1、Memcached的网络模型
Memcached的网络模型是基于Libevent网络库开发的,同时Memcached采用多线程的工作方式,工作线程和主线程之间采用pipe进行通信。Memcached的网络线程模型主要涉及两个主要文件:memcached.c 和thread.c文件。
Memcached的网络模型流程大致如下:
1、memcached会在main函数中创建主线程的event_base,将监听端口的socket注册到主线程的event_base,由主线程来监听和接受客户端连接。
2、main函数创建主线程的同时,也会创建N个工作线程,每个工作线程都拥有各自的event_base 和LIBEVENT_THREAD数据结构来存储线程的信息(线程基本信息、线程队列、pipe文件描述符)。工作线程会将pipe管道的接收端 fd 注册到自己的event_base。
3、当有新连接建立时,主线程会通过accept 函数来与客户端建立新连接,同时将新连接相关的信息填入CQ_ITEM结构并放入工作线程的conn_queue队列,同时向选定的工作线程的管道写入字符,以此触发工作线程的libevent事件。
4、主线程是通过求余数的方式来选择线程池中的一个工作线程,工作线程得到通知后,会从conn_queue队列中取出CQ_ITEM,并将fd注册到工作线程的Libevent实例上,从而由工作线程来处理该连接的所有后续事件。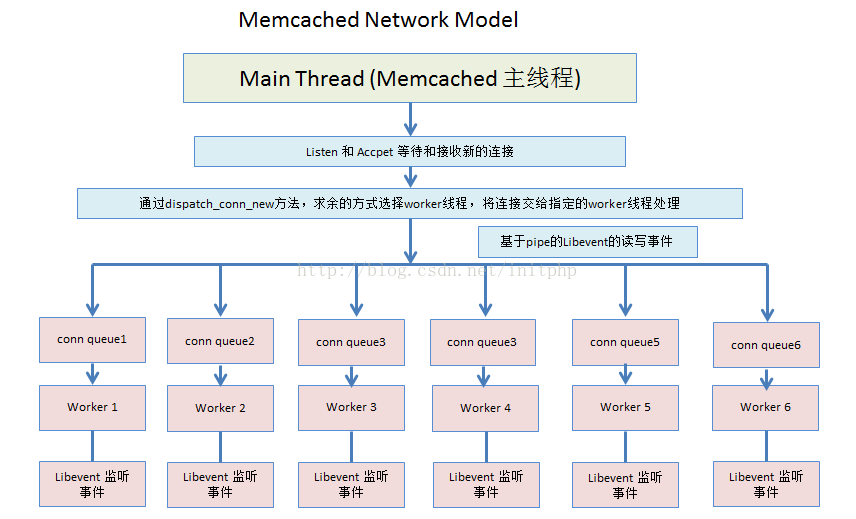
整体框架图:

2、主线程初始化逻辑
主线程的主要工作就是监听端口和初始化工作线程。下面代码值列出一部分相关内容。
int main (int argc, char **argv) { //这个方法主要用来创建工作线程 memcached_thread_init(settings.num_threads, NULL); errno = 0; if (settings.port && server_sockets(settings.port,tcp_transport,portnumber_file)) { vperror("failed to listen on TCP port %d", settings.port); exit(EX_OSERR); } /* enter the event loop */ //这边开始进行主线程的事件循环 if (event_base_loop(main_base, 0) != 0) { retval = EXIT_FAILURE; } }
memcached会通过memcached_thread_init 方法来创建工作线程。
void memcached_thread_init(int nthreads, void *arg) { //......省略部分代码 for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { int fds[2]; //这边会创建pipe,主要用于主线程和工作线程之间的通信 if (pipe(fds)) { perror("Can't create notify pipe"); exit(1); } // threads是每个线程都拥有的基本结构:LIBEVENT_THREAD threads[i].notify_receive_fd = fds[0]; threads[i].notify_send_fd = fds[1]; //这个方法非常重要,主要是创建每个线程自己的libevent的event_base //监听自己的通信管道接收端,同时初始化工作队列 setup_thread(&threads[i]); /* Reserve three fds for the libevent base, and two for the pipe */ stats_state.reserved_fds += 5; } /* Create threads after we've done all the libevent setup. */ //这里是循环创建线程 //线程创建的回调函数是worker_libevent for (i = 0; i < nthreads; i++) { create_worker(worker_libevent, &threads[i]); } /* Wait for all the threads to set themselves up before returning. */ pthread_mutex_lock(&init_lock); wait_for_thread_registration(nthreads); pthread_mutex_unlock(&init_lock); }
setup_thread 方法创建线程自己的event_base,工作线程在初始化时会将pipe的写事件注册到event_base,其写事件回调函数为 thread_libevent_process。当主线程接受到客户端连接时,向工作线程的pipe写字符,就会触发工作线程的thread_libevent_process 回调函数。
static void setup_thread(LIBEVENT_THREAD *me) { //.......省略部分代码 //每个独立的线程都应该有自己独立的event_base me->base = event_init(); if (! me->base) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't allocate event base "); exit(1); } /* Listen for notifications from other threads */ //这边非常重要,这边主要创建pipe的读事件EV_READ的监听 //当pipe中有写入事件的时候,libevent就会回调thread_libevent_process方法 event_set(&me->notify_event, me->notify_receive_fd, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, thread_libevent_process, me); event_base_set(me->base, &me->notify_event); //添加事件操作 if (event_add(&me->notify_event, 0) == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't monitor libevent notify pipe "); exit(1); } //初始化一个工作队列 me->new_conn_queue = malloc(sizeof(struct conn_queue)); if (me->new_conn_queue == NULL) { perror("Failed to allocate memory for connection queue"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } cq_init(me->new_conn_queue); //初始化线程锁 if (pthread_mutex_init(&me->stats.mutex, NULL) != 0) { perror("Failed to initialize mutex"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } me->suffix_cache = cache_create("suffix", SUFFIX_SIZE, sizeof(char*), NULL, NULL); if (me->suffix_cache == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create suffix cache "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } }
以上是工作线程创建时初始化event_base的部分,真正创建线程的方法是 memcached_thread_init 中的create_work方法。
//真正创建工作线程 static void create_worker(void *(*func)(void *), void *arg) { pthread_attr_t attr; int ret; pthread_attr_init(&attr); if ((ret = pthread_create(&((LIBEVENT_THREAD*)arg)->thread_id, &attr, func, arg)) != 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't create thread: %s ", strerror(ret)); exit(1); } }
create_worker方法在创建线程时,指定了线程的运行函数为worker_libevent,工作线程的运行函数其实就是进入事件循环,等待监听的事件触发。
//工作线程运行函数 static void *worker_libevent(void *arg) { //......省略部分代码 register_thread_initialized(); //这个方法主要是开启事件的循环 //每个线程中都会有自己独立的event_base和事件的循环机制 //memcache的每个工作线程都会独立处理自己接管的连接 event_base_loop(me->base, 0); //销毁event_base event_base_free(me->base); return NULL; }
到目前为止,每个工作线程的初始化工作已经完成,每个工作线程只监听了pipe的写事件,其回调函数为thread_libevent_process。
//管道有数据写入时的回调函数 static void thread_libevent_process(int fd, short which, void *arg) { LIBEVENT_THREAD *me = arg; CQ_ITEM *item; char buf[1]; conn *c; unsigned int timeout_fd; //回调函数中回去读取pipe中的信息 //主线程中如果有新的连接,会向其中一个线程的pipe中写入1 //这边读取pipe中的数据,如果为1,则说明从pipe中获取的数据是正确的 if (read(fd, buf, 1) != 1) { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Can't read from libevent pipe "); return; } switch (buf[0]) { case 'c': //从工作线程的队列中获取一个CQ_ITEM连接信息 item = cq_pop(me->new_conn_queue); //如果item不为空,则需要进行连接的接管 if (NULL == item) { break; } switch (item->mode) { case queue_new_conn: //conn_new这个方法非常重要,主要是创建socket的读写等监听事件。 //init_state 为初始化的类型,主要在drive_machine中通过这个状态类判断处理类型 c = conn_new(item->sfd, item->init_state, item->event_flags, item->read_buffer_size, item->transport, me->base); if (c == NULL) { if (IS_UDP(item->transport)) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on UDP socket "); exit(1); } else { if (settings.verbose > 0) { fprintf(stderr, "Can't listen for events on fd %d ", item->sfd); } close(item->sfd); } } else { c->thread = me; } break; case queue_redispatch: conn_worker_readd(item->c); break; } cqi_free(item); break; /* we were told to pause and report in */ case 'p': register_thread_initialized(); break; /* a client socket timed out */ case 't': if (read(fd, &timeout_fd, sizeof(timeout_fd)) != sizeof(timeout_fd)) { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Can't read timeout fd from libevent pipe "); return; } conn_close_idle(conns[timeout_fd]); break; } }
在新连接到来时,会调用conn_new 函数,监听新连接的读写事件。并且读写事件的回调函数为event_handler,event_handler方法的核心是 drive_machine,在这个函数中,memcached会根据连接的不同状态来进行不同的操作。
//主线程主要是监听用户的socket连接事件;工作线程主要监听socket的读写事件 //当用户socket的连接有数据传递过来的时候,就会调用event_handler这个回调函数 conn *conn_new(){ //......省略部分代码 event_set(&c->event, sfd, event_flags, event_handler, (void *)c); event_base_set(base, &c->event); }
static void drive_machine(conn *c) { //......省略部分代码 while (!stop) { //这边通过state来处理不同类型的事件 switch(c->state) { //这边主要处理tcp连接,只有在主线程的下,才会执行listening监听操作 //监听状态 case conn_listening: //...... //等待状态,等待客户端的数据报文到来 case conn_waiting: //...... //读取事件 //例如有用户提交数据过来的时候,工作线程监听到事件后,最终会调用这块代码 //读取数据的事件,当客户端有数据报文上传的时候,就会触发libevent的读事件 case conn_read: //...... } } return; }
drive_machine方法也是主线程event_base 回调函数的核心,主线程的socket是通过main函数中server_sockets方法创建的,而server_sockets中主要调用了server_socket这个方法,我们可以看下server_socket这个方法:
