1.Spring 简介
Spring的基础架构起源于2000年早期,它是Rod Johnson在一些成功的商业项目中构建的基础设施
2002后期,Rod Johnson发布了《Expert One-on-One J2EE Design and Development》一书
2003年2月Spring框架正式成为一个开源项目,并发布于SourceForge中
1.2 Spring工作原理
Spring是一种用JavaBean配置应用程序的方法
运用SpringIOC,通过setter方法来暴露一个类的任何依赖关系(如一个数据库连接),只要在Spring中进行配置来解决依赖性,不用编写一个数据库连接
运用Spring AOP 可以解决公共代码重复问题
1.3 Spring框架简介
Spring框架
轻量级
容器
开源框架
用于解决企业应用程序开发复杂性
一个轻量级的IOC和AOP容器框架
一个解决了许多J2EE开发中常见的问题的强大框架
1.4 Spring框架简介
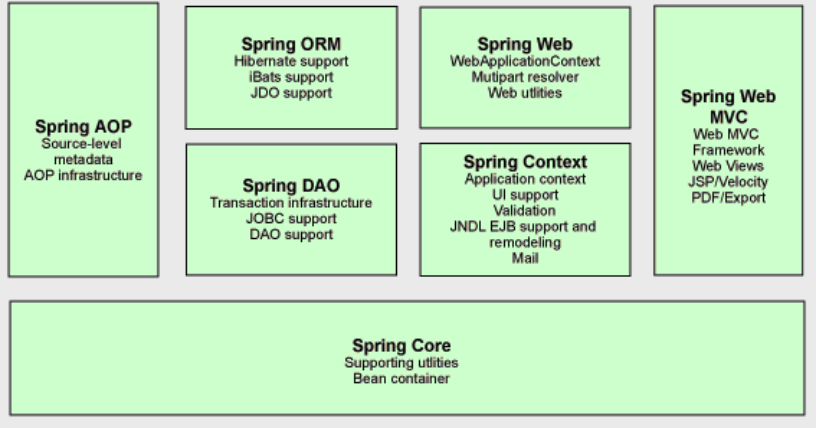
Spring框架有7个模块, 每个模块都可以单独存在,或者与其他一个或多个模块联合实现
2.1 Spring Bean 封装机制
Spring以Bean的方式管理所有的组件,J2EE的全部组件都被视为Bean管理
Spring负责创建Bean的实例,并管理其生命周期
Bean在Spring的容器中运行,无须知道Spring容器的存在也可以使用Spring的一些特性

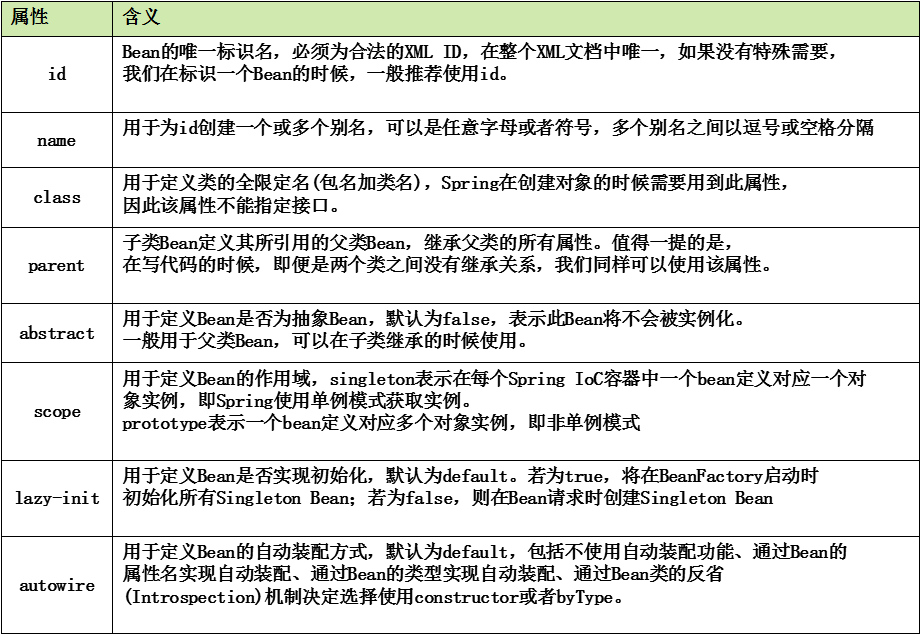
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> 5 <bean id=“user" class="com.hr.g3.persist.UserVo" 6 abstract="false" lazy-init="default" autowire="default" 7 dependency-check="default"> 8 </bean> 9 </beans>

1 <bean 2 id="beanId" 3 name ="beanName" 4 class="beanClass" 5 parent="parentBean" 6 abstract="true | false" 7 scope="prototype|singleton" 8 lazy-init="true | false | default" 9 autowire="no | byName | by Type | constructor | auto detect |default"> 10 </ bean>
BeanFactory
BeanFactory由org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory接口定义
BeanFactory是工厂模式(Factory pattern)的实现,负责创建和管理bean
BeanFactory接口包含以下基本方法
containsBean(String name)
getBean(String name)
getBean(String name,Class class)
getType(String name)
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext是基于BeanFactory之上的,提供了应用程序框架服务,扩展的新功能如下
提供国际化的支持
资源访问,如URL和文件
事件传递
载入多个配置文件等
搜索classpath路径,以classpath路径下的applicationContext.xml和bean.xml创建ApplicationContext
1 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“applicationContext.xml”);//单个文件 2 3 4 BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{“applicationContext.xml”,“bean.xml”}); //多个文件
按照指定路径下的applicationContext.xml和bean.xml创建ApplicationContext
BeanFactory beanFactory = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( new String[]{ "/WebRoot/WEB-INF/classes/applicationContext.xml", "/WebRoot/WEB-INF/classes/bean.xml"});
ApplicationContext接口的重要方法
1 (1)containsBean(String name)方法。 2 //判断Spring容器是否包含ID为 user的Bean 3 boolean flag=applicationContext.containsBean("user"); 4 5 (2)getBean(String name)方法。 6 //返回ID为 user的Bean 7 UserVo userBean= (UserVo)applicationContext.getBean("user"); 8 9 10 (3)getType(String name)方法 11 //返回:ID为 user 的类型 12 Class beanType= applicationContext.getType("user");
3.Spring依赖注入 (非注解)
设值注入的优点
如果依赖关系(或继承关系)较为复杂 ,设值注入模式往往更为简洁 有些地方有其局限性
直观,更加自然
构造注入的优点
构造期即创建一个完整、合法的对象
避免了繁琐的setter方法的编写
无需担心在调用过程中执行setter方法对组件依赖关系产生破坏
在构造函数中决定依赖关系的注入顺序
自动注入
简化配置文件
3.1接口与实体类

