https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Wmx915VJ1omZH_qWMibM0w
CREATE TABLE `table1` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL, `age` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL, `sponsor_id` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '业务发起人', `gmt_create_user` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '创建人id', `gmt_create` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', `gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', `gmt_modified_user` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改人id', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=12 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='测试表1'; CREATE TABLE `table2` ( `kid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL, `sponsor_id` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '业务发起人', `type` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '创建人id', `gmt_create` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', `gmt_modified` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改时间', `gmt_modified_user` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '修改人id', PRIMARY KEY (`kid`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=12 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='测试表2';
插入数据:
INSERT INTO `table1`(`id`, `name`, `age`, `sponsor_id`, `gmt_create_user`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (1, 't1', '11', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:34:03', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table1`(`id`, `name`, `age`, `sponsor_id`, `gmt_create_user`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (2, 't2', '12', '10', 2, '2018-10-10 20:34:03', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table1`(`id`, `name`, `age`, `sponsor_id`, `gmt_create_user`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (3, 't3', '13', '10', 3, '2018-10-10 20:34:03', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table1`(`id`, `name`, `age`, `sponsor_id`, `gmt_create_user`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (4, 't4', '14', '20', 4, '2018-10-10 20:34:03', NULL, NULL);
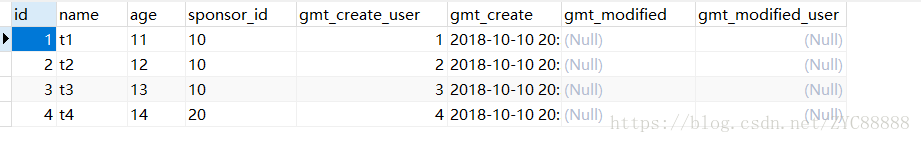
INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (1, 't1', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (2, 't2', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (3, 't3', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (4, 't4', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (5, 't5', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (6, 't6', '10', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (7, 't7', '10', 2, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL); INSERT INTO `table2`(`kid`, `name`, `sponsor_id`, `type`, `gmt_create`, `gmt_modified`, `gmt_modified_user`) VALUES (8, 't1', '11', 1, '2018-10-10 20:38:10', NULL, NULL);
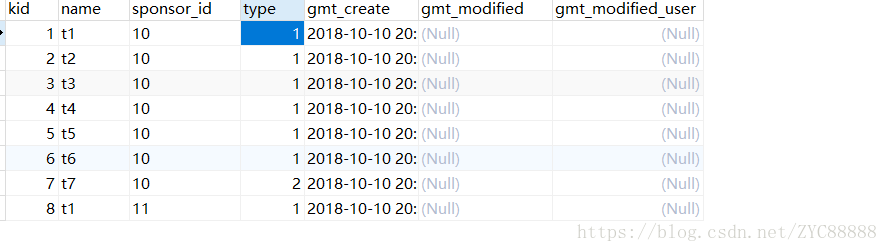
查询异常:
SELECT a.*, b.type FROM table1 a LEFT JOIN table2 b ON a.sponsor_id = b.sponsor_id WHERE b.type = 1 AND a.sponsor_id = 10;
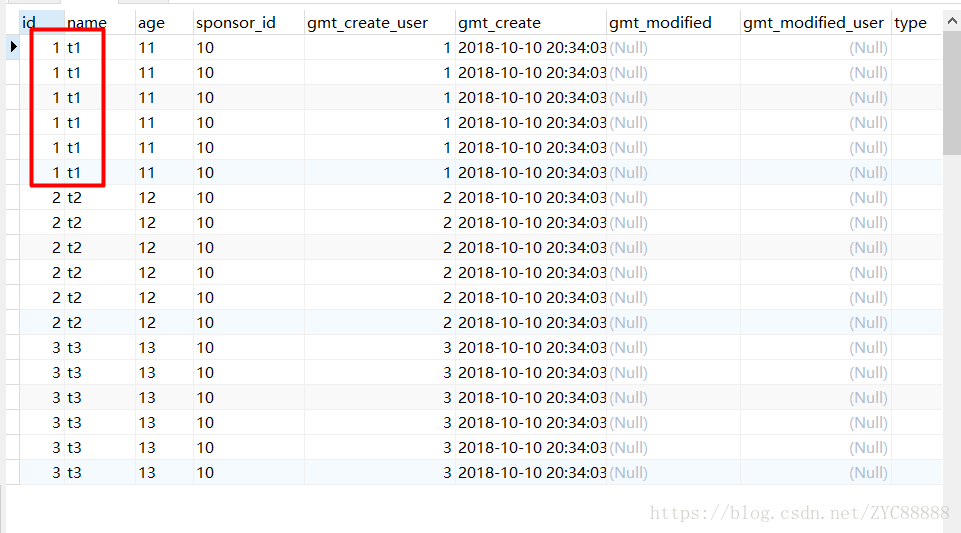
简单说明问题出现的原因:
MySQL left join 语句格式为:A LEFT JOIN B ON 条件表达式
left join 是以A表为基础,A表即左表,B表即右表。
左表(A)的记录会全部显示,而右表(B)只会显示符合条件表达式的记录,如果在右表(B)中没有符合条件的记录,则记录不足的地方为NULL。
使用left join, A表与B表所显示的记录数为 1:1 或 1:0,A表的所有记录都会显示,B表只显示符合条件的记录。
但如果B表符合条件的记录数大于1条,就会出现1:n的情况,这样left join后的结果,记录数会多于A表的记录数。
所以解决办法 都是从一个出发点出发,使A表与B表所显示的记录数为 1:1对应关系。
解决方法:
使用非唯一标识的字段做关联
1 DISTINCT
select DISTINCT(id) from a left join b on a.id=b.aid DISTINCT查询结果是 第一个表唯一的数据 重复的结果没显示出来
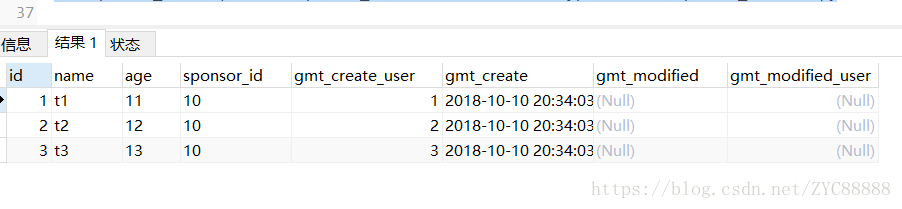
SELECT DISTINCT(a.id), a.*, b.type FROM table1 a LEFT JOIN table2 b ON a.sponsor_id = b.sponsor_id WHERE b.type = 1 AND a.sponsor_id = 10;
SELECT DISTINCT a.*, b.type FROM table1 a LEFT JOIN table2 b ON a.sponsor_id = b.sponsor_id WHERE b.type = 1 AND a.sponsor_id = 10;
2 GROUP BY
select * from a left join(select id from b group by id) as b on a.id=b.aid拿出b表的一条数据关联 使A表与B表所显示的记录数为 1:1对应关系。
SELECT a.*, b.type FROM table1 a LEFT JOIN ( SELECT * FROM table2 GROUP BY sponsor_id ) AS b ON a.sponsor_id = b.sponsor_id WHERE b.type = 1 AND a.sponsor_id = 10;
3 max取唯一
