.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] the rectangle-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing the next week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { //the statement of xy_rect class class xy_rect : public intersect { public: xy_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the x-y plane @param: the boundary of x axis the boundary of y axis the value of z axis the material of rectangle */ xy_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _x1, _x2; rtvar _y1, _y2; rtvar _other; }; //the statement of xz_rect class class xz_rect : public intersect { public: xz_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the x-z plane @param: the boundary of x axis the boundary of z axis the value of y axis the material of rectangle */ xz_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar y0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _x1, _x2; rtvar _z1, _z2; rtvar _other; }; //the statement of yz_rect class class yz_rect : public intersect { public: yz_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the y-z plane @param: the boundary of y axis the boundary of z axis the value of x axis the material of rectangle */ yz_rect(rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar x0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _z1, _z2; rtvar _y1, _y2; rtvar _other; }; // the implementation of xy_rect class inline xy_rect::xy_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z0, material* mat) :_x1(x1) , _x2(x2) , _y1(y1) , _y2(y2) , _other(z0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool xy_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().z()) / sight.direction().z(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar x = sight.origin().x() + t*sight.direction().x(); rtvar y = sight.origin().y() + t*sight.direction().y(); if (x < _x1 || x > _x2 || y < _y1 || y > _y2) return false; info._u = (x - _x1) / (_x2 - _x1); info._v = (y - _y1) / (_y2 - _y1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(0, 0, 1); return true; } aabb xy_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_x1, _y1, _other - 0.0001), rtvec(_x2, _y2, _other + 0.0001)); } // the implementation of xz_rect class inline xz_rect::xz_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar y0, material* mat) :_x1(x1) , _x2(x2) , _z1(z1) , _z2(z2) , _other(y0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool xz_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().y()) / sight.direction().y(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar x = sight.origin().x() + t*sight.direction().x(); rtvar z = sight.origin().z() + t*sight.direction().z(); if (x < _x1 || x > _x2 || z < _z1 || z > _z2) return false; info._u = (x - _x1) / (_x2 - _x1); info._v = (z - _z1) / (_z2 - _z1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(0, 1, 0); return true; } aabb xz_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_x1, _other - 0.0001, _z1), rtvec(_x2, _other + 0.0001, _z2)); } // the implementation of yz_rect class inline yz_rect::yz_rect(rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar x0, material* mat) :_y1(y1) , _y2(y2) , _z1(z1) , _z2(z2) , _other(x0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool yz_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().x()) / sight.direction().x(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar y = sight.origin().y() + t*sight.direction().y(); rtvar z = sight.origin().z() + t*sight.direction().z(); if (y < _y1 || y > _y2 || z < _z1 || z > _z2) return false; info._u = (y - _y1) / (_y2 - _y1); info._v = (z - _z1) / (_z2 - _z1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(1, 0, 0); return true; } aabb yz_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_other - 0.0001, _y1, _z1), rtvec(_other + 0.0001, _y2, _z2)); } }// rt namespace

