一、HttpInvoker是常用的Java同构系统之间方法调用实现方案,是众多Spring项目中的一个子项目。顾名思义,它通过HTTP通信即可实现两个Java系统之间的远程方法调用,使得系统之间的通信如同调用本地方法一般。
二、他有点类似于Java的服务远程调用RMI,但是两个基于的协议不一样。RMI是直接服务器直接的调用,需要防火墙单独放开端口。而HttpInvoker是基于http协议进行远程方法调用的。需要容器支持。
三、RMI的实现过程参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ll409546297/p/8948185.html
四、我这里中间件使用的是jetty来嵌入启动的,可以参考jetty的启动方式:https://www.cnblogs.com/ll409546297/p/9338837.html
五、HttpInvoker实现例子:
1、服务端:
1)提供远程调用的借口和实现类
package com.pinnet.remote; public interface IRemoteService { String show(); }
package com.pinnet.remote.impl; import com.pinnet.remote.IRemoteService; public class RemoteServiecImpl implements IRemoteService { public String show() { System.out.println("show"); return "show"; } }
2)服务端bean的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="remoteService" class="com.pinnet.remote.impl.RemoteServiecImpl"/> <bean name="/remoteService" class="org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerServiceExporter"> <property name="service" ref="remoteService"/> <property name="serviceInterface" value="com.pinnet.remote.IRemoteService"/> </bean> </beans>
3)有人会问相对于RMI怎么没有注册端口,因为这里是基于http协议,所以,是使用web服务的容器接口
2、客户端:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="remoteService" class="org.springframework.remoting.httpinvoker.HttpInvokerProxyFactoryBean"> <property name="serviceUrl" value="http://localhost:8090/remoteService"/> <property name="serviceInterface" value="com.pinnet.remote.IRemoteService"/> </bean> </beans>
端口:是服务端的容器端口,接口是公用的
3、测试:
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext client = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-httpinvoker-client.xml"); IRemoteService remoteService = (IRemoteService) client.getBean("remoteService"); String show = remoteService.show(); System.out.println(show); }
服务端:

客户端:

六、HttpInvoker源码分析(来至:https://charpty.com)
1、服务端
1)服务端主入口由HttpInvokerServiceExporter实现,它的工作大致流程如下
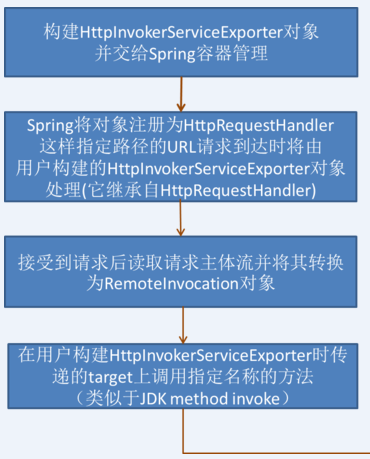
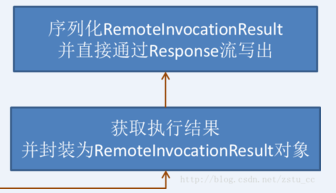
2)HttpInvokerServiceExporter实现了HttpRequestHandler,这使得其拥有处理HTTP请求的能力,按照Spring MVC的架构,它将被注册到HandlerMapping的BeanNameMapping中,这设计到Spring MVC如何处理请求,可以关注我的相关文章。服务端的重要任务就是读取并解析RemoteInvocation,再返回RemoteInvocationResult,剩下的都只是标准IO流的读写。
HttpInvokerProxyFactoryBean, 和Spring用到的众多设计相同,该类的结构使用了模板设计方法,该类提供实现了几个模板方法,整体逻辑由父类HttpInvokerClientInterceptor的实现,主要流程如下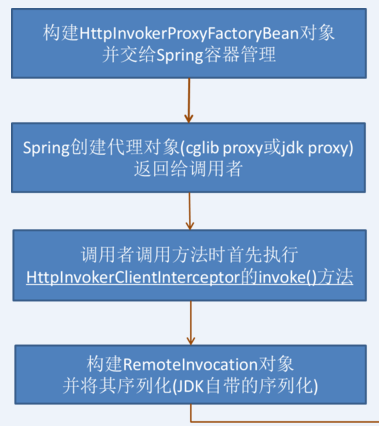
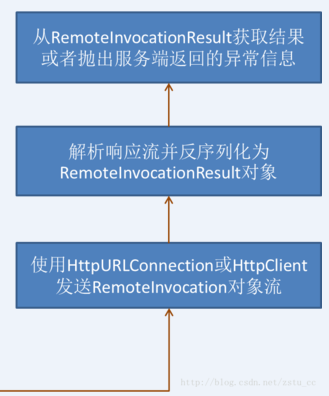
2)我们最关心的是当我们调用接口的方法时,HttpInvoker是如何做到调用到远方系统的方法的,其实HttpInvokerProxyFactoryBean最后返回的是一个代理类(Cglib Proxy或者Jdk Proxy),我们调用接口的任何方法时,都会先执行HttpInvokerClientInterceptor的invoke()方法。
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { if (AopUtils.isToStringMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod())) { return "HTTP invoker proxy for service URL [" + this.getServiceUrl() + "]"; } else { RemoteInvocation invocation = this.createRemoteInvocation(methodInvocation); RemoteInvocationResult result = null; try { result = this.executeRequest(invocation, methodInvocation); } catch (Throwable var5) { throw this.convertHttpInvokerAccessException(var5); } try { return this.recreateRemoteInvocationResult(result); } catch (Throwable var6) { if (result.hasInvocationTargetException()) { throw var6; } else { throw new RemoteInvocationFailureException("Invocation of method [" + methodInvocation.getMethod() + "] failed in HTTP invoker remote service at [" + this.getServiceUrl() + "]", var6); } } } }
六、本博客后面源码部分,部分来至https://charpty.com