实践三 网络嗅探与协议分析
(1)找一个抓包软件,根据源码分析其功能,设计的模块。
tcpdump是由美国的Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory开发。使用了libpcap,独立于系统的接口,它可以将网络中传送的数据包完全截获下来提供分析。它支持针对网络层、协议、主机、网络或端口的过滤,并提供and、or、not等逻辑语句来帮助你去掉无用的信息。
网络数据包的传递过程:
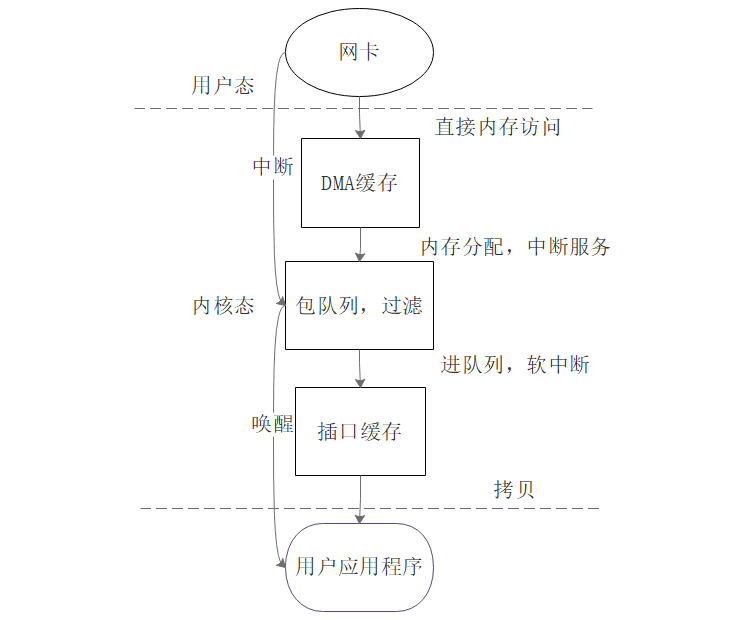
数据包的传递主要通过libpcap库来实现,tcpdump调用libpcap的api函数,由libpcap进入到内核态到链路层来抓包,可以根据用户设置用于数据包过滤减少应用程序的数据包的包数和字节数从而提高性能。tcpdump底层原理其实就是libpcap的实现原理,现在libpcap成为独立的库和API,来满足网络嗅探。
| libpcap常用函数 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| pcap_open_offine | 打开一个保存的文件。 |
| pcap_setfilter | 设置过滤器。 |
| pcap_open_live | 打开选择的设备。 |
| pcap_lookupdev | 如果分组捕获设备未曾指定(-i命令行选项),该函数选择一个设备。 |
| pcap_next | 接收一个包。 |
| pcap_dump | 将包写入到pcap_dump_t结构体。 |
| pcap_loopupnet | 返回分组捕获设备的网络地址和子网掩码,然后在调用pcap_compile时必须指定这个子网掩码。 |
| pcap_compile | 把cmd字符数组中构造的过滤器字符串编译成一个过滤器程序,存放在fcode中。 |
| pcap_setfilter | 把编译出来的过滤器程序装载到分组捕获设备,同时引发用该过滤器选取的分组的捕获。 |
| pcap_datalink | 返回分组捕获设备的数据链路类型。 |
,
根据官网的链接,我们找到tcpdump的主要源码tcpdump.c,进行分析。
源码中引用了很多头文件,主要分析一下netdissect.h以及interface.h。
在netdissect.h里定义了一个数据结构struct netdissect_options来描述tcdpump支持的所有参数动作,每一个参数有对应的flag, 在tcpdump 的main 里面, 会根据用户的传入的参数来增加相应flag数值, 最后根据这些flag数值来实现特定动作。各个参数含义请参考源代码注释。
struct netdissect_options {
int ndo_aflag; /* 解析网络和广播地址 */
int ndo_eflag; /* 打印以太网报头 */
int ndo_fflag; /* 不翻译“外国”IP地址 */
int ndo_Kflag; /* 不检查TCP校验和 */
//不将地址转换为名字
int ndo_nflag; /* 丢弃地址及编号 */
int ndo_Nflag; /* 删除已打印的主机名域 */
int ndo_qflag; /* 快速(更短)输出 */
int ndo_Rflag; /* AH/ESP中的打印序列#字段*/
int ndo_sflag; /* 使用libsmi解析OID */
int ndo_Sflag; /* 打印原始TCP序列 */
// 报文到达时间
int ndo_tflag; /* 打印数据包到达时间 */
int ndo_Uflag; /* 未缓冲的转储文件输出 */
int ndo_uflag; /* 打印未编码NFS句柄 */
//详细信息
int ndo_vflag; /* 冗余 */
// 十六进制打印报文
int ndo_xflag; /* 十六进制打印报文 */
// 十六进制和ASCII码打印报文
int ndo_Xflag; /* 十六进制/ASCII码打印报文 */
//以ASCII码显示打印报文
int ndo_Aflag; /* 将TAB、LF、CR和PACE作为图形字符,只在ASCII中打印数据包*/