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public interface Display { 7 void printDisplayInfo(); 8 9 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public class Computer { 7 private MainFrame mainFrame;//主机 8 private Display display;//显示器接口 9 10 public Computer() { 11 } 12 13 public Computer(MainFrame mainFrame, Display display) { 14 this.mainFrame = mainFrame; 15 this.display = display; 16 } 17 18 //输出计算机配置信息 19 public void printComputerInfo(){ 20 System.out.println("计算机配置如下:"); 21 mainFrame.printMainFrameInfo();//输出主机信息 22 display.printDisplayInfo();//输出显示器信息 23 24 } 25 26 public MainFrame getMainFrame() { 27 return mainFrame; 28 } 29 30 public void setMainFrame(MainFrame mainFrame) { 31 this.mainFrame = mainFrame; 32 } 33 34 public Display getDisplay() { 35 return display; 36 } 37 38 public void setDisplay(Display display) { 39 this.display = display; 40 } 41 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public class LgDisplay implements Display{ 7 8 //LG显示器 9 public void printDisplayInfo() { 10 System.out.println("显示器:LG显示器"); 11 } 12 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public class MainFrame { 7 private String modelType; //型号 8 //输出主机信息 9 public void printMainFrameInfo(){ 10 System.out.println("主机型号:"+modelType); 11 } 12 13 public String getModelType() { 14 return modelType; 15 } 16 17 public void setModelType(String modelType) { 18 this.modelType = modelType; 19 } 20 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public class SamSungDisplay implements Display{ 7 8 //三星显示器 9 public void printDisplayInfo() { 10 System.out.println("显示器:三星显示器"); 11 } 12 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 7 */ 8 public class TestBean { 9 private List list; 10 private Map map; 11 private Properties prop; 12 private Set set; 13 14 public List getList() { 15 return list; 16 } 17 18 public void setList(List list) { 19 this.list = list; 20 } 21 22 public Map getMap() { 23 return map; 24 } 25 26 public void setMap(Map map) { 27 this.map = map; 28 } 29 30 public Properties getProp() { 31 return prop; 32 } 33 34 public void setProp(Properties prop) { 35 this.prop = prop; 36 } 37 38 public Set getSet() { 39 return set; 40 } 41 42 public void setSet(Set set) { 43 this.set = set; 44 } 45 }

1 package cn.yunhe.entity; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 5 */ 6 public class UserVo { 7 private int id; 8 private String name; 9 private int age; 10 11 public void printInfo(){ 12 System.out.println("姓名:"+name+",年龄:"+age); 13 } 14 15 public int getId() { 16 return id; 17 } 18 19 public void setId(int id) { 20 this.id = id; 21 } 22 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 27 public void setName(String name) { 28 this.name = name; 29 } 30 31 public int getAge() { 32 return age; 33 } 34 35 public void setAge(int age) { 36 this.age = age; 37 } 38 }
3.2配置文件

