conn结构主要是存储单个客户端的连接详情信息。每一个客户端连接到Memcached都会有这么一个数据结构。
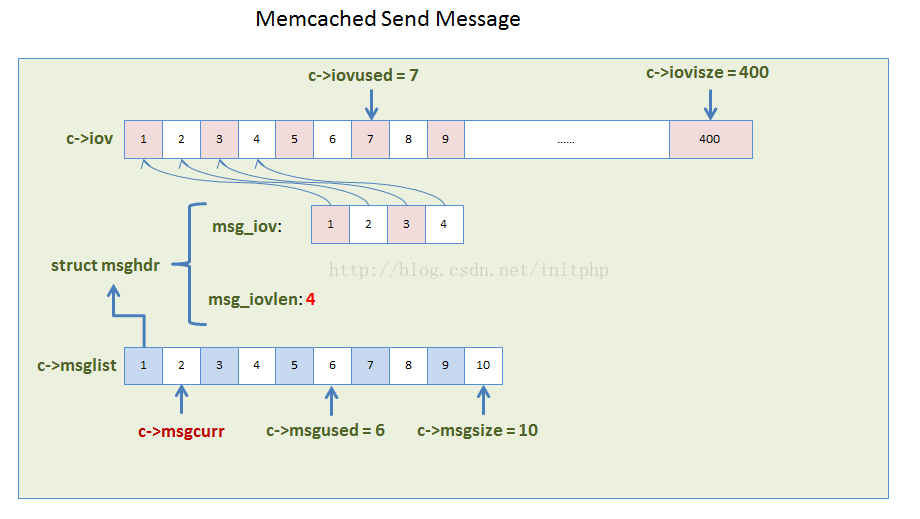
typedef struct conn conn; struct conn { //.... /* data for the mwrite state */ //iov主要存储iov的数据结构 //iov数据结构会在conn_new中初始化,初始化的时候,系统会分配400个iovec的结构,最高水位600个 struct iovec *iov; //iov的长度 int iovsize; /* number of elements allocated in iov[] */ //iovused 这个主要记录iov使用了多少 int iovused; /* number of elements used in iov[] */ //msglist主要存储msghdr的列表数据结构 //msglist数据结构在conn_new中初始化的时候,系统会分配10个结构 struct msghdr *msglist; //msglist的长度,初始化为10个,最高水位100,不够用的时候会realloc,每次扩容都会扩容一倍 int msgsize; /* number of elements allocated in msglist[] */ //msglist已经使用的长度 int msgused; /* number of elements used in msglist[] */ //这个参数主要帮助记录那些msglist已经发送过了,哪些没有发送过。 int msgcurr; /* element in msglist[] being transmitted now */ int msgbytes; /* number of bytes in current msg */ }
我们可以看一下conn_new这个方法,在这个方法里面会对iov和msglist两个参数进行初始化。
conn *conn_new(const int sfd, enum conn_states init_state,const int event_flags, const int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport, struct event_base *base)
{ //...省略部分代码 c->iov = (struct iovec *) malloc(sizeof(struct iovec) * c->iovsize); //初始化iov c->msglist = (struct msghdr *) malloc(sizeof(struct msghdr) * c->msgsize); //初始化msglist }
数据结构关系图(iov和msglist之间的关系):
从process_get_command开始
我们继续从process_get_command,获取memcached的缓存数据这个方法开始。
在这个方法中,我们主要看add_iov这个方法。Memcached主要是通过add_iov方法,将需要发送给客户端的数据装到iov和msglist结构中去的。
/* ntokens is overwritten here... shrug.. */ //处理GET请求的命令 static inline void process_get_command(conn *c, token_t *tokens, size_t ntokens, bool return_cas) { //处理GET命令 char *key; size_t nkey; int i = 0; item *it; //&tokens[0] 是操作的方法 //&tokens[1] 为key //token_t 存储了value和length token_t *key_token = &tokens[KEY_TOKEN]; char *suffix; assert(c != NULL); do { //如果key的长度不为0 while (key_token->length != 0) { key = key_token->value; nkey = key_token->length; //判断key的长度是否超过了最大的长度,memcache key的最大长度为250 //这个地方需要非常注意,我们在平常的使用中,还是要注意key的字节长度的 if (nkey > KEY_MAX_LENGTH) { //out_string 向外部输出数据 out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format"); while (i-- > 0) { item_remove(*(c->ilist + i)); } return; } //这边是从Memcached的内存存储快中去取数据 it = item_get(key, nkey); if (settings.detail_enabled) { //状态记录,key的记录数的方法 stats_prefix_record_get(key, nkey, NULL != it); } //如果获取到了数据 if (it) { //c->ilist 存放用于向外部写数据的buf //如果ilist太小,则重新分配一块内存 if (i >= c->isize) { item **new_list = realloc(c->ilist, sizeof(item *) * c->isize * 2); if (new_list) { //存放需要向客户端写数据的item的列表的长度 c->isize *= 2; //存放需要向客户端写数据的item的列表,这边支持 c->ilist = new_list; } else { STATS_LOCK(); stats.malloc_fails++; STATS_UNLOCK(); item_remove(it); break; } } /* * Construct the response. Each hit adds three elements to the * outgoing