关于springboot想必很多人都在使用,由于公司项目一直使用的是SpringMVC,所以自己抽空体验了一下springboot的简单使用。
-
环境搭建
springbooot的环境搭建可以说很灵活,可以新建maven普通项目来手动搭建,当然也可以使用Spring的STS来搭建,由于IDE使用eclipse,所以就直接使用STS插件。
1. 在eclipse的Marketplace中搜索STS,后直接下载安装即可。
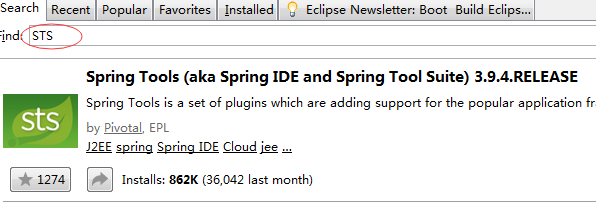
2. 安装好后,在新建项目中就可以看到springboot的相关内容,选择第二个新建springboot
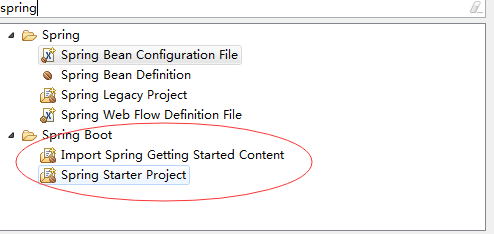
3. 第三步就是选择对应的依赖,当然你可以将需要的依赖全部添加,也可以先添加当前需要的,随后用到什么在添加。
-
代码结构
Springboot的启动很简单,如下:
1 package com.yongcheng.liuyang; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 @SpringBootApplication 7 public class DemoApplication { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); 11 } 12 }
其中最主要的是@SpringBootApplication的注解,当然从启动过程也可以发现,springboot其实质还是运行在web容器中,
接下来就写一个springmvc中经常用到的Controller很简单的测试下,当然前端页面我们选择了官方推荐的thymeleaf,
所以首先要在pom.xml中导入这个依赖包,如下:
<!-- thymeleaf模板引擎包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
controller的写法和springmvc一样,熟悉springmvc的基本不用多说,直接上代码:
1 package com.yongcheng.liuyang.controller; 2 3 import org.slf4j.Logger; 4 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 5 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 6 import org.springframework.ui.Model; 7 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 8 9 import com.yongcheng.liuyang.entity.AuthorSetting; 10 11 @Controller 12 @RequestMapping(value="/") 13 public class UserLoginController { 14 15 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserLoginController.class); 16 17 18 @RequestMapping("/test") 19 public String testthymeleaf(Model model) 20 { 21 model.addAttribute("singlePerson", new AuthorSetting("zhangsan",18)); 22 return "viewTest"; 23 } 24 }
由于我们需要返回页面所以使用的是@Controller注解,当然如果你要返回json数据,那么你的注解当然是@RestController
接下就是前台的页面

1 <!DOCTYPE html SYSTEM "http://www.thymeleaf.org/dtd/xhtml1-strict-thymeleaf-4.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" 3 xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> 4 <head> 5 <meta content="text/html" charset="UTF-8"> 6 <link th:src="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet"> 7 <link th:src="@{/css/bootstrap-theme.min.css}" rel="stylesheet"> 8 9 <script th:src="@{/js/jquery-3.2.1.min.js}" type="text/javascript"></script> 10 <script th:src="@{/js/bootstrap.min.js}" type="text/javascript"></script> 11 12 <title>thymeleaf简单实用</title> 13 </head> 14 <body> 15 <div class="panel panel-primary"> 16 <div class="panel-heading"> 17 <h3 class="panel-title">访问model</h3> 18 </div> 19 <div class="panel-body"> 20 <span th:text="${singlePerson.name}"></span> 21 </div> 22 </div> 23 </body> 24 </html>
注意html文件中引入xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org",其次就是这里的动态加载使用th:dom选择,比如项目中的th:text,
URL使用@{},比如项目中css和js的引入。
这样子整个问题就算解决了吗?没有,了解springmvc的都知道,springmvc在解析JSP文件时需要配置对应的文件前后缀,比如如下的配置:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="internalResourceViewResolver" > <!-- 自动添加到路径中的前缀 --> <property name="prefix" value="/jsp/" /> <!-- 自动添加到路径中的后缀 --> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean>
在springboot中一样也要配置这样的,其中springboot的所有配置信息都在application.properties或者application.yml文件中,
那么如何配置对应的thymeleaf的视图解析配置参数呢?
由于小编选择的是yml,配置参数如下:
spring:
thymeleaf:
prefix: "classpath:/templates/"
suffix: ".html"
当然如果你的项目结构绝对严谨的话,比如使用STS创建的项目,那么其实上面的是可以不配置的,具体原因可参见ThymeleafProperties类。
重要提示:
为了让项目正常加载bean,main函数所在类的一定要是其它类的父包,否则无法扫描到配置的bean。
好了,以上就是springboot+thymeleaf的简单使用。