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 6 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 7 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 12 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd"> 13 14 <context:component-scan base-package="cn.yunhe.entity"/> 15 <bean id="user" class="cn.yunhe.entity.UserVo"/> 16 <bean id="mainFrame" class="cn.yunhe.entity.MainFrame"> 17 <property name="modelType" value="三星高配主机"/> 18 </bean> 19 <bean id="lg" class="cn.yunhe.entity.LgDisplay"/> 20 <bean id="samsung" class="cn.yunhe.entity.SamSungDisplay"/> 21 22 <!--设值注入是指通过setter方法传入被调用者的实例--> 23 <!--<bean id="computer" class="cn.yunhe.entity.Computer"> 24 <property name="mainFrame" ref="mainFrame"/> 25 <property name="display" ref="lg"/> 26 </bean>--> 27 <!--构造注入是指通过构造方法完成依赖关系的注入--> 28 <bean id="computer2" class="cn.yunhe.entity.Computer"> 29 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="mainFrame"/> 30 <constructor-arg index="1" ref="samsung"/> 31 </bean> 32 33 <!--Spring容器可以自动注入(autowire)相互协作bean之间的关联关系--> 34 <!--no : 不适用自动的装配,必须通过ref元素指定依赖。这是默认设置。 35 由于显式指定协作者可以使配置更灵活、更清晰,因此对于较大的 36 部署配置,推荐采用该设置。--> 37 <!--byName :根据属性名自动装配。此选项将检查容器并根据名字查找与属 38 性完全一致的bean,并将其与属性自动装配--> 39 <!--byType :如果容器中存在一个与指定属性类型相同的bean,那么将与该 40 属性自动装配。如果存在多个该类型的bean,那么将会抛出异 41 常,并指出不能使用byType方式进行自动装配。若没有找到相 42 匹配的bean,则属性不会被设置。--> 43 <bean id="computer" class="cn.yunhe.entity.Computer" autowire="byName"> 44 <property name="display" ref="lg"/> 45 </bean> 46 47 <!--集合属性--> 48 <bean id="testBean" class="cn.yunhe.entity.TestBean"> 49 <property name="list"> 50 <list> 51 <value>aaa</value> 52 <value>bbb</value> 53 <value>ccc</value> 54 </list> 55 </property> 56 <property name="map"> 57 <map> 58 <entry key="k1" value="v1"/> 59 </map> 60 </property> 61 <property name="prop"> 62 <props> 63 <prop key="k1" >str1</prop> 64 </props> 65 </property> 66 <property name="set"> 67 <set> 68 <value>ddd</value> 69 <value>eee</value> 70 </set> 71 </property> 72 </bean> 73 </beans>
3.3 测试类

1 package cn.yunhe.demo; 2 3 import cn.yunhe.entity.Computer; 4 import cn.yunhe.entity.TestBean; 5 import cn.yunhe.entity.UserVo; 6 import org.junit.Before; 7 import org.junit.Test; 8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 10 11 import java.util.List; 12 13 /** 14 * Created by Administrator on 2017/7/11. 15 */ 16 public class Demo { 17 18 ApplicationContext applicationContext =null; 19 @Before 20 public void init(){ 21 //以classpath路径下的applicationContex.xml创建Spring容器 22 applicationContext =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 23 } 24 25 @Test 26 public void test1(){ 27 //从Spring容器中获取ID 为user的Bean 28 UserVo user=applicationContext.getBean("user",UserVo.class); 29 //封装姓名和年龄 30 user.setName("张三丰"); 31 user.setAge(100); 32 //输出该bean的信息 33 user.printInfo(); 34 } 35 36 @Test//Spring的设值注入方式 //自动注入也有用这个例子 37 //设值注入是指通过setter方法传入被调用者的实例 38 public void test2(){ 39 Computer computer= applicationContext.getBean("computer", Computer.class); 40 computer.printComputerInfo(); 41 } 42 43 @Test//Spring的构造注入方式 44 //构造注入是指通过构造方法完成依赖关系的注入 45 public void test3(){ 46 Computer computer=applicationContext.getBean("computer2",Computer.class); 47 computer.printComputerInfo(); 48 } 49 50 @Test//集合属性 51 public void test4(){ 52 TestBean testBean=applicationContext.getBean("testBean",TestBean.class); 53 List<String>list = testBean.getList(); 54 for (String str:list){ 55 System.out.println(str); 56 } 57 } 58 59 }
4.注解实现Spring注入
@Component 注解配置bean @Component注解唯一的一个可选参数是value,用于指定bean的名称(即id值,所以必须是唯一的)
1 @Component(”computer”) 2 public class Computer { } 3 @Component 4 public class MainFrame {} 5 @Component 6 public class SamSungDisplay implements Display {} 7 @Component 8 public class LgDisplay implements Display {}
只需在配置文件中配置以下代码 扫描@Component标注的类
1 <context:component-scan 2 base-package="s3spring.ch1.annotation.computer"/>
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器获取bean
Computer c = ac.getBean(Computer.class);
使用 @Scope注解配置bean 的作用域
@Scope定义bean的作用域,singleton表示在Spring loC容器中一个bean的定义对应一个对象实例,Spring使用单例模式获取实例
prototype 表示一个bean定义对应多个对象实例,即非单例模式,常称作多例
1 @Component 2 @Scope(value="prototype") 3 public class Computer { …… }
使用@Autowired注解
可以对类成员变量、方法及构造函数进行标注,以完成自动装配依赖的工作
@Autowired 默认按 byType 自动注入
1 @Component 2 @Scope("prototype") 3 public class Computer { 4 @Autowired 5 private MainFrame mainFrame;// 主机 6 @Autowired 7 private Display display;// 显示器接口 8 ……
多个bean导致的创建bean失败的问题
把属性名称做为依赖bean名称
@Qualifier 注解明确指定依赖bean的名称(就是显示器接口被多个类实现,导致使用该接口时不知道调那个类,就需要在这里声明一下)
1 @Component 2 @Scope("prototype") 3 public class Computer { 4 @Autowired 5 private MainFrame mainFrame;// 主机 6 @Autowired 7 @Qualifier("samSungDisplay")//表明是用的三星的 8 private Display display;// 显示器接口 9 …… 10 }
注解的运行流程
1.首先根据属性的类型在Spring 应用容器中查找类型匹配的bean
2.如果没有类型匹配的bean,抛出BeanCreationException;如果只有一个,则注入依赖,完成自动装配;如果不只一个,则继续执行步骤3;
3.如果通过 @Qualifier指定了bean 名称,则从所有符合类型的bean中返回指定的bean,完成自动装配;如果没有通过 @Qualifier制定bean 名称,则通过反射技术获取当前属性的名称作为bean 名称返回指定的bean,完成自动装配;
使用@Resource注解注入依赖
@Resource 默认按 byName 自动注入 用法与上边使用@Autowire相同
1 @Component 2 @Scope("prototype") 3 public class Computer { 4 @Resource 5 private MainFrame mainFrame;//采用属性名称作为依赖bean的名称 6 7 @Resource(name="samSungDisplay") 8 private Display display;// 采用@name参数值作为依赖bean的名称 9 …… 10 }
使用JSR-250规范定义的注解
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy
@PostConstruct 注解的方法将在类实例化后调用,
@PreDestroy注解的方法将在类销毁之前调用 ConfigurableApplicationContext close方法
1 @PostConstruct 2 public void postConstruct1(){ 3 System.out.println("执行postConstruct1"); 4 } 5 6 @PreDestroy 7 public void preDestroy1(){ 8 System.out.println("执行preDestroy1"); 9 }
