Map阶段总共五个步骤:如图就是分区操作
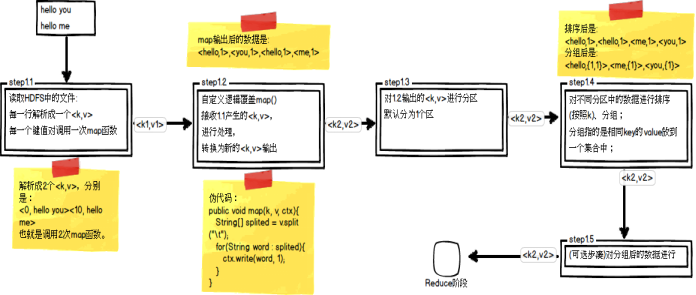
哪个key到哪个Reducer的分配过程,是由Partitioner规定的。
Hadoop内置Partitioner
MapReduce的使用者通常会指定Reduce任务和Reduce任务输出文件的数量(R)。
用户在中间key上使用分区函数来对数据进行分区,之后在输入到后续任务执行进程。一个默认的分区函数式使用hash方法(比如常见的:hash(key) mod R)进行分区。hash方法能够产生非常平衡的分区。
Hadoop中自带了一个默认的分区类HashPartitioner,它继承了Partitioner类,提供了一个getPartition的方法。
/** Partition keys by their {@link Object#hashCode()}. */
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,int numReduceTasks) {
return
(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
将key均匀布在Reduce Tasks上
(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
如果Key为Text的话,Text的hashcode方法跟String的基本一致,都是采用的Horner公式计算,得到一个int整数。但是,如果string太大的话这个int整数值可能会溢出变成负数,所以和整数的上限值Integer.MAX_VALUE(即0111111111111111)进行与运算,然后再对reduce任务个数取余,这样就可以让key均匀分布在reduce上。
一般我们都会使用默认的分区函数HashPartitioner。
public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, KpiWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, KpiWritable value, int numPartitions) {
// 实现不同的长度不同的号码分配到不同的reduce task中
int numLength = key.toString().length();
if (numLength == 11) return 0;
else return 1;
}
}
排序例子:
package mapreduce01;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class sort {
static String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://master:9000/sort";
static String OUTPUT_PATH="hdfs://master:9000/output";
static class MyMapper extends Mapper<Object,Object,IntWritable,NullWritable>{
IntWritable output_key = new IntWritable();
NullWritable output_value = NullWritable.get();
protected void map(Object key,Object value,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
int val = Integer.parseInt(value.toString().trim());
output_key.set(val);
context.write(output_key, output_value);
}
}
public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<IntWritable, NullWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(IntWritable key, NullWritable value, int numPartitions) {
// 实现不同的长度不同的号码分配到不同的reduce task中
// int numLength = key.toString().length();
if (key.get() >1000) return 0;
else return 1;
}
}
static class MyReduce extends Reducer<IntWritable,NullWritable,IntWritable,IntWritable> {
IntWritable output_key = new IntWritable();
//IntWritable input_key=new IntWritable();
int num=0;
protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<NullWritable> values,Context context) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
output_key.set(num++);
context.write(output_key, key);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Path outputpath = new Path(OUTPUT_PATH);
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = outputpath.getFileSystem(conf);
if(fs.exists(outputpath)){
fs.delete(outputpath,true);
}
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,INPUT_PATH);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputpath);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
job.setReducerClass(MyReduce.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
小结:
分区Partitioner主要作用在于以下两点 根据业务需要,产生多个输出文件。
多个reduce任务并发运行,提高整体job的运行效率。