一、函数分类
1、单行函数
如:concat、length、ifnull等
2、分组函数
功能:做统计使用,又称 统计函数、聚合函数、组函数
二、字符函数
1、length:获取参数值的字节个数
# length select length('hellow world'); -- 结果为12 # 结果为14,因为客户端的字符集为utf-8,该字符集中一个汉字占3个字节,一个英文为一个字节 select length('数据库niubi'); # 查看字符集 show variables like '%char%';
2、caocat:拼接字符串
3、upper:将小写字符转换为大写字符
# 小写转换为大写 select upper("21Fad撒旦法");
4、lower:将大写字符转变为小写字符
# 大写转换为小写 select lower("FAF")
5、substr:截取字符串
# 从指定索引位开始截取 -- 注:1、索引位从1开始 -- 2、按字符计数 select substr("世界你好",3) -- 结果:你好 # 从指定位置开始截取指定长度字符 -- 2:表示从第二位开始截取 -- 3:表示一共需要截取3位 select substr("世界你好啊",2,3) -- 结果:界你好
6、instr:返回子串中指定字符串第一次出现的索引位,如果找不到就返回0
select instr("世界你真的真挺好真挺",'真挺') -- 结果:6
7、trim:去除前后指定字符串,默认去除前后空格
# 去除字符串前后空格 select trim(" hellow world "); -- 结果:hellow world # 去除指定字符串 select trim("ee" from "eee测试eee测试eee"); -- 结果:e测试eee测试e
8、lapd:在左边用指定字符填充指定长度
select lpad("测试",4,'e'); -- 结果:ee测试 # 如果字符串长度少于指定长度则会对字符串进行截图 select lpad("测试",1,'e'); -- 结果:测
9、rapd:在右边填充指定长度的字符串
select rpad("测试",4,'e'); -- 结果:测试ee # 如果字符串长度少于指定长度则会对字符串进行截图 select rpad("测试",1,'e'); -- 结果:测
10、replace:替换
如果指定替换的字符串未找到则会返回原字符串
select replace("我好世界我好","我好","你好"); -- 结果:你好世界你好
三、数学函数
1、# round():四舍五入
# round():四舍五入 select round(1.34); -- 结果:1 select round(1.57); -- 结果:2 select round(-1); -- 结果:-1 select round(1.764,2); -- 结果:1.76
2、ceil():向上取整,取大于指定数值最靠近的整数
# ceil():向上取整,取大于指定数值最靠近的整数 select ceil(1.2); -- 结果:2 select ceil(1); -- 结果:1 select ceil(-1); -- 结果:-1
3、floor():向下取整,取小于指定数值最靠近的整数
# floor():向下取整,取小于指定数值最靠近的整数 select floor(1.2); -- 结果:1 select floor(1); -- 结果:1 select floor(-1.2); -- 结果:-2
4、truncate():截取
# truncate():截取 select truncate(1.6999,1); -- 结果:1.6 select truncate(1.6999,0); -- 结果:1
5、mod():取余
# mod():取余 select mod(10,3); -- 结果:1(等同于10%3)
6、rand():取0到1的随机数
# rand()返回0到1之间的随机数 select rand(); select ceiling(rand()*12);
四、日期函数
1、now:返回当前系统时间
# now:返回当前系统时间 select now(); -- 结果:2022-03-04 20:17:03
2、curdate:返回当前系统日期
# curdate:返回当前系统日期 select curdate(); -- 结果:2022-03-04
3、curtime:返回当前系统时间(不包含日期)
# curtime:返回当前系统时间(不包含日期) select curtime(); -- 结果:20:17:03
4、获取指定部分:年、月、日、时、分、秒
# 获取年 select year(now()); -- 结果:2022 select year('1998-01-01'); -- 结果:1998 # 获取月 select month(now()); -- 结果:03 select monthname(now()); -- 结果:March # 获取日 select day(now()); -- 结果:04 # 获取时 select hour(now()); -- 结果:20 # 获取分 select minute(now()); -- 结果:23 # 获取秒 select second(now()); -- 结果:45
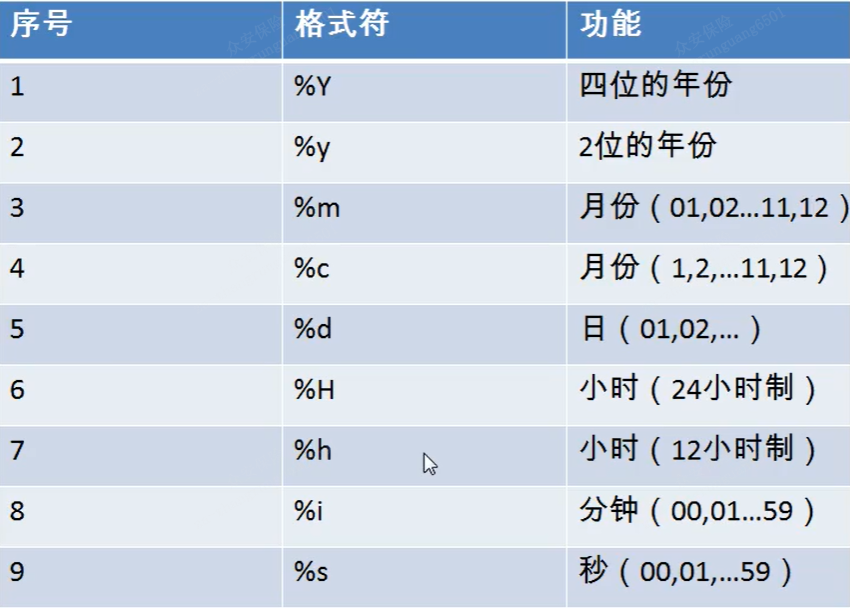