static int server_socket(const char *interface, int port, enum network_transport transport,FILE *portnumber_file) { //创建一个新的事件 //我们发现上面的工作线程也是调用这个方法,但是区别是这个方法指定了state的类型为:conn_listening //注意这边有一个conn_listening,这个参数主要是指定调用drive_machine这个方法中的conn_listen代码块。 if (!(listen_conn_add = conn_new(sfd, conn_listening,EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 1,transport, main_base))) { fprintf(stderr, "failed to create listening connection "); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } listen_conn_add->next = listen_conn; listen_conn = listen_conn_add; }
conn_new 方法已经介绍过了,该方法最终会进入drive_machine方法,并且连接状态为 conn_listening。memcached在 conn_listening的状态时,会调用dispath_conn_new来将新连接的相关信息push到工作线程的队列中。
case conn_listening: addrlen = sizeof(addr); sfd = accept(c->sfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, &addrlen); if (sfd == -1) { if (use_accept4 && errno == ENOSYS) { use_accept4 = 0; continue; } perror(use_accept4 ? "accept4()" : "accept()"); if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) { /* these are transient, so don't log anything */ stop = true; } else if (errno == EMFILE) { if (settings.verbose > 0) fprintf(stderr, "Too many open connections "); accept_new_conns(false); stop = true; } else { perror("accept()"); stop = true; } break; } if (!use_accept4) { if (fcntl(sfd, F_SETFL, fcntl(sfd, F_GETFL) | O_NONBLOCK) < 0) { perror("setting O_NONBLOCK"); close(sfd); break; } } if (settings.maxconns_fast && stats_state.curr_conns + stats_state.reserved_fds >= settings.maxconns - 1) { str = "ERROR Too many open connections "; res = write(sfd, str, strlen(str)); close(sfd); STATS_LOCK(); stats.rejected_conns++; STATS_UNLOCK(); } else { //如果客户端用socket连接上来,则会调用这个分发逻辑的函数 //这个函数会将连接信息分发到某一个工作线程中,然后工作线程接管具体的读写操作 dispatch_conn_new(sfd, conn_new_cmd, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, DATA_BUFFER_SIZE, c->transport); } stop = true; break;
dispath_conn_new 方法其实就是申请CQ_ITEM结构来保存连接信息,并将该结构PUSH到选定线程的队列中,同时向该线程的pipe写入字符,触发该工作线程的libevent网络时间,从源码也可以发现,memcached选择工作线程的方式是通过取余数来实现的。
void dispatch_conn_new(int sfd, enum conn_states init_state, int event_flags, int read_buffer_size, enum network_transport transport) { //每个连接连上来的时候,都会申请一块CQ_ITEM的内存块,用于存储连接的基本信息 CQ_ITEM *item = cqi_new(); char buf[1]; //如果item创建失败,则关闭连接 if (item == NULL) { close(sfd); /* given that malloc failed this may also fail, but let's try */ fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory for connection object "); return ; } //这个方法非常重要。主要是通过求余数的方法来得到当前的连接需要哪个线程来接管 //而且last_thread会记录每次最后一次使用的工作线程,每次记录之后就可以让工作线程进入一个轮询,保证了每个工作线程处理的连接数的平衡 int tid = (last_thread + 1) % settings.num_threads; //获取线程的基本结构 LIBEVENT_THREAD *thread = threads + tid; last_thread = tid; item->sfd = sfd; item->init_state = init_state; item->event_flags = event_flags; item->read_buffer_size = read_buffer_size; item->transport = transport; item->mode = queue_new_conn; //向工作线程的队列中放入CQ_ITEM cq_push(thread->new_conn_queue, item); MEMCACHED_CONN_DISPATCH(sfd, thread->thread_id); buf[0] = 'c'; //向工作线程的pipe中写入1 //工作线程监听到pipe中有写入数据,工作线程接收到通知后,就会向thread->new_conn_queue队列中pop出一个item,然后进行连接的接管操作 if (write(thread->notify_send_fd, buf, 1) != 1) { perror("Writing to thread notify pipe"); } }
以下是储存连接信息的CQ_ITEM结构以及每个线程的处理队列结构。处理队列结构实际上是链表实现的。
//储存连接信息的CQ_ITEM结构 typedef struct conn_queue_item CQ_ITEM; struct conn_queue_item { int sfd; //socket的fd enum conn_states init_state; //事件类型 int event_flags; //libevent的flags int read_buffer_size; //读取的buffer的size enum network_transport transport; CQ_ITEM *next; //下一个item的地址 }; //每个线程的处理队列结构。 typedef struct conn_queue CQ; struct conn_queue { CQ_ITEM *head; CQ_ITEM *tail; pthread_mutex_t lock; }