//默认的打印函数
void (*ndo_default_print)(netdissect_options *,
register const u_char *bp, register u_int length);
void (*ndo_info)(netdissect_options *, int verbose);
}
interface.h是接口头文件,定义了一堆宏方便调用struct netdissect_options里的成员。
#ifndef NETDISSECT_REWORKED
extern netdissect_options *gndo;
#define nflag gndo->ndo_nflag
#define tflag gndo->ndo_tflag
#define vflag gndo->ndo_vflag
#define xflag gndo->ndo_xflag
#define Xflag gndo->ndo_Xflag
#endif
源码还定义了一些信号传递的静态变量,如
extern int dflag;
int dflag; /* 打印过滤器 */
static int Gflag; /* 在多少秒之后转储文件 */
static int Gflag_count; /* 用Gflag交替创建的文件数 */
static time_t Gflag_time; /* 最后一time_t转储文件被交替 */
static int Lflag; /* 列出可用的数据链接类型和退出 */
...
定义命令选项。
除了g、k、o和P之外,所有的字母都用于短选项。
#define SHORTOPTS "aAb" B_FLAG "c:C:d" D_FLAG "eE:fF:G:hHi:" I_FLAG j_FLAG J_FLAG "KlLm:M:nNOpq" Q_FLAG "r:s:StT:u" U_FLAG "vV:w:W:xXy:Yz:Z:#"
定义了静态长选项。
static const struct option longopts[] = {
#if defined(HAVE_PCAP_CREATE) || defined(_WIN32)
{ "buffer-size", required_argument, NULL, 'B' }, #缓冲大小
#endif
{ "list-interfaces", no_argument, NULL, 'D' }, #接口列表
#ifdef HAVE_PCAP_FINDALLDEVS_EX
{ "list-remote-interfaces", required_argument, NULL, OPTION_LIST_REMOTE_INTERFACES }, #远端接口列表
#endif
{ "help", no_argument, NULL, 'h' }, #帮助
{ "interface", required_argument, NULL, 'i' }, #接口
#ifdef HAVE_PCAP_CREATE
{ "monitor-mode", no_argument, NULL, 'I' }, #监测模式
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_PCAP_SET_TSTAMP_TYPE
{ "time-stamp-type", required_argument, NULL, 'j' }, #时间戳状态
{ "list-time-stamp-types", no_argument, NULL, 'J' }, #时间戳状态列表
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_PCAP_SET_TSTAMP_PRECISION
{ "micro", no_argument, NULL, OPTION_TSTAMP_MICRO},
{ "nano", no_argument, NULL, OPTION_TSTAMP_NANO},
{ "time-stamp-precision", required_argument, NULL, OPTION_TSTAMP_PRECISION},#时间戳精度
#endif
...
main函数可以分为三个部分:
第一部分是用struct netdissect_options数据结构作为一个参数集合, 并用getopt框架来处理argv的参数逻辑,如case 'i'表示-i,用来指定网口,-x表示以十六进制打印报文,-X也是同样的功能。
while (
(op = getopt_long(argc, argv, SHORTOPTS, longopts, NULL)) != -1)
switch (op) {
case 'i':
device = optarg;
break;
case 'x':
++ndo->ndo_xflag;
++ndo->ndo_suppress_default_print;
break;
case 'X':
++ndo->ndo_Xflag;
++ndo->ndo_suppress_default_print;
break;
第二部分是使用libpcap库函数来搭建与底层IPC通道。 其中最重要的API有三个, 第一个是pcap_lookupdev(), 查找可用网口
#ifdef HAVE_PCAP_FINDALLDEVS
/* 找到接口列表,选择第一个接口。*/
if (pcap_findalldevs(&devlist, ebuf) == -1)
error("%s", ebuf);
if (devlist == NULL)
error("no interfaces available for capture");
device = strdup(devlist->name);
pcap_freealldevs(devlist);
#else
/*使用pcap_lookupdev()接口选择网口 */
device = pcap_lookupdev(ebuf);
if (device == NULL)
error("%s", ebuf);
#endif
}
第二个是pcap_open_live(),打开指定设备并将其配置为混杂模式返回句柄:
if (ndo->ndo_snaplen == 0)
ndo->ndo_snaplen = MAXIMUM_SNAPLEN;
pc = pcap_open_live(device, ndo->ndo_snaplen, !pflag, timeout, ebuf);
if (pc == NULL) {
/*如果“没有这样的设备”失败,这意味着接口不存在;返回NULL,以便调用者可以看到设备名称是否实际上是接口索引。*/
if (strstr(ebuf, "No such device") != NULL)
return (NULL);
error("%s", ebuf);
}
if (*ebuf)
warning("%s", ebuf);
#endif /* HAVE_PCAP_CREATE */
return (pc);
第三个是使用pcap_loop()持续获取报文数据,调用回调函数进行打印处理。
do {
status = pcap_loop(pd, cnt, callback, pcap_userdata);
if (WFileName == NULL) {
/*打印数据包, 刷新打印输出,因此它不会与错误输出混合。*/
if (status == -2) {
putchar('
');
}
(void)fflush(stdout);
}
if (status == -2) {
/*如果正在读取多个文件(通过-V)和设置这些文件,立刻打断。*/
VFileName = NULL;
ret = NULL;
}
if (status == -1) {
/*发生错误,用日志记录*/
(void)fprintf(stderr, "%s: pcap_loop: %s
",
program_name, pcap_geterr(pd));
}
if (RFileName == NULL) {
/*
* We're doing a live capture. Report the capture
* statistics.