data list: * "VALUE " * key * " " + flags + " " + data length + " " + data (with ) */ //初始化返回出去的数据结构 if (return_cas) { //...... } else { MEMCACHED_COMMAND_GET(c->sfd, ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes, ITEM_get_cas(it)); //将需要返回的数据填充到IOV结构中 //命令:get userId //返回的结构: //VALUE userId 0 5 //55555 //END if (<strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">add_iov</span></strong>(c, "VALUE ", 6) != 0 || <strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">add_iov</span></strong>(c, ITEM_key(it), it->nkey) != 0 || <strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">add_iov</span></strong>(c, ITEM_suffix(it), it->nsuffix + it->nbytes) != 0) { item_remove(it); break; } } if (settings.verbose > 1) { int ii; fprintf(stderr, ">%d sending key ", c->sfd); for (ii = 0; ii < it->nkey; ++ii) { fprintf(stderr, "%c", key[ii]); } fprintf(stderr, " "); } /* item_get() has incremented it->refcount for us */ pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); c->thread->stats.slab_stats[it->slabs_clsid].get_hits++; c->thread->stats.get_cmds++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); item_update(it); *(c->ilist + i) = it; i++; } else { pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); c->thread->stats.get_misses++; c->thread->stats.get_cmds++; pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); MEMCACHED_COMMAND_GET(c->sfd, key, nkey, -1, 0); } key_token++; } /* * If the command string hasn't been fully processed, get the next set * of tokens. */ //如果命令行中的命令没有全部被处理,则继续下一个命令 //一个命令行中,可以get多个元素 if (key_token->value != NULL) { ntokens = tokenize_command(key_token->value, tokens, MAX_TOKENS); key_token = tokens; } } while (key_token->value != NULL); c->icurr = c->ilist; c->ileft = i; if (return_cas) { c->suffixcurr = c->suffixlist; c->suffixleft = i; } if (settings.verbose > 1) fprintf(stderr, ">%d END ", c->sfd); /* If the loop was terminated because of out-of-memory, it is not reliable to add END to the buffer, because it might not end in . So we send SERVER_ERROR instead. */ //添加结束标志符号 if (key_token->value != NULL || <strong><span style="color:#FF0000;">add_iov</span></strong>(c, "END ", 5) != 0 || (IS_UDP(c->transport) && build_udp_headers(c) != 0)) { out_of_memory(c, "SERVER_ERROR out of memory writing get response"); } else { //将状态修改为写,这边读取到item的数据后,又开始需要往客户端写数据了。 conn_set_state(c, conn_mwrite); c->msgcurr = 0; } }
add_iov 方法
add_iov方法,主要作用:
1. 将Memcached需要发送的数据,分成N多个IOV的块
2. 将IOV块添加到msghdr的结构中去。
