基础概念
js 本身是基于面向对象开发的语言
=> 封装 继承 多态
封装: 类也是一个函数,把实现一个代码的功能进行封装,以此实现 低耦合高内聚
多态: 重载 重写
重写:子类重写父类上的方法
重载:相同的方法,由于参数或者返回值不同,具备了不同的功能。
js中的重载:同一个方法内,根据传参不同实现不同的功能
继承:子类继承父类中的方法
继承目的
让子类的实例也具备父类中私有属性和公共方法
1.原型链继承
(让子类的原型等于父类的实例即可)
现在来看一个例子
原型继承特点
1.父类中私有和公有的属性方法,最后都变为子类实例公有的。
2.原型链继承并不会把父类的属性方法‘拷贝’给子类,而是让子类基于__proto__原型链找到自己定义的属性和方法。
** 注意:**进行修改的话,会使父类的属性和方法也会进行修改。这样不仅会影响其他父类的实例,也影响其他子类的实例
代码
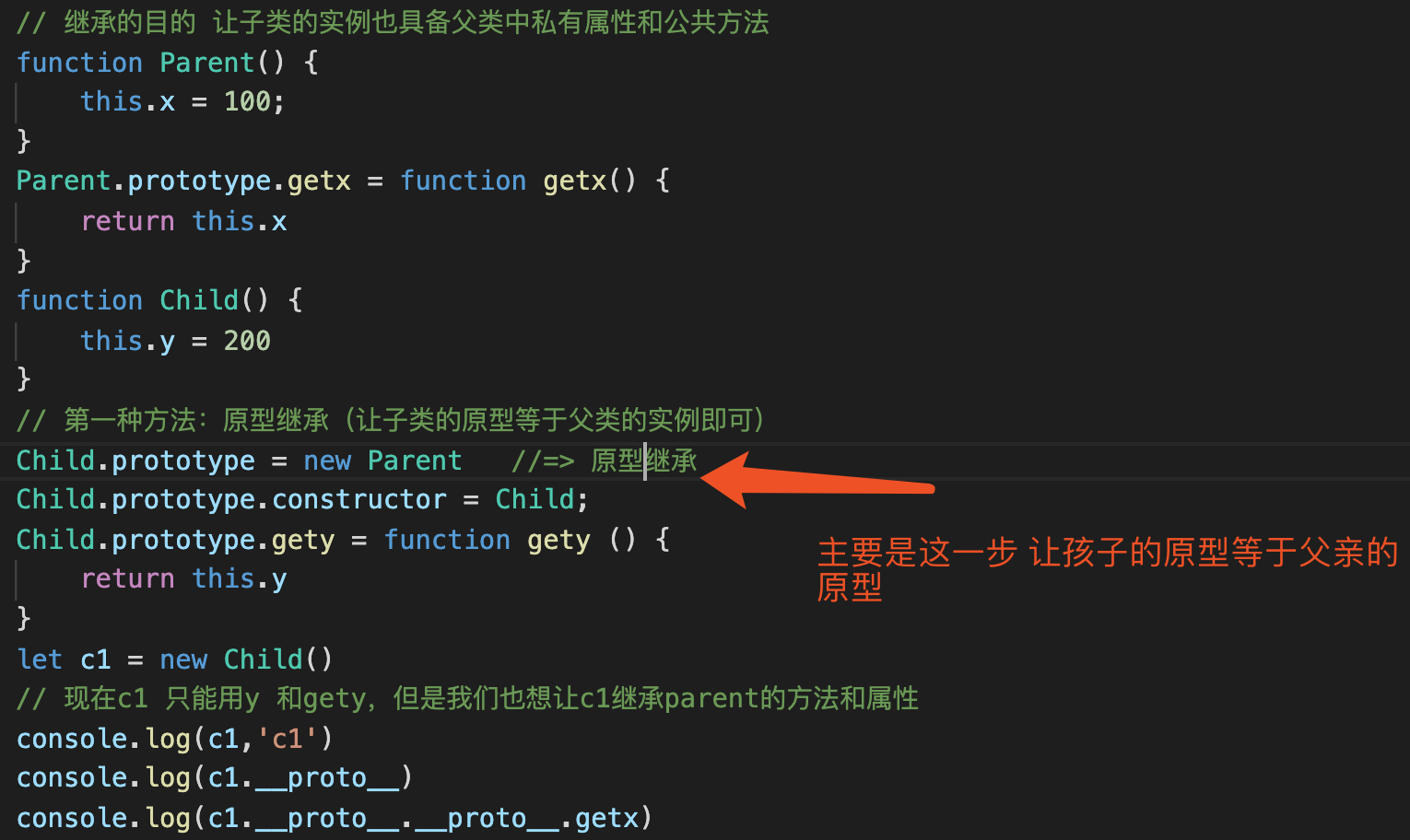
// 继承的目的 让子类的实例也具备父类中私有属性和公共方法
function Parent() {
this.x = 100;
}
Parent.prototype.getx = function getx() {
return this.x
}
function Child() {
this.y = 200
}
// 第一种方法:原型继承(让子类的原型等于父类的实例即可)
Child.prototype = new Parent //=> 原型继承
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
Child.prototype.gety = function gety () {
return this.y
}
let c1 = new Child()
// 现在c1 只能用y 和gety,但是我们也想让c1继承parent的方法和属性