*/
info(1);
}
pcap_close(pd);
if (VFileName != NULL) {
ret = get_next_file(VFile, VFileLine);
if (ret) {
int new_dlt;
RFileName = VFileLine;
pd = pcap_open_offline(RFileName, ebuf);
if (pd == NULL)
error("%s", ebuf);
#ifdef HAVE_CAPSICUM
cap_rights_init(&rights, CAP_READ);
if (cap_rights_limit(fileno(pcap_file(pd)),
&rights) < 0 && errno != ENOSYS) {
error("unable to limit pcap descriptor");
}
#endif
new_dlt = pcap_datalink(pd);
if (new_dlt != dlt) {
/*新文件具有与前一个不同的链路层头类型。*/
if (WFileName != NULL) {
/*编写与p cap文件匹配的原始数据包,由于pcap文件不支持多个不同的链路层头类型,所以在这里失败了。*/
error("%s: new dlt does not match original", RFileName);
}
/*打印解码的数据包,切换到新的DLT,更改打印机,更改DLT名称,并使用新的DLT重新编译过滤器。*/
dlt = new_dlt;
ndo->ndo_if_printer = get_if_printer(ndo, dlt);
if (pcap_compile(pd, &fcode, cmdbuf, Oflag, netmask) < 0)
error("%s", pcap_geterr(pd));
}
/*在新文件上设置过滤器*/
if (pcap_setfilter(pd, &fcode) < 0)
error("%s", pcap_geterr(pd));
/*报告新文件*/
dlt_name = pcap_datalink_val_to_name(dlt);
fprintf(stderr, "reading from file %s", RFileName);
if (dlt_name == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, ", link-type %u", dlt);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, ", link-type %s (%s)",
dlt_name,
pcap_datalink_val_to_description(dlt));
}
fprintf(stderr, ", snapshot length %d
", pcap_snapshot(pd));
}
}
}
while (ret != NULL);
if (count_mode && RFileName != NULL)
fprintf(stderr, "%u packet%s
", packets_captured,
