概述
lambda表达式是JDK 1.8提供的一种新特性,它使得Java也能像C#和C++语言一样进行简单的“函数式编程”,这不仅简化了某些通用结构的实现方式,也大大增强了Java语言的表达功能。
lambda表达式是基于数学中的λ演算得名,本质上就是一个没有方法名的匿名方法。
lambda表达式的使用
lambda表达式不是独立执行的,而是经常被应用在函数式接口(functional interface)定义的抽象方法的实现中。
函数式接口
函数式接口是指只包含一个抽象方法的接口。函数式接口的抽象方法指明了接口的目标用途。
定义了函数式接口之后,就可以把lambda表达式赋值给该接口的一个引用,lambda表达式定义了函数式接口声明的抽象方法的行为。
例如:定义一个接口Computer,其中只有一个抽象方法compute(),则Computer是一个函数式接口。

1 interface Computer { 2 3 int compute(int x, int y); 4 5 }
lambda表达式格式
lambda表达式类似于匿名内部类,表达式本身实现了函数式接口的唯一抽象方法,而表达式返回的结果是一个函数式接口类型。
lambda表达式通常以“(参数) -> {方法体}”这样的格式书写,其中“->”被称为lambda运算符或箭头运算符,具体有2种形式:
省略参数类型:(参数1, 参数2, ...) -> {方法体}
指定参数类型:(类型1 参数1, 类型2 参数2, ...) -> {方法体}
如果方法体内只有一个语句,且该语句的返回值类型与抽象方法定义的返回值类型相同,则可以省略“{ }”和return关键字。

1 @Test 2 void testLambda() { 3 Computer add = (x, y) -> x + y; 4 /*********************************** 5 等同于: 6 Computer add = new Computer() { 7 8 @Override 9 public int compute(int x, int y) { 10 return x + y; 11 } 12 13 }; 14 ***********************************/ 15 }
需要注意的是,如果方法体内只有一个语句,而该语句的返回值类型与抽象方法定义的返回值类型不同,则不能省略“{ }”和return关键字。
如果将compute()方法返回值类型改为void,则上面的代码会报错,提示void类型方法不能返回一个值。
如果方法体内有多个语句,则需要使用“{ }”括起来。

1 @Test 2 void testLambda() { 3 Computer add = (x, y) -> { 4 int result = x + y; 5 return result; 6 }; 7 /*********************************** 8 等同于: 9 Computer add = new Computer() { 10 11 @Override 12 public int compute(int x, int y) { 13 int result = x + y; 14 return result; 15 } 16 17 }; 18 ***********************************/ 19 }
示例
传统用法:

1 @Test 2 void testTraditional() { 3 Computer add = new Computer() { 4 5 @Override 6 public int compute(int x, int y) { 7 return x + y; 8 } 9 10 }; 11 System.out.println("加法计算器:"); 12 System.out.println("90+15=" + add.compute(90, 15)); 13 }
lambda表达式用法:

1 @Test 2 void testLambda() { 3 Computer add = (x, y) -> x + y; 4 System.out.println("加法计算器:"); 5 System.out.println("90+15=" + add.compute(90, 15)); 6 }
输出结果:
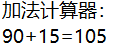
方法引用
方法引用是lambda表达式的另一种更为简洁的用法。需要注意的是,引用的方法是当前类可以访问到的方法。方法引用分为3种形式:
类方法的方法引用
类方法的方法引用的格式为:引用类的类名 :: 引用类的类方法名。该方式需要抽象方法的参数与引用的类方法的参数一致,返回值类型也要一致。
定义一个Computer函数式接口,该接口中有一个抽象方法compute()。

1 interface Computer { 2 3 int compute(int x, int y); 4 5 }
定义一个ComputerImpl类,该类中有一个类方法add()。

1 class ComputerImpl { 2 3 static int add(int x, int y) { 4 return x + y; 5 } 6 7 }
类方法的方法引用。

1 @Test 2 void testMethodReferences() { 3 Computer add = ComputerImpl :: add; 4 }
实例方法的方法引用
实例方法的方法引用有两种格式:
通过实例引用实例方法
通过实例引用实例方法的格式为:引用类的类实例 :: 引用类的实例方法名。该方式需要抽象方法的参数与引用的实例方法的参数一致,返回值类型也要一致。
定义一个Computer函数式接口,该接口中有一个抽象方法compute()。

1 interface Computer { 2 3 float compute(int x, int y); 4 5 }
定义一个ComputerImpl类,该类中有一个实例变量f和一个实例方法divide()。

1 class ComputerImpl { 2 3 float f; 4 5 float divide(int x, int y) { 6 return x / y * f; 7 } 8 9 }
通过实例引用实例方法的方法引用。

1 @Test 2 void testMethodReferences() { 3 ComputerImpl computerImpl = new ComputerImpl(); 4 computerImpl.f = 1.0f; 5 Computer divide = computerImpl :: divide; 6 }
通过类名引用实例方法
通过类名引用实例方法的格式为:引用类的类名 :: 引用类的实例方法名。该方式需要抽象方法的第一个参数为引用类实例,之后的参数与引用的实例方法的参数一致,返回值类型也要一致。注意引用类实例参数必须是抽象方法的第一个参数,不能放在其他位置。
定义一个Computer函数式接口,该接口中有一个抽象方法compute()。

1 interface Computer { 2 3 float compute(ComputerImpl computer, int x, int y); 4 5 }
定义一个ComputerImpl类,该类中有一个实例变量f和一个实例方法divide()。

1 class ComputerImpl { 2 3 float f; 4 5 float divide(int x, int y) { 6 return x / y * f; 7 } 8 9 }
通过类名引用实例方法的方法引用。

1 @Test 2 void testMethodReferences() { 3 Computer divide = ComputerImpl :: divide; 4 }
两种方式的区别
通过实例引用实例方法是先创建一个实例,然后通过实例引用实例方法。当实例改变时,需要再次引用实例方法。
通过类名引用实例方法是直接通过类名引用实例方法。这种方式引用实例方法需要抽象方法的第一个参数为引用类的实例。当实例改变时,只需在调用方法时传入新的实例即可,无需再次引用实例方法。
构造方法的方法引用
构造方法的方法引用的格式为:引用类的类名 :: new。该方式需要抽象方法的参数与构造方法的参数一致,返回值类型为引用类的类型。
定义一个Computer函数式接口,该接口中有一个抽象方法newInstance()。

1 interface Computer { 2 3 ComputerImpl newInstance(int x, int y); 4 5 }
定义一个ComputerImpl类,该类中有两个实例变量x和y,以及一个带参构造方法。

1 class ComputerImpl { 2 3 int x; 4 int y; 5 6 public ComputerImpl(int x, int y) { 7 this.x = x; 8 this.y = y; 9 } 10 11 }
构造方法的方法引用。

1 @Test 2 void testMethodReferences() { 3 Computer computer = ComputerImpl :: new; 4 }