static int add_iov(conn *c, const void *buf, int len) { struct msghdr *m; int leftover; bool limit_to_mtu; assert(c != NULL); do { //消息数组 msglist 存储msghdr结构 //这边是获取最新的msghdr数据结构指针 m = &c->msglist[c->msgused - 1]; /* * Limit UDP packets, and the first payloads of TCP replies, to * UDP_MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE bytes. */ limit_to_mtu = IS_UDP(c->transport) || (1 == c->msgused); /* We may need to start a new msghdr if this one is full. */ //如果msghdr结构中的iov满了,则需要使用更新的msghdr数据结构 if (m->msg_iovlen == IOV_MAX || (limit_to_mtu && c->msgbytes >= UDP_MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE)) { //添加msghdr,这个方法中回去判断初始化的时候10个msghdr结构是否够用,不够用的话会扩容 add_msghdr(c); //指向下一个新的msghdr数据结构 m = &c->msglist[c->msgused - 1]; } //确认IOV的空间大小,初始化默认是400个,水位600 //如果IOV也不够用了,就会去扩容 if (ensure_iov_space(c) != 0) return -1; /* If the fragment is too big to fit in the datagram, split it up */ if (limit_to_mtu && len + c->msgbytes > UDP_MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE) { leftover = len + c->msgbytes - UDP_MAX_PAYLOAD_SIZE; len -= leftover; } else { leftover = 0; } m = &c->msglist[c->msgused - 1]; //m->msg_iov参数指向c->iov这个结构。 //具体m->msg_iov如何指向到c->iov这个结构的,需要看一下add_msghdr这个方法 //向IOV中填充BUF m->msg_iov[m->msg_iovlen].iov_base = (void *) buf; //buf的长度 m->msg_iov[m->msg_iovlen].iov_len = len; //填充长度 c->msgbytes += len; c->iovused++; m->msg_iovlen++; //msg_iovlen + 1 buf = ((char *) buf) + len; len = leftover; } while (leftover > 0); return 0; }
add_msghdr 方法 msghdr扩容
在add_iov方法中,我们可以看到,当IOV块添加满了之后,会调用这个方法扩容msgdhr的个数。
这个方法主要两个作用:
1. 检查c->msglist列表长度是否够用。
2. 使用最新的c->msglist中的一个msghdr元素,并且将msghdr->msg_iov指向c->iov最新未使用的那个iov的指针地址。
static int add_msghdr(conn *c) { //c->msglist 这个列表用来存储msghdr结构 struct msghdr *msg; assert(c != NULL); //如果msglist的长度和已经使用的长度相等的时候,说明msglist已经用完了,需要扩容 if (c->msgsize == c->msgused) { //扩容两倍 msg = realloc(c->msglist, c->msgsize * 2 * sizeof(struct msghdr)); if (!msg) { STATS_LOCK(); stats.malloc_fails++; STATS_UNLOCK(); return -1; } c->msglist = msg; //将c->msglist指向当前新的列表 c->msgsize *= 2; //size也会跟着增加 } //msg重新指向未使用的msghdr指针位置 msg = c->msglist + c->msgused; /* this wipes msg_iovlen, msg_control, msg_controllen, and msg_flags, the last 3 of which aren't defined on solaris: */ //将新的msghdr块初始化设置为0 memset(msg, 0, sizeof(struct msghdr)); //新的msghdr的msg_iov指向 struct iovec *iov结构 msg->msg_iov = &c->iov[c->iovused]; if (IS_UDP(c->transport) && c->request_addr_size > 0) { msg->msg_name = &c->request_addr; msg->msg_namelen = c->request_addr_size; } c->msgbytes = 0; c->msgused++; if (IS_UDP(c->transport)) { /* Leave room for the UDP header, which we'll fill in later. */ return add_iov(c, NULL, UDP_HEADER_SIZE); } return 0; }
ensure_iov_space 方法 IOV扩容
这个方法主要检查c->iov是否还有剩余空间,如果不够用了,则扩容2倍。