select * from a left join (select max(id) from table group by id) as b on a.id=b.aid 拿出b表的最后一条数据关联
SELECT a.*, b.type FROM table1 a LEFT JOIN ( SELECT MAX( kid ), type, sponsor_id FROM table2 GROUP BY sponsor_id ) AS b ON a.sponsor_id = b.sponsor_id WHERE b.type = 1 AND a.sponsor_id = 10;
4 IN巧用
SELECT a.* FROM table1 a WHERE a.sponsor_id IN ( SELECT sponsor_id FROM table2 WHERE type = 1 AND sponsor_id = 10 );
SELECT a.*, 1 FROM table1 a WHERE a.sponsor_id IN ( SELECT sponsor_id FROM table2 WHERE type = 1 AND sponsor_id = 10 );
PS:
- 表结构
- Left Join
- Right Join
- Inner Join
- 表的关联修改和删除
- 笛卡尔积
1、表结构
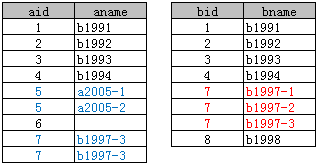
2、Left Join
示例:2.1
Select * From A left join B on A.aid = B.bid;
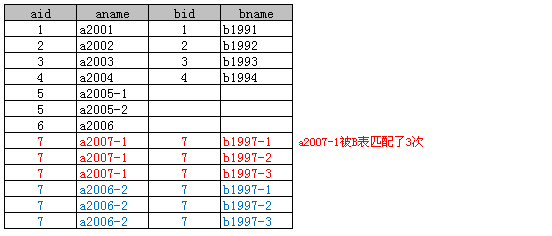
left join是以A表的记录为基础的,A可以看成左表,B可以看成右表,left join是以左表为准的。换句话说,左表A的记录将会全部表示出来,而右表B只会显示符合搜索条件的记录(例子中为: A.aid = B.bid),B表记录不足的地方均为NULL.
- A表所有记录都会显示,A表中没有被匹配的行(如aid=5、6的行)相应内容则为NULL。
- 返回的记录数一定大于A表的记录数,如A表中aid=7行被B表匹配了3次(因为B表有三行bid=7)。
注意:在Access中A.aid、B.bid不能缩写成aid、bid,否则会提示“不支持链接表达式”,这一点不同于Where查询。
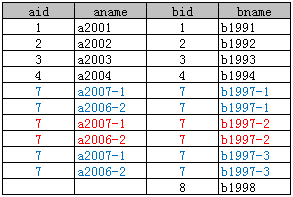
3、Right Join
Select * From A right join B on A.aid = B.bid;
4、Inner Join
Select * From A inner join B on A.aid = B.bid;
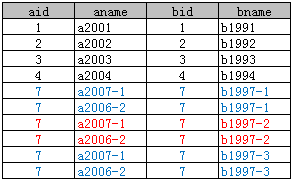
这里只显示出了 A.aid = B.bid的记录.这说明inner join并不以谁为基础,它只显示符合条件的记录。
inner join 等同于Where查询如:
Select * From A, B Where A.aid = B.bid
5、表的关联修改和删除
update A left join B on A.aid = B.bid
set A.aname = B.bname
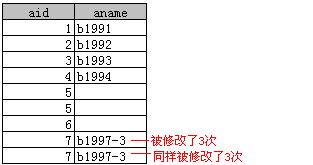
示例:5.1.2
Where条件查询在上面的SQL中同样可以使用,其作用的表也是Select查询出的关联表。如下SQL
update A left join B on A.aid = B.bid set A.aname = B.bname where A.aid <> 5
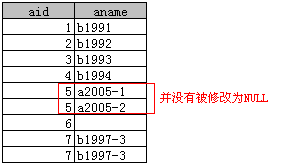
对比第一次update可以发现,aid=5的并没有被更新。
这里只讲述left join,因为right join 和 inner join的处理过程等同于left join。另外Access中update语句中不能含有From关键字,这一点不同于其他数据库。
5.2删除
在Access中是不可以通过Left Join、Right Join、Inner Join来删除某张表的记录
示例:5.2.2
Delete From A inner join B on A.aid = B.bid
where B.bname = "b1991"
上述SQL的本意是删除A表中aid=1的记录,但执行后表A和表B均未发生任何变化。若想实现此目的,下述SQL可以实现
Delete From A
Where A.aid In (Select bid From B Where B.bname="b1991")