https://vjudge.net/problem/2135388/origin
Describe
You are given an integer sequence 1,2,…,n. You have to divide it into two sets A and B in such a way that each element belongs to exactly one set and |sum(A)−sum(B)| is minimum possible.
The value |x| is the absolute value of x and sum(S) is the sum of elements of the set S.
Input
The first line of the input contains one integer n (1≤n≤2⋅109).
Output
Print one integer — the minimum possible value of |sum(A)−sum(B)| if you divide the initial sequence 1,2,…,n into two sets A and B.
Examples
Input
3
Output
0
Input
5
Output
1
Input
6
Output
1
Note
Some (not all) possible answers to examples:
In the first example you can divide the initial sequence into sets A={1,2} and B={3} so the answer is 0.
In the second example you can divide the initial sequence into sets A={1,3,4} and B={2,5} so the answer is 1.
In the third example you can divide the initial sequence into sets A={1,4,5} and B={2,3,6} so the answer is 1.
这是一道思维题,刚拿到题的时候毛了,这是什么题,DP背包容量为1/2值的和;不难发现这个题是个防爆零的送分题。
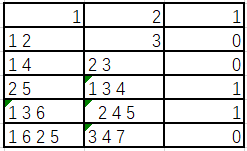
在表格中不难看出,当数字个数为偶数个时,要平分到两个组合,如果平分后个数为奇数肯定数组中间的两个值被分开,最小差值唯一,123456 分1 / 6 分2 / 5 分3 /4,差值为1; 当个数为奇数个时便有如下方法如果去掉最大之后,按照偶数分析。
AC代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define mst(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof(a))
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define maxn 100
#define Abs(a) ((a)>0?(a):-(a))
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n%2==1) {
n=n-1;
n/=2;
if(n%2==1) cout<<'0'<<endl;
else cout<<'1'<<endl;
return 0;
}
else
{
n=n/2;
if(n%2==0) cout<<'0'<<endl;
else cout<<'1'<<endl;
return 0;
}
}