static int ensure_iov_space(conn *c) { assert(c != NULL); //如果IOV也使用完了....IOV,分配新的IOV if (c->iovused >= c->iovsize) { int i, iovnum; struct iovec *new_iov = (struct iovec *) realloc(c->iov, (c->iovsize * 2) * sizeof(struct iovec)); if (!new_iov) { STATS_LOCK(); stats.malloc_fails++; STATS_UNLOCK(); return -1; } c->iov = new_iov; c->iovsize *= 2; //扩容两倍 /* Point all the msghdr structures at the new list. */ for (i = 0, iovnum = 0; i < c->msgused; i++) { c->msglist[i].msg_iov = &c->iov[iovnum]; iovnum += c->msglist[i].msg_iovlen; } } return 0; }
conn_mwrite
conn_mwrite状态在drive_machine这个方法中。主要就是向客户端写数据了。
从上面的add_iov方法中,我们知道Memcached会将需要待发送的数据写入c->msglist结构中。
真正写数据的方法是transmit。
//drive_machine方法 //这个conn_mwrite是向客户端写数据 case conn_mwrite: if (IS_UDP(c->transport) && c->msgcurr == 0 && build_udp_headers(c) != 0) { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Failed to build UDP headers "); conn_set_state(c, conn_closing); break; } //transmit这个方法非常重要,主要向客户端写数据的操作都在这个方法中进行 //返回transmit_result枚举类型,用于判断是否写成功,如果失败,则关闭连接 switch (transmit(c)) { //如果向客户端发送数据成功 case TRANSMIT_COMPLETE: if (c->state == conn_mwrite) { conn_release_items(c); /* XXX: I don't know why this wasn't the general case */ if (c->protocol == binary_prot) { conn_set_state(c, c->write_and_go); } else { //这边是TCP的状态 //状态又会切回到conn_new_cmd这个状态 //conn_new_cmd主要是继续解析c->rbuf容器中剩余的命令参数 conn_set_state(c, conn_new_cmd); } } else if (c->state == conn_write) { if (c->write_and_free) { free(c->write_and_free); c->write_and_free = 0; } conn_set_state(c, c->write_and_go); } else { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Unexpected state %d ", c->state); conn_set_state(c, conn_closing); } break;
transmit 方法
//这个方法主要向客户端写数据 //如果数据没有发送完,则会一直循环conn_mwrite这个状态,直到数据发送完成为止 static enum transmit_result transmit(conn *c) { assert(c != NULL); //每次发送之前,都会来校验前一次的数据是否发送完了 //如果前一次的msghdr结构体内的数据已经发送完了,则c->msgcurr指针就会往后移动一位, //移动到下一个等待发送的msghdr结构体指针上 //c->msgcurr初始值为:0 if (c->msgcurr < c->msgused && c->msglist[c->msgcurr].msg_iovlen == 0) { /* Finished writing the current msg; advance to the next. */ c->msgcurr++; } //如果c->msgcurr(已发送)小于c->msgused(已使用),则就可以知道还没发送完,则需要继续发送 //如果c->msgcurr(已发送)等于c->msgused(已使用),则说明已经发送完了,返回TRANSMIT_COMPLETE状态 if (c->msgcurr < c->msgused) { ssize_t res; //从c->msglist取出一个待发送的msghdr结构 struct msghdr *m = &c->msglist[c->msgcurr]; //向客户端发送数据 res = sendmsg(c->sfd, m, 0); //发送成功的情况 if (res > 0) { pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); c->thread->stats.bytes_written += res; pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex); /* We've written some of the data. Remove the completed iovec entries from the list of pending writes. */ //这边会检查发送了多少 while (m->msg_iovlen > 0 && res >= m->msg_iov->iov_len) { res -= m->msg_iov->iov_len; m->msg_iovlen--; m->msg_iov++; } /* Might have written just part of the last iovec entry; adjust it so the next write will