PLURAL_SUFFIX(packets_captured));
free(cmdbuf);
pcap_freecode(&fcode);
exit_tcpdump(status == -1 ? 1 : 0);
}
第三部分是实现callback 函数,tcpdump.c里的callback函数只做了一个封装,并用到第二部分中pcap_loop()持续获取报文数据,最终调用的是参数pcap_userdata里提供的特定数据链路层的打印函数,
/*CALLBACK函数封装*/
static void CALLBACK verbose_stats_dump(PVOID param _U_,
BOOLEAN timer_fired _U_)
{
print_packets_captured();
}
u_char *pcap_userdata;
...
/*调用参数pcap_userdata进行打印*/
do {
status = pcap_loop(pd, cnt, callback, pcap_userdata);
if (WFileName == NULL) {
/*
* We're printing packets. Flush the printed output,
* so it doesn't get intermingled with error output.
*/
if (status == -2) {
/*
* We got interrupted, so perhaps we didn't
* manage to finish a line we were printing.
* Print an extra newline, just in case.
*/
putchar('
');
}
(void)fflush(stdout);
...
-h显示帮助信息
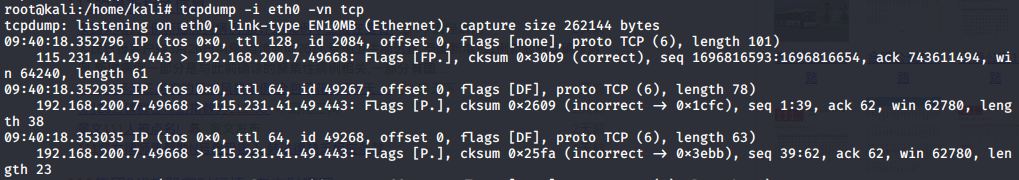
-i选项表示选择网卡,-vn表示不把网络地址转换成名字,并且输出一个包含ttl和服务类型的信息
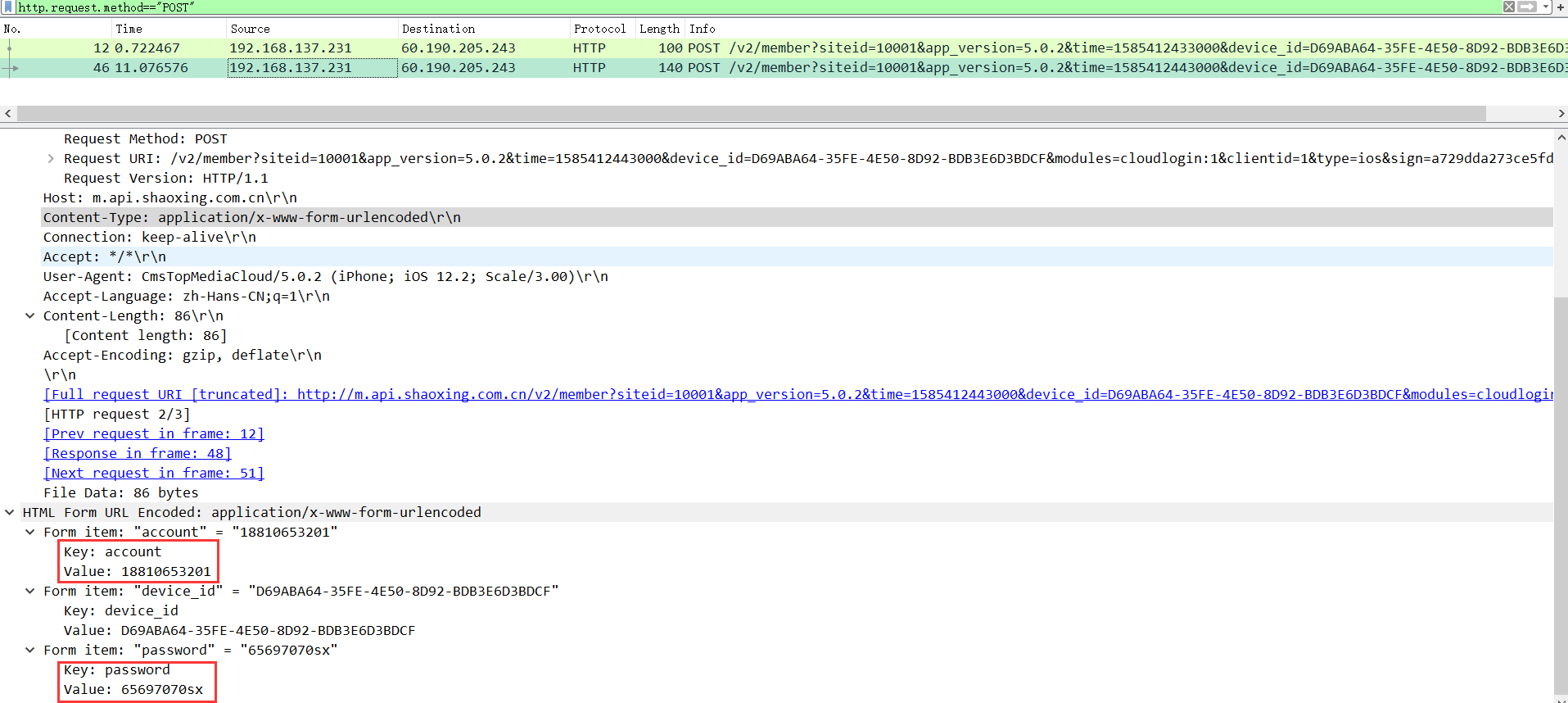
(2)找一个网站或者搭建一个本地网站,登录网站,并嗅探,分析出账号和密码。
登录一个比较旧的水木社区,注册用户louhao123,密码65697070Sx!,然后用wireshark监听HTTP协议POST信息
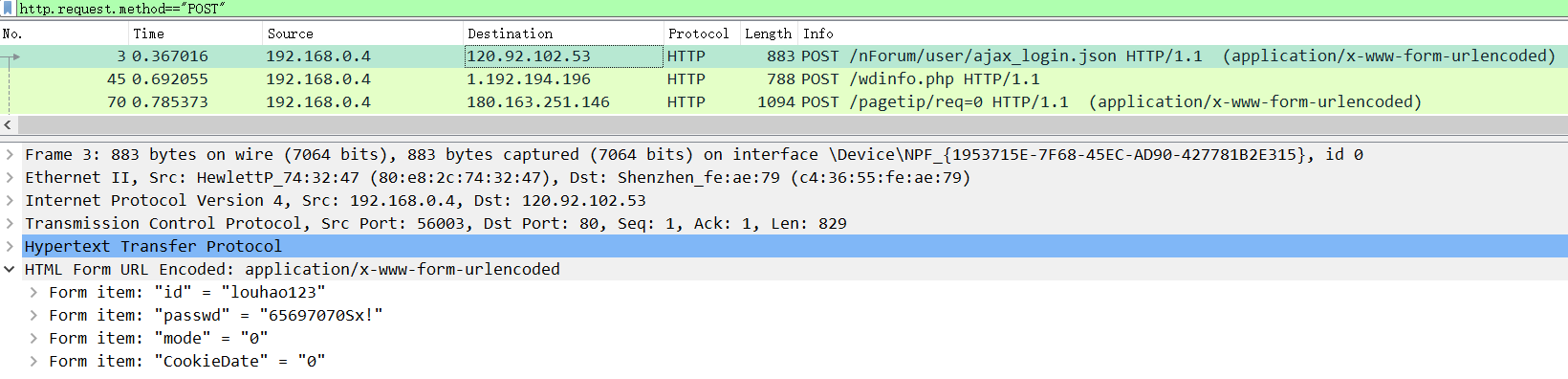
可以检测到从本地发送到论坛IP的数据报中账号和密码的信息。
(3)抓取手机App的登录过程数据包,分析账号和密码。
在电脑上开启网络共享
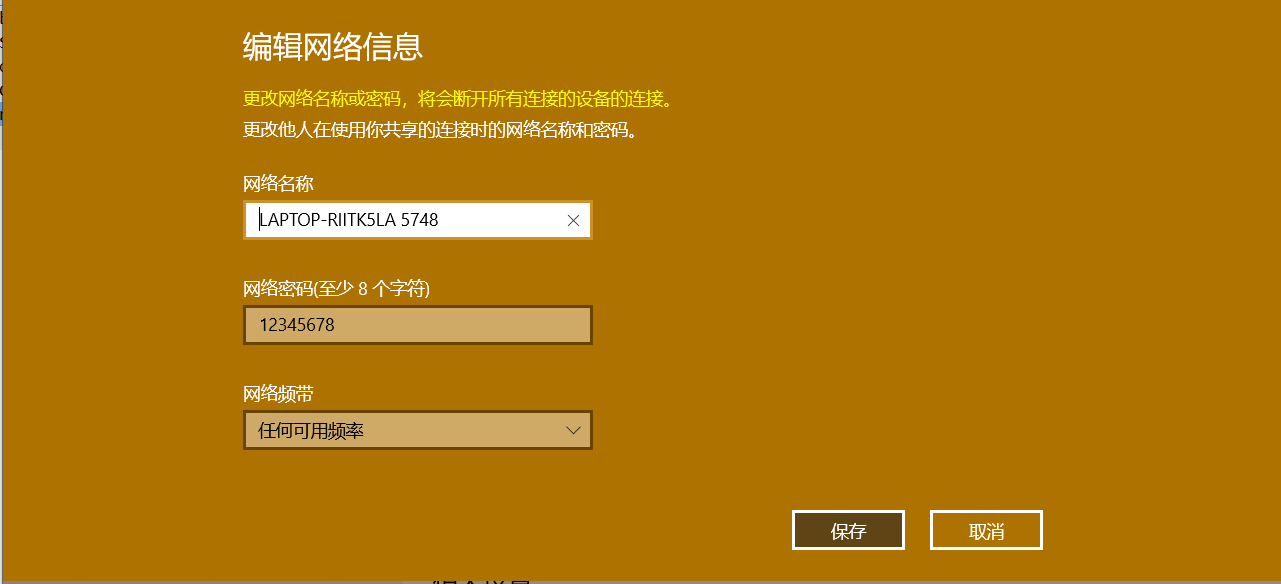
在手机中搜索LAPTOP-RIITK5LA 5748的无线局域网并连接。
刚开始查了天涯论坛,数据中收到了cookie的信息,账号以明文形式传递,密码则无从入手,用在线网站加解密,也无法恢复有信息的内容,缺失现在前段至少都会进行重要信息的加密。
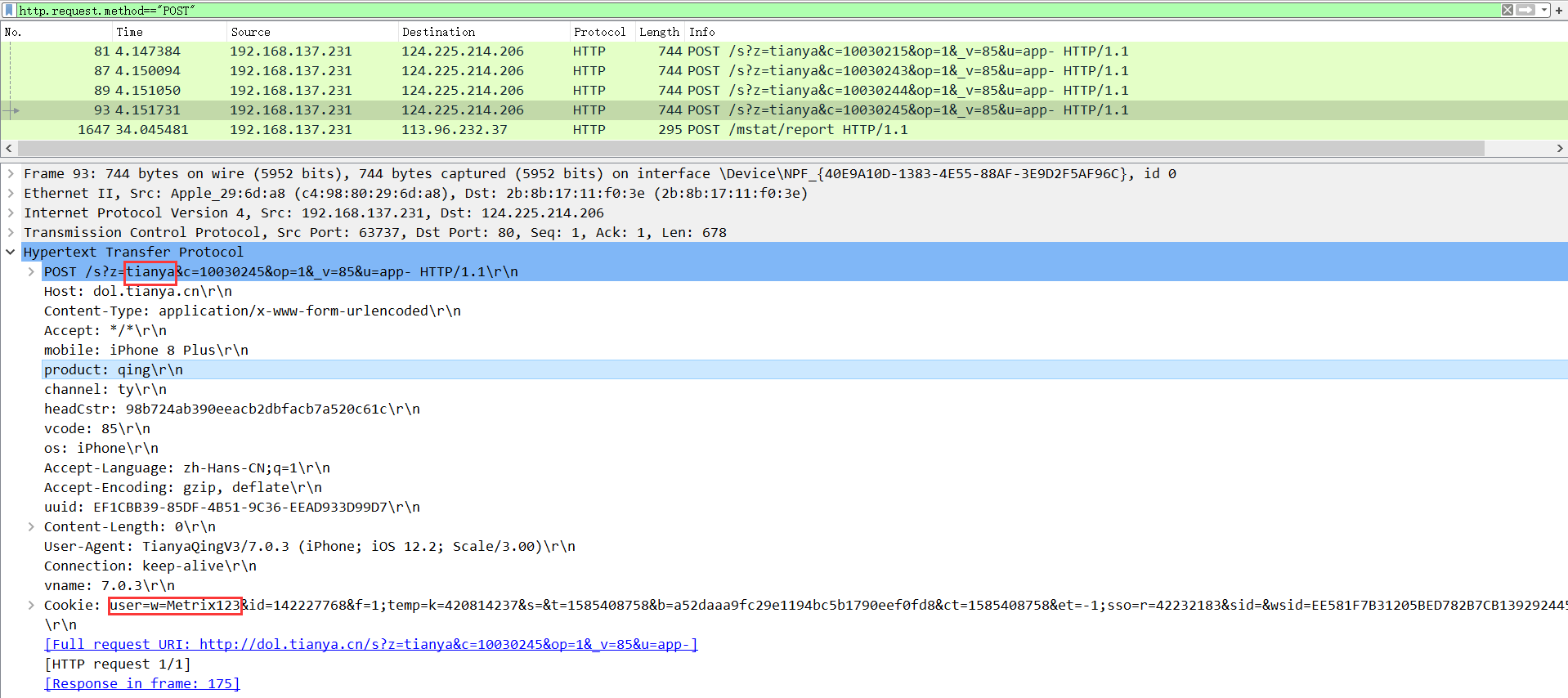
后来又搜了一些比较小众的app,其中一个越牛新闻的本地app竟然完全用明文传递用户和密码,存在明显的账号隐患。