console.log(c1,'c1')
console.log(c1.__proto__)
console.log(c1.__proto__.__proto__.getx)
2call继承
(只能继承父类中私有的,不能继承父类中公有的)

代码
// 第二种继承方式:call继承(只能继承父类中私有的,不能继承父类中公有的)
function Parent() {
this.x = 100;
}
Parent.prototype.getx = function getx() {
return this.x
}
function Child() {
// 在子类构造函数中,把父类当做普通方法执行(没有父类的实例,父类原型上的那些东西也就和它没关系了)
// this -> child的实例c2
Parent.call(this) //this.x = 100 相当于强制给c2这个实例设置一个私有属性x,属性值为100,相当于
//让子类实例继承了父类的私有属性,并且也变为了子类私有的属性 ’拷贝式‘
this.y = 200
}
Child.prototype.gety = function gety() {
return this.y
}
let c2 = new Child()
// 现在c2 只能用y 和gety,但是我们也想让c1继承parent的方法和属性
console.log(c2,'c2')
3.寄生组合继承(call 继承 + 另类原型继承)
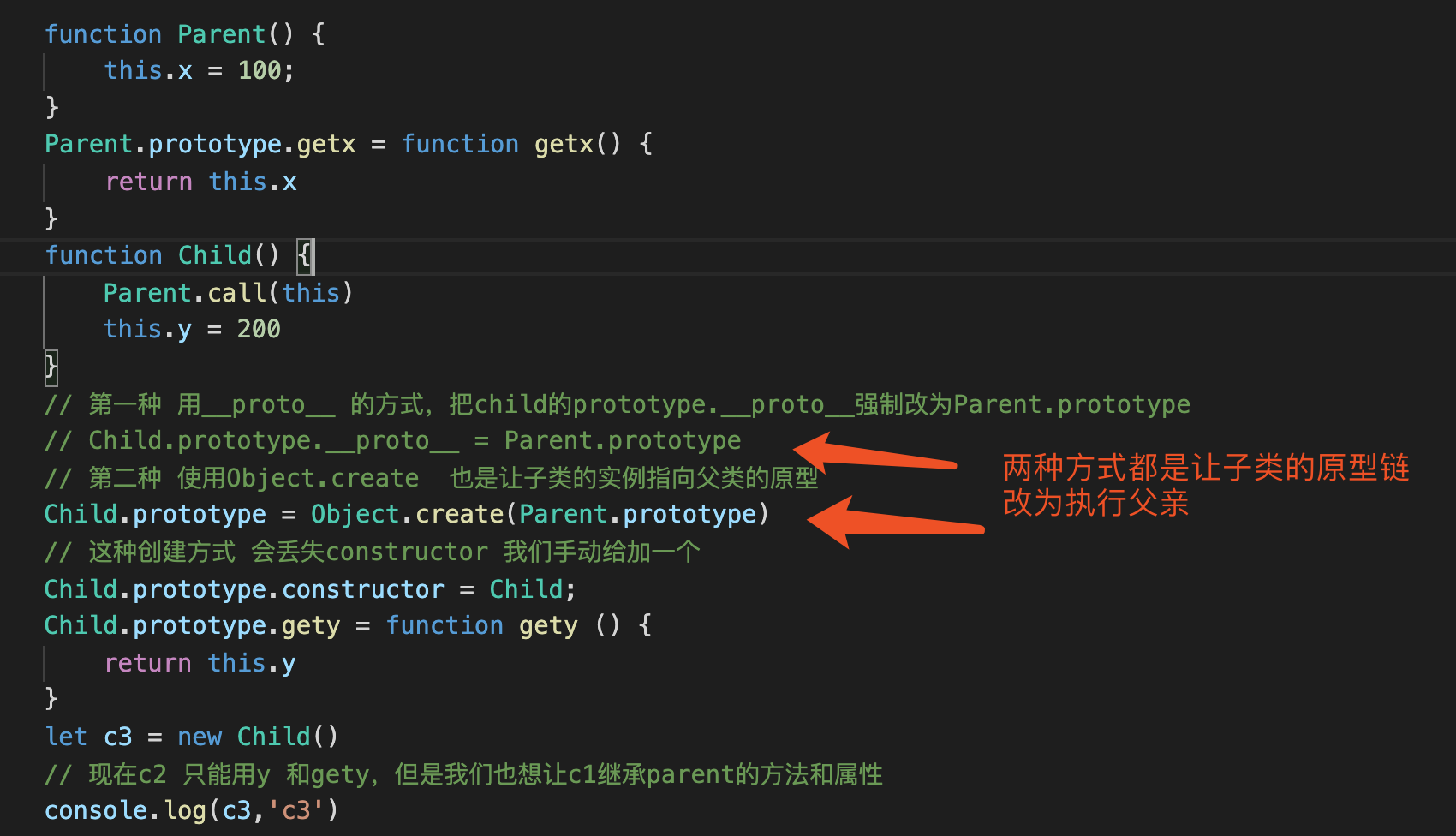
代码
function Parent() {
this.x = 100;
}
Parent.prototype.getx = function getx() {
return this.x
}
function Child() {