do the rest. */ if (res > 0) { m->msg_iov->iov_base = (caddr_t) m->msg_iov->iov_base + res; m->msg_iov->iov_len -= res; } return TRANSMIT_INCOMPLETE; } //发送失败的情况 if (res == -1 && (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK)) { if (!update_event(c, EV_WRITE | EV_PERSIST)) { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't update event "); conn_set_state(c, conn_closing); return TRANSMIT_HARD_ERROR; } return TRANSMIT_SOFT_ERROR; } /* if res == 0 or res == -1 and error is not EAGAIN or EWOULDBLOCK, we have a real error, on which we close the connection */ if (settings.verbose > 0) perror("Failed to write, and not due to blocking"); if (IS_UDP(c->transport)) conn_set_state(c, conn_read); else conn_set_state(c, conn_closing); return TRANSMIT_HARD_ERROR; } else { return TRANSMIT_COMPLETE; } }
conn_shrink 方法
当数据发送成功后,会跳转到conn_new_cmd这个状态继续处理,然后进入reset_cmd_handler方法,然后进入conn_shrink方法。
conn_shrink主要是用于检查读取和发送的buf的大小,是否超过了预定的水位,如果超过了,则需要重新realloc。
//重新设置命令handler static void reset_cmd_handler(conn *c) { c->cmd = -1; c->substate = bin_no_state; if (c->item != NULL) { item_remove(c->item); c->item = NULL; } conn_shrink(c); //这个方法是检查c->rbuf容器的大小 //如果剩余未解析的命令 > 0的话,继续跳转到conn_parse_cmd解析命令 if (c->rbytes > 0) { conn_set_state(c, conn_parse_cmd); } else { //如果命令都解析完成了,则继续等待新的数据到来 conn_set_state(c, conn_waiting); } }
//检查rbuf的大小 static void conn_shrink(conn *c) { assert(c != NULL); if (IS_UDP(c->transport)) return; //如果bufsize大于READ_BUFFER_HIGHWAT(8192)的时候需要重新处理 //DATA_BUFFER_SIZE等于2048,所以我们可以看到之前的代码中对rbuf最多只能进行4次recalloc if (c->rsize > READ_BUFFER_HIGHWAT && c->rbytes < DATA_BUFFER_SIZE) { char *newbuf; if (c->rcurr != c->rbuf) memmove(c->rbuf, c->rcurr, (size_t) c->rbytes); //内存移动 newbuf = (char *) realloc((void *) c->rbuf, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE); if (newbuf) { c->rbuf = newbuf; c->rsize = DATA_BUFFER_SIZE; } /* TODO check other branch... */ c->rcurr = c->rbuf; } if (c->isize > ITEM_LIST_HIGHWAT) { item **newbuf = (item**) realloc((void *) c->ilist, ITEM_LIST_INITIAL * sizeof(c->ilist[0])); if (newbuf) { c->ilist = newbuf; c->isize = ITEM_LIST_INITIAL; } /* TODO check error condition? */ } //如果大于c->msglist的水位了,则重新realloc if (c->msgsize > MSG_LIST_HIGHWAT) { struct msghdr *newbuf = (struct msghdr *) realloc((void *) c->msglist, MSG_LIST_INITIAL * sizeof(c->msglist[0])); if (newbuf) { c->msglist = newbuf; c->msgsize = MSG_LIST_INITIAL; } /* TODO check error condition? */ } //如果大于c->iovsize的水位了,则重新realloc if (c->iovsize > IOV_LIST_HIGHWAT) { struct iovec *newbuf = (struct iovec *) realloc((void *) c->iov, IOV_LIST_INITIAL * sizeof(c->iov[0])); if (newbuf) { c->iov = newbuf; c->iovsize = IOV_LIST_INITIAL; } /* TODO check return value */ } }