/// box.hpp // https://www.cnblogs.com/lv-anchoret/p/10307569.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] the box-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing the next week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { // the statement of box class class box: public intersect { public: box() { } box(const rtvec& pointmin, const rtvec& pointmax, material * mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; /* public: // the normal of xy_rect, the normal's direction is + inline const rtvec& xy_n() const { return _list[0].Getnormal(); } // the normal of xy_rect, the normal's direction is - inline const rtvec& xy_nflip() const { return _list[1].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& xz_n() const { return _list[2].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& xz_nflip() const { return _list[3].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& yz_n() const { return _list[4].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& yz_nflip() const { return _list[5].Getnormal(); } inline void set_xy_material(material* m) { _list[0].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xy_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[1].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xz_material(material* m) { _list[2].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xz_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[3].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_yz_material(material* m) { _list[4].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_yz_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[5].setmaterial(m); } */ private: rtvec _min; rtvec _max; intersections* _list; //rectangles* _list; }; // the implementation of box class inline box::box(const rtvec& pointmin, const rtvec& pointmax, material * mat) :_min(pointmin) ,_max(pointmax) { intersect ** list = new intersect*[6]; list[0] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _max.z(), mat); list[1] = new flip_normal(new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), mat)); list[2] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.y(), mat); list[3] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.y(), mat)); list[4] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.x(), mat); list[5] = new flip_normal(new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.x(), mat)); _list = new intersections(list, 6); /* rectangle ** list = new rectangle*[6]; list[0] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _max.z(), mat); list[1] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), mat, true); list[2] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.y(), mat); list[3] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.y(), mat, true); list[4] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.x(), mat); list[5] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.x(), mat, true); _list = new rectangles(list, 6);*/ } bool box::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { return _list->hit(sight, t_min, t_max, info); } aabb box::getbox()const { return aabb(_min, _max); } } // rt namespace
为了统一测试效果,所以把main文件代码也贴在下面了
#define LOWPRECISION //#define uvwtest //#define listtest //#define accumulatetest //#define attenuationtest //#define colortest #define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION #include <fstream> #include <stbstb_image.h> #include "include extureRTtexture.hpp" #include "includematerialRTmaterial.hpp" #include "includehitRThit.hpp" #include "camera.hpp" using namespace rt; rtvec lerp(const ray& sight, intersect* world, int depth) { hitInfo info; if (world->hit(sight, (rtvar)0.001, rtInf(), info)) { ray scattered; rtvec attenuation; rtvec light = info._materialp->emitted(info._u, info._v, info._p); if (depth < 50 && info._materialp->scatter(sight, info, attenuation, scattered)) return light + attenuation * lerp(scattered, world, depth + 1); else return light; } else return rtvec(); } void Cornell(intersections** scene, camera** cam, rtvar aspect) { intersect ** list = new intersect*[9]; size_t cnt = 0; material * red = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.65, 0.05, 0.05))); material * blue = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.05, 0.05, 0.73))); material * white = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.88, 0.88, 0.88))); material * green = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.12, 0.45, 0.15))); material * light = new areaLight(new constant_texture(rtvec(20, 20, 20))); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new yz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, green)); list[cnt++] = new yz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, red); list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(200, 350, 220, 340, 550, light); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(200, 350, 220, 340, 550, light)); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, white)); list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, white); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xy_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, blue)); list[cnt++] = new translate(new rotate_x(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(165, 165, 165), white), -45), -30), rtvec(130, 200, 65)); list[cnt++] = new translate(new rotate_z(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(165, 330, 165), white), 30), 20), rtvec(265, 60, 295)); *scene = new intersections(list, cnt); rtvec lookfrom(278, 278, -800); rtvec lookat(278, 278, 0); rtvar dist_to_focus = 10.0; rtvar aperture = 0.; rtvar vfov = 40.0; *cam = new camera(lookfrom, lookat, rtvec(0, 1, 0), vfov, 1, aperture, dist_to_focus, 0., 1.); } void build_1_1() { stds ofstream file("graph-1-1.ppm"); size_t W = 200, H = 200, sample = 200; if (file.is_open()) { file << "P3 " << W << " " << H << " 255 " << stds endl; intersections * world; camera * cma; Cornell(&world, &cma, (rtvar)W / H); for (int y = H - 1; y >= 0; --y) for (int x = 0; x < W; ++x) { rtvec color; for (int cnt = 0; cnt < sample; ++cnt) { lvgm::vec2<rtvar> para{ (lvgm::rand01() + x) / W, (lvgm::rand01() + y) / H }; color += lerp(cma->get_ray(para), world, 0); } color /= sample; #ifdef colortest if (color.x() < 0)stds cout << "color.x < 0 " << stds endl; if (color.y() < 0)stds cout << "color.y < 0 " << stds endl; if (color.z() < 0)stds cout << "color.z < 0 " << stds endl; #endif color = rtvec(sqrt(color.r()), sqrt(color.g()), sqrt(color.b())); //gamma 校正 int r = int(255.99 * color.r()); int g = int(255.99 * color.g()); int b = int(255.99 * color.b()); file << r << " " << g << " " << b << stds endl; } file.close(); if (world)delete world; if (cma)delete cma; stds cout << "complished" << stds endl; } else stds cerr << "open file error" << stds endl; } int main() { build_1_1(); }
Chapter4 Important Sampling Materials
我们的目标就是向光源发送额外的光线使得我们的图片噪声更少
让我们假定我们发送的一束朝向光源的光线的pdf为pLight(direction)
让我们假定一个和s有关的pdf函数,我们叫它为pSurface(direction)
我们可以把两者进行线性组合,得到一个综合的pdf,最简单的形式如下
p(direction) = 0.5*pLight(direction) + 0.5*pSurface(direction)
其实,只要我们的权重是正的,并且加起来等于1,也就是我们经常提到的——pdf积分一定要能积到1,任意pdf函数组合形成的pdf只要满足这两点都是合理的,所以我们可以将几个分量因素的pdf组合控制,使我们的pdf函数更加贴近真实效果。虽然我们可以使用任何的pdf,但是它一定不能改变我们收敛的答案,这是最重要的一点
因此,这就是一个关于寻找pdf的小游戏,要弄清楚如何使s(direction)*color(direction)大的pdf更大,也就是找到合适的pdf,创造更真实的颜色比例效果
对于漫反射(diffuse or Lambertian)表面,我们猜测它更偏重color(direction)因子。 对于镜面(metal)材质表面来说,s()因子只在一个方向附近很大,所以它更重要。
事实上,大多数渲染器将镜面设计成一种特殊情况,只是隐含地使用s / p 进行计算,所以,我们的代码目前也是这样。
我们今天先来测试一下漫反射表面,我们用之前的Cornell盒子做测试,为了方便,我们把相机的设置也放在里面,因为很多时候放在外面,经常换场景,无法记录每个场景采用的合适的摄像机参数,所以就把它和场景放在一起了。
already中的main函数中有Cornell函数,这里就不贴了
我们先用之前的方法跑一个200*200的图,sample为200,光线渲染路径计算递归上限50次
可能效果不是很好,但是噪声多一点,方便看效果
用时如图
效果如图
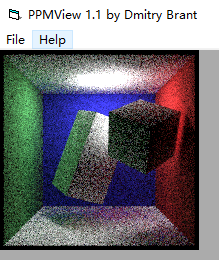
我们的目的是减少噪声,我们将构造一个pdf,使得更多的光线反射到光源
趁着等待渲染的时间,再叨叨两句我们的核心思想,我们的渲染路径是这样计算的
首先我们从eye(或者 camera)发射采样光线,它指向投影屏幕的一个像素位置,也就是当前采样光线正在计算的那个像素位置。
然后光线以射线的形式计算eye与投影屏幕之间所有的几何体交点,得到与eye最近的那个,然后我们以那个交点为落脚点,作为新的eye,按照光学表面散射原理计算新的射线的方向(结合具体的材质),然后继续测交。
如果在递归深度上限范围内没有找到光源,那么说明该像素位置不会有光传入眼睛,也就是当前像素位置是黑色的;如果它找到光源了,也就是经过多次散射最后指向了光源,那么就说明光源发出的光线可以沿着我们的路径逆向进入眼睛,那么我们就看到了这个像素,那么如何计算像素值呢?
