1. 集合与数组存储数据概述:
集合、数组都是对多个数据进行存储操作的结构,简称Java容器。
说明:此时的存储,主要指的是内存层面的存储,不涉及到持久化的存储(.txt,.jpg,.avi,数据库中)
2. 数组存储的特点:
> 一旦初始化以后,其长度就确定了。
> 数组一旦定义好,其元素的类型也就确定了。我们也就只能操作指定类型的数据了。
* 比如:String[] arr;int[] arr1;Object[] arr2;
3. 数组存储的弊端:
* > 一旦初始化以后,其长度就不可修改。
* > 数组中提供的方法非常限,对于添加、删除、插入数据等操作,非常不便,同时效率不高。
* > 获取数组中实际元素的个数的需求,数组没有现成的属性或方法可用
* > 数组存储数据的特点:有序、可重复。对于无序、不可重复的需求,不能满足。
4. 集合存储的优点:
解决数组存储数据方面的弊端。
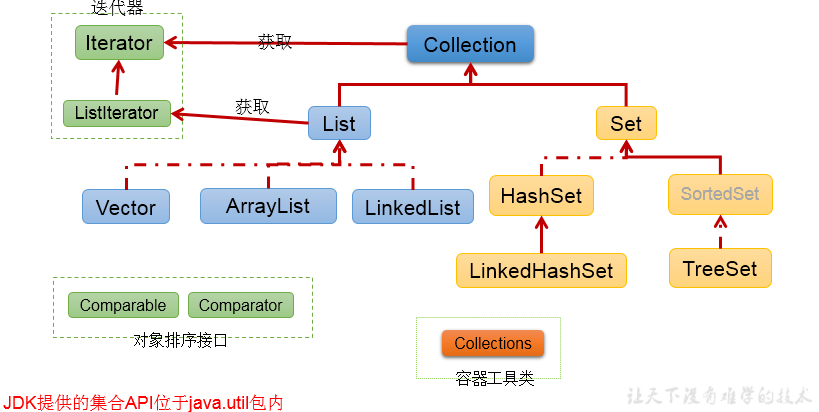
单列集合框架结构
|----Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
* |----List接口:存储有序的、可重复的数据。 -->“动态”数组
* |----ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
* |----Set接口:存储无序的、不可重复的数据 -->高中讲的“集合”
* |----HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet
2.Collection接口常用方法:
add(Object obj),addAll(Collection coll),
size(),isEmpty(),clear();
contains(Object obj),containsAll(Collection coll),
remove(Object obj),removeAll(Collection coll),retainsAll(Collection coll),equals(Object obj);
hasCode(),toArray(),iterator();
package main;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Author lx
* @Description add(),addAll(),size(),clear(),isEmpty()----Collection中的五个方法
* @Date 21:40 2020/8/11
* @Version
*/
public class firthMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
//all(object e):将元素e添加到集合coll中
coll.add(234);
coll.add("AA");
coll.add("HH");
coll.add(new Date());
//size():获取添加元素的个数
System.out.println(coll.size());//4
System.out.println(coll);
//addAll(collection coll1):将coll1集合中的元素添加到当前集合中
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(33);
coll1.add("haha");
coll.addAll(coll1);
System.out.println(coll);
System.out.println(coll.size()); //6
//isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
boolean empty = coll.isEmpty();
System.out.println(empty);
//clear();
coll.clear();
System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());
}
}
package main;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author lx
* @Description
* @Date 15:11 2020/8/12
* @Version
*/
public class sixMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("AA");
coll.add("BB");
coll.add("tt");
coll.add(123);
coll.add(new String("li"));
//1.contains(object obj)方法 判断当前集合中是否包含obj
boolean a = coll.contains(123);
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(coll.contains(new String("li")));
//2.containsAll(collection coll1) 判断coll1所有元素是否都存在于当前集合中
Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,"AAl");
boolean cal = coll.containsAll(coll1);
System.out.println(cal);
//3.remove(object obj)从当前集合中移除当前obj元素
Collection coll2 = new ArrayList();
coll2.add(123);
coll2.add(456);
coll2.add("jj");
coll2.add(new String("yy"));
coll2.remove("jj");
System.out.println(coll2);
//4.removeAll(collection coll2) 从当前集合中移除coll2中的所有元素
System.out.println(coll);
coll.removeAll(coll2);
System.out.println("*********");
System.out.println(coll);
//5.retainsAll(collection coll3)获取当前集合和coll3集合的交集,并返回给当前集合
Collection coll3 = Arrays.asList(123,"BB");
coll.retainAll(coll3);
System.out.println("***"+coll);
//6.equals(object obj)
Collection coll4 = new ArrayList();
coll4.add("AA");
coll4.add("BB");
coll4.add("tt");
coll4.add(123);
coll4.add(new String("li"));
Collection coll5 = new ArrayList();
coll5.add("AA");
coll5.add("BB");
coll5.add("tt");
coll5.add(123);
coll5.add(new String("li"));
System.out.println(coll4.equals(coll5));
//7.hashcode():返回当前对象的哈希值
System.out.println(coll.hashCode());
//8.集合----->数组:toArray()
Object[] array = coll5.toArray();
for(int i =0 ;i<array.length; i++){
System.out.println("array:"+array[i]);
}
//扩展 9.数组------>集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法asList(T ... t)
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"jj", "dd", "bb"});
System.out.println(strings);
}
}