/**
* Consumer<T> : 消费型接口
* void accept(T t);
*
* Supplier<T> : 供给型接口
* T get();
*
* Function<T, R> : 函数型接口
* R apply(T t);
*
* Predicate<T> : 断言型接口
* boolean test(T t);
*
*
*/
@Test public void test1() { happy(10000,x -> System.out.println("喜欢大保健,每次消费"+ x)); happy(10000,x -> { double a = x*100; }); } public void happy(double money, Consumer<Double> con) { con.accept(money); }
test1结果:

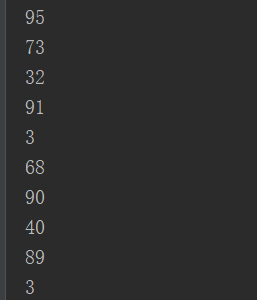
//Supplier<T> 供给型接口: @Test public void test2(){ List<Integer> numList = getNumList(10,() -> (int)(Math.random()*100)); for(Integer num : numList) { System.out.println(num); } } //需求:产生指定个数的整数,并放入集合中 public List<Integer> getNumList(int num, Supplier<Integer> sup) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < num ; i++) { Integer n = sup.get(); list.add(n); } return list; }
test2结果:
//Function<T, R> 函数式接口 @Test public void test3() { Integer num = strHandler("123",(x) -> Integer.valueOf(x) +10000); System.out.println(num); } //用于处理字符串 public Integer strHandler(String str, Function<String,Integer> fun) { return fun.apply(str); }
test3结果:

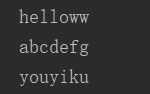
//Predicate<T> 断言型接口 @Test public void test4() { List<String> list = Arrays.asList("helloww","www","abcdefg","ss","youyiku"); List<String> strings = filterStr(list, (x) -> x.length() > 3); for(String s: strings) { System.out.println(s); } } //需求,将满足条件的字符串,放入集合中 public List<String> filterStr(List<String> list, Predicate<String> pre) { List<String> strList = new ArrayList<>(); for(String str: list) { if(pre.test(str)) { strList.add(str); } } return strList; }
test 4结果: