题目一: 想问一个问题:Spark Streaming 如何保证有序消费 kafka数据?topic多分区
如果是全局有序 kafka只有在单partition才生效,多partitions不支持全局有序,或者比较难;
如果是局部有序 可以利用 相同的key映射到同一个partition的特点 保证 key内有序,
例如:指定key(比如order id),具有同1个key的所有消息,会发往同1个partition。也是有序的
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/bigtree_3721/article/details/80953197
2019-08-14
题目二:一个值得注意的点: val traffic = temp(2).trim.toLong
在做toLong 转换的时候,一定要try catch
之前: val traffic = temp(2).trim.toLong
之后:
var traffic = 0L // 考虑到流量这个值可能脏数据,无法toLong
try{
traffic = temp(2).trim.toLong // 考虑到空格的情况
}catch {
case e:Exception => traffic = 0L
}
2019-08-16
题目三:java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded
at java.util.Arrays.copyOf(Arrays.java:3230)
/**
* Returns a Java list that contains all rows in this Dataset.
*
* Running collect requires moving all the data into the application's driver process, and
* doing so on a very large dataset can crash the driver process with OutOfMemoryError.
*
* @group action
* @since 1.6.0
*/
def collectAsList(): java.util.List[T] = withAction("collectAsList", queryExecution) { plan =>
val values = collectFromPlan(plan)
java.util.Arrays.asList(values : _*)
}
参考:https://www.xttblog.com/?p=3347
题目四:以WordCount为例,分别画出Spark和MapReduce执行流程
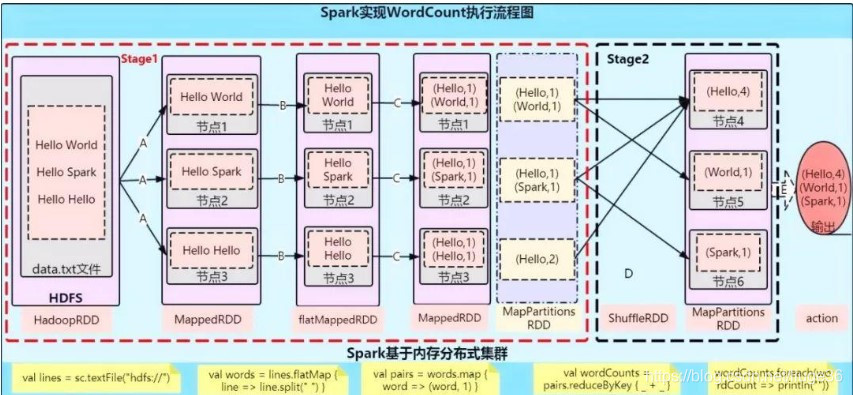
几点说明:
A步骤:val lines = sc.textFile("") 从hdfs的block块中读取数据的时候,是按照默认分区为2 进行读取,
即:1个RDD2个partition。
B步骤:val words = lines.flatMap(line => line.split(",")) flatMap本身就是将每一个输入项映射到0个或多个输出项(因此包含的是Seq 而不是单个项)
即:将数据打扁,一个二维数据搞成一维的
C步骤:val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1)) Map是每一个元素都作用上相同的一个函数操作
D步骤:val wordClunts = pairs.reduceBykey(+) reduceBykey 算子会先在Map端做一个聚合【通过MapPartition操作完成】,然后再将聚合的数据进行shuffle操作
E步骤:wordClunts.collect().foreach(println) 将结果全部放入一个集合中,拉回到Driver端
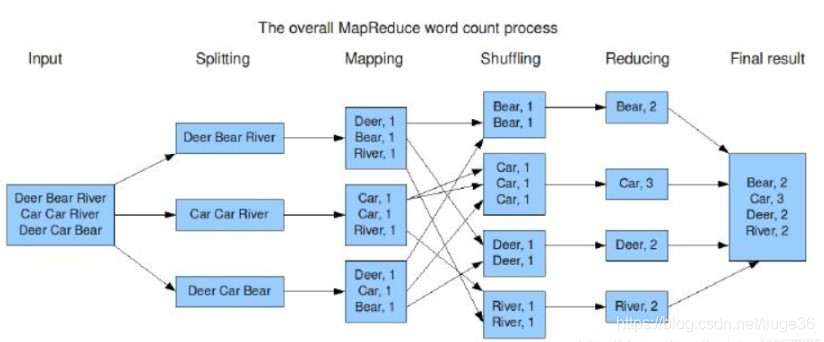
参照https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41227335/article/details/88364913