Parent.call(this)
this.y = 200
}
// 第一种 用__proto__ 的方式,把child的prototype.__proto__强制改为Parent.prototype
// Child.prototype.__proto__ = Parent.prototype
// 第二种 使用Object.create 也是让子类的实例指向父类的原型
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype)
// 这种创建方式 会丢失constructor 我们手动给加一个
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
Child.prototype.gety = function gety () {
return this.y
}
let c3 = new Child()
// 现在c2 只能用y 和gety,但是我们也想让c1继承parent的方法和属性
console.log(c3,'c3')
4es6 中的类和继承
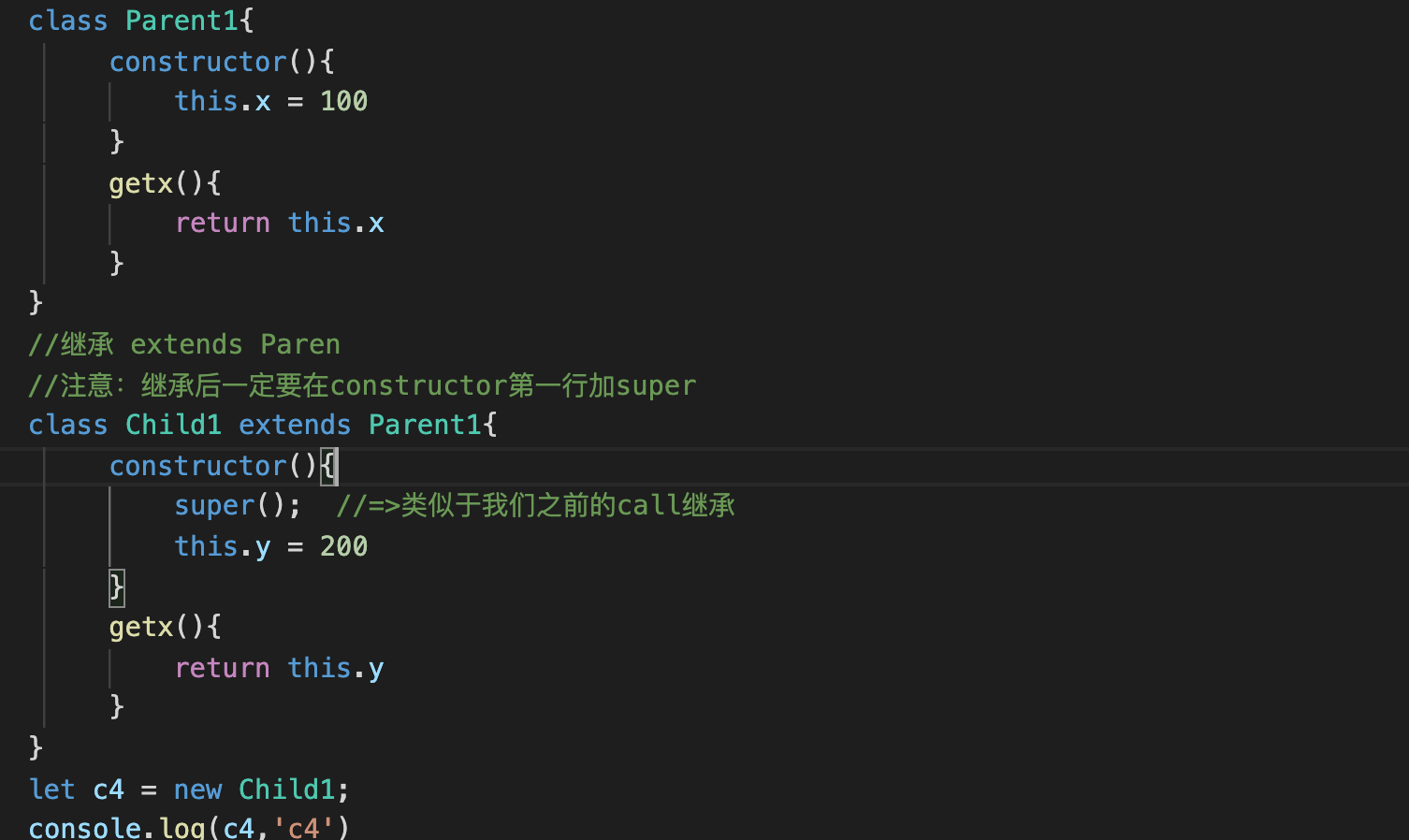
代码
class Parent1{
constructor(){
this.x = 100
}
getx(){
return this.x
}
}
//继承 extends Paren
//注意:继承后一定要在constructor第一行加super
class Child1 extends Parent1{
constructor(){
super(); //=>类似于我们之前的call继承
this.y = 200
}
getx(){
return this.y
}
}
let c4 = new Child1;
console.log(c4,'c4')