5、str_to_date:将字符通过指定格式转换为日期
select str_to_date('2-02 2022 19:23:23','%m-%d %y'); -- 结果:2022-02-02
6、date_format:将日期转换为字符
select date_format('2022-02-01','%y年%m月-%d日'); -- 结果:22年02月-01日
五、日期函数
1、查看当前数据库系统版本
select version();
2、查看当前用户
select user();
3、password()返回该字符的密码形式
# password()返回该字符的密码形式 select password('ces'); -- 结果:*A671B6D306655A35C8EB6F3ABBE6E9441F0DE79D
4、md5():返回字符的md5加密形式
select md5('ces');
六、流程控制函数
1、if函数(if...else..)
# if函数 判断10是否大于5,如果大于就返回“是”否则就返回“不是” select if(10>5, "是", "不是"); -- 结果:是
七、case函数
1、使用方法一
语法:(如果then后面是语句需要加;,如果不是则不需要添加;else可写可不写;)
case 要判断的字段或者表达式
when 常量1 then 要显示的值1或者语句1;
when 常量2 then 要显示的值2或者语句2;
...
else 要显示的值N或者语句N;
end
# 查询员工的工资,要求 # 部门号=30,显示的工资为1.1倍 # 部门号=40,显示的工资为1.2倍 # 部门号=50,显示的工资为1.3倍 # 其他部门,显示工资为原工资 select salary 原始工资,department_id, case department_id when 30 then salary*1.1 when 40 then salary*1.2 when 50 then salary*1.3 else salary end as 新工资 from employees;
2、使用方法二
语法:(如果then后面是语句需要加;,如果不是则不需要添加;else可写可不写;)
case
when 条件1 then 要显示的值1或语句1;
when 条件2 then 要显示的值2或语句2;
.....
else 要显示的值n或语句n
end
/* 查询员工的工资,要求 部门号>20000,显示工资等级为A 部门号>15000,显示工资等级为B 部门号>1000,显示工资等级为C 其他工资,显示工资等级为D */ select salary,department_id, case when salary>20000 then 'A' when salary>15000 then 'B' when salary>10000 then 'C' else 'D' end 工资等级 from employees;
八、练习
# 显示系统时间(注:日期+时间) select now() as 当前系统时间; select * from employees; # 查询员工号、姓名、工资,以及工资提高20%之后的结果 select employee_id,concat(first_name,last_name) 姓名, salary 原工资,salary*1.2 提薪 from employees; # 将员工的姓名按首要字母排序,并写出姓名的长度 select concat(first_name,last_name) 姓名, length(concat(first_name,last_name)) 姓名长度 from employees order by 姓名 asc; select concat(first_name,last_name) 姓名,substr(concat(first_name,last_name),1,1) 首字母, length(concat(first_name,last_name)) 姓名长度 from employees order by 首字母 asc; # 做一个查询,产生下面的结果 select concat(concat(first_name,last_name),' earns ',salary,' monthly but wants ',salary*3) 期望薪资 from employees; # 使用case——then,按照下面的条件 select job_id, case job_id when 'AD_PRES' then 'a' when 'ST_MAN' then 'b' when 'IT_PROG' then 'c' else 'd' end grade from employees;