这就涉及到了路径渲染方程,里面有一个rgb分量衰减比例控制参数,它依据材质和纹理计算得出,这是之前的,我们现在要加上pdf函数,帮助我们更逼真地计算像素值
好了,唠完了,上图片

貌似没区别,但是我们下面还会继续优化
刚刚那个图跑了53min,接下来你就会知道为什么时间还多了
我们要把重要性采样嵌入进去,首先MC模拟f(x)的积分形式为
f(r)/p(r)
对于Lambertian材质,我们用上一篇的pdf函数:
p(direction) = cosθ/π
所以我们修改material基类如下:
/// material.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the material-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { // the statement of material class class material { public: /* @brief: produce a scattered ray @param: InRay -> Incident light info -> the information of intersect-point(hit-point) attenuation -> when scattered, how much the ray should be attenuated by tis reflectance R scattered -> as we talk, it is a new sight; or it is the scattered ray with the intersect-point pdf -> the Important Sample's pdf function @retur: the function calculate a scattered ray or not */ virtual bool scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { return false; } /* @brief: produce a scattered ray @param: InRay -> Incident light info -> the information of intersect-point(hit-point) scattered -> as we talk, it is a new sight; or it is the scattered ray with the intersect-point @retur: the function calculate a scattered ray or not */ virtual rtvar scatter_pdf(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const { return false; } virtual bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const { return false; } /* @brief: 自发光 @param: 纹理所需信息 @retur: 纹理像素值 */ virtual rtvec emitted(rtvar u, rtvar v, const rtvec& p)const { return rtvec(); } }; }
/// diffuse.hpp // https://www.cnblogs.com/lv-anchoret/p/10198423.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] one of the materials // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class texture; // the statement of lambertian class class lambertian : public material { public: lambertian(texture* _tex); rtvar scatter_pdf(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const; bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const; public: const texture* get_texture()const { return _albedo; } void set_texture(texture* tex) { _albedo = tex; } protected: texture* _albedo; }; // the implementation of lambertian class inline lambertian::lambertian(texture* _tex) :_albedo(_tex) { } rtvar lambertian::scatter_pdf(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const { rtvar cosine = dot(info._n, scattered.direction().ret_unitization()); if (cosine < 0)cosine = 0; return cosine / π; } bool lambertian::scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { rtvec target = info._p + info._n + lvgm::random_unit_sphere(); scattered = ray{ info._p, (target - info._p).ret_unitization(), rIn.time() }; attenuation = _albedo->value(info._u, info._v, info._p); pdf = dot(info._n, scattered.direction()) / π; return true; } } // rt namespace
以及主函数中的lerp函数
rtvec lerp(const ray& sight, intersect* world, int depth) { hitInfo info; if (world->hit(sight, (rtvar)0.001, rtInf(), info)) { ray scattered; rtvec emitted = info._materialp->emitted(info._u, info._v, info._p); rtvar pdf; rtvec albedo; if (depth < 50 && info._materialp->scatter(sight, info, albedo, scattered, pdf)) return emitted + albedo *info._materialp->scatter_pdf(sight, info, scattered)*lerp(scattered, world, depth + 1) / pdf; else return emitted; } else return rtvec(); }
所以,它运行时间多了3min,新代码的运算只增无减
解释一些东西:
scatter_pdf函数里面的cosine值是散射光线和表面法线的夹角,所以大于90°无效,表示采样失败,上一篇说过
scatter函数还是原来的差不多
上述是基于上一本书的第一次修改
下面来进行第二次修改
我们尝试一下不同的采样策略,比如,我们选择从表面的上半球部分随机采样(可以把物体放入球坐标系中,我们只取上半球部分),那么我们的p(direction) = 1/(2π)
因为球体的球面度是4πsr,所以半球就是2πsr,采取表面均匀采样的话,就是一立体角对应的球面度量1sr,所以就是1/(2π)
bool lambertian::scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { rtvec direction; do{ direction = lvgm::random_unit_sphere(); } while (dot(direction, info._n) < 0); scattered = ray{ info._p,direction.ret_unitization(),rIn.time() }; attenuation = _albedo->value(info._u, info._v, info._p); pdf = 0.5 / π; return true; }
按理说应该得到同上述两张图片相同的图片,但是可能事与愿违

书作者采用的是咱们2-7教程里面的如下图左上角那张,而我们今天采用的是右下角那张,因为它让问题看的更清楚

下面是书中的结尾

其实你看一下这张图顶部的白光(这一变化更容易让我们捕捉到),就可以验证作者所提出的问题
本来是周六就写了这篇的草稿的,但是因为抄错代码了,出不来效果,白天调了好久。。。可能不适合抄东西。。
感谢您的阅读,生活愉快~
