1.web项目首先回去读取web.xml. web.xml中有如下配置
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:/spring-context*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
关于classpath*:/spring-context*.xml
举个简单的例子,在我的web.xml中是这么定义的:classpath*:META-INF/spring/application-context.xml
那么在META-INF/spring这个文件夹底下的所有application-context.xml都会被加载到上下文中,这些包括META-INF/spring文件夹底下的 application-context.xml,META-INF/spring的子文件夹的application-context.xml以及jar中的application-context.xml。
如果我在web.xml中定义的是:classpath:META-INF/spring/application-context.xml
那么只有META-INF/spring底下的application-context.xml会被加载到上下文中
这里的"/",指的是.classpath文件中指定的路径: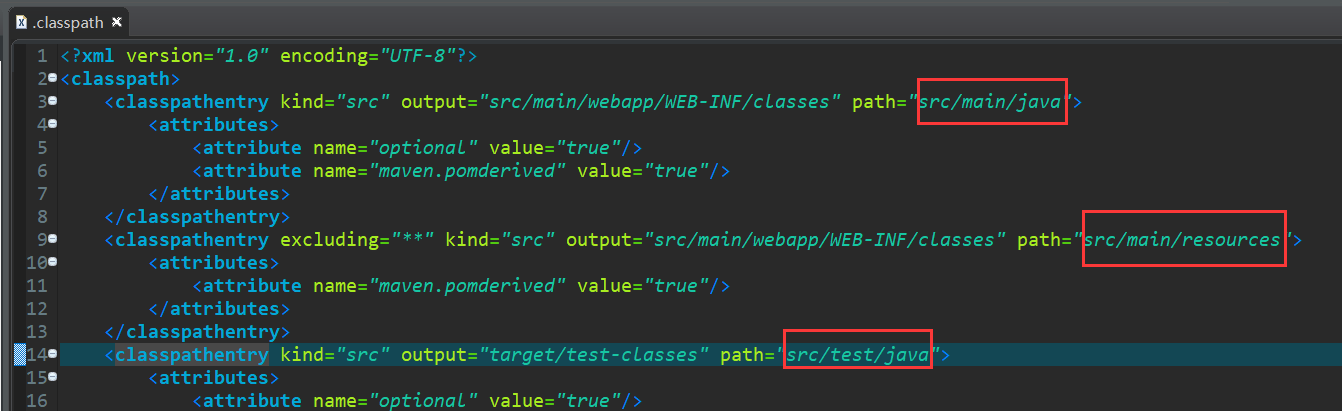
,上面标注的就是"/"所指的路径。只要你是你的配置文件匹配设置的格式(spring-context*.xml)放在这下面任何位置的可以,自己可以测试一下
补充:
1.)关于.classpath文件的查看可以去项目存放的位置(workplace)下查看,也可以在eclipse中navigator视图中进行查看
2.)navigator视图是在window---->show view----->other------>navigator,在改视图下,你在你的项目里面,你会看到.classpath的文件.
2.web.xml中加载spring-mvc.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:/spring-mvc*.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
3.比较web.xml引入xml文件的方式和xml文件引入properties文件的方式
web.xml中
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:/spring-context*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
xml文件中
<context:property-placeholder ignore-unresolvable="true" location="classpath:jlightspeed.properties" />