spring serious of blog edit by 马士兵教育
Maven方式创建Spring工程
工程创建
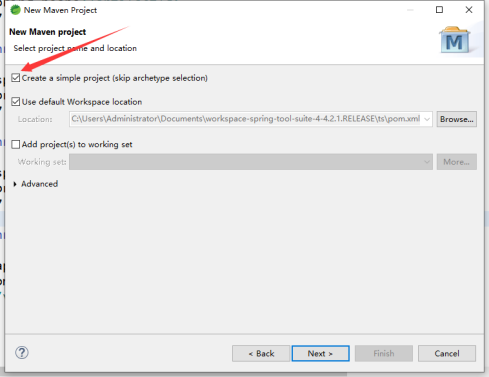
1.新建项目 选择Maven Project

2.勾选 Create a simple project
3.添加项目信息
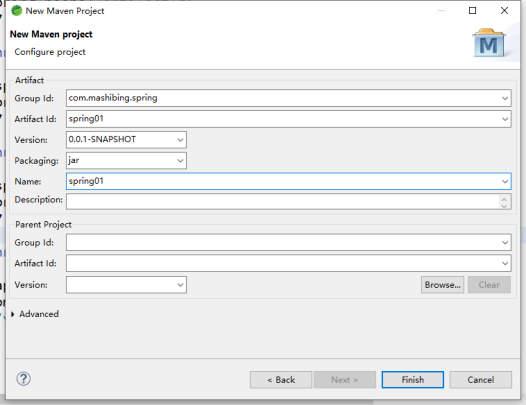
l Group id :包名
l Artifact id:标识名
l Name:项目名
依赖引入
Maven 中央仓库
使用国内镜像
创建一个maven的配置文件
参照:
http://maven.apache.org/settings.html
Pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-beans --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>5.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>5.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/commons-lang3 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> <version>3.9</version> </dependency>
空值注入
Value标签
标识空值 或空字符串 “”
<property name="name"><value></value></property>
Null标签
标识Null
<property name="name"><null></null></property>
工厂方式注入
为满足更复杂的需求,Spring也提供了工厂方式来创建更加灵活的Bean。
留意观察工厂类和实现类的创建次数
动态工厂
抽象接口 Car
public interface Car { public String getName(); public String getPrice(); }
实现类 BMW车
public class Bmw implements Car{ public String getName() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return "别摸我"; } public String getPrice() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return "500000RMB"; } }
汽车工厂类 CarFactory
public class CarFactory { public Car getCar(String name) throws Exception{ if (name.endsWith("bmw")) { return new Bmw(); }else { throw new Exception("car not fond"); } } }
Bean配置
<bean id="carFactory" class="com.msb.CarFactory"></bean> <bean id="car" factory-bean="carFactory" factory-method="getCar" > <constructor-arg value="bmw"></constructor-arg> </bean>
静态工厂
Bean配置
<bean id="carStatic" class="com.msb.CarFactoryStatic" factory-method="getCar"> <constructor-arg value="bmw"></constructor-arg> </bean>
工厂类
public class CarFactoryStatic { public static Car getCar(String name) throws Exception{ if (name.endsWith("bmw")) { return new Bmw(); }else { throw new Exception("car not fond"); } } }
autowire自动注入
使用自动需要在配置文件中bean上添加autowire
<bean id="person" class="com.msb.Person" autowire="byName"> </bean> <bean id="pet" class="com.msb.Pet"> <property name="name" value="kele"></property> </bean>
实体
public class Person { private String name; private Pet pet; } public class Pet { private String name; }
可选两种类型
byName
byName方式自动注入:要求注入的bean的id必须和被注入的bean对象的属性名一致
byType
byType方式自动注入:要求注入的bean的对象类型与被注入的bean对象类型一致,并且在配置文件中的Bean相同类型必须唯一
如果存在多个,会抛异常:
No qualifying bean of type 'com.msb.Pet' available: expected single matching bean but found 2: pet,pet2
全局空值自动注入
在首行Beans标签下添加default-autowire属性。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-autowire="byType" >
annotation注解注入
使用注解需要导入AOP包
在配置文件中添加Context约束
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd " >
<context:component-scan>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.msb"></context:component-scan>
component-scan可以自动扫描包内容,并注册Bean到Spring容器
@Component
在需要注册到容器的类上添加@Component标签,标识这个类由Spring容器接管
约定大于配置
在一个类上添加@Component默认会使用首字母小写的类名作为ID注册到Spring容器。
如果需要手动指定Bean Id可以使用@Component("p")
同属@Component的额外三个注解
@Controller @Service @Repository
这三个注意在MVC开发中会经常用到,除了注解名字和Component不一样之外,其余功能都一样。
Spring额外提供这三个注解的目的主要是为了区分MVC中每个类的区别。
@Scope
使用注解注册Bean 默认的作用域还是singleton,可以使用@Scope("prototype")改变对象作用域
@Value
在使用注解给对象注入值的时候,不再需要Get/Set方法
基础类型
使用@Value注解
@Value("小明")
private String name;
对象引用
@Autowired
private Pet MyPet;
使用@Autowired注解
默认是ByType的,如果需要ByName需要配合@Qualifier注解
@Autowired()
@Qualifier("p2")
private Pet MyPet;
面向切面编程 代码增强
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程。
面向切面,是与OOP(Object Oriented Programming)面向对象编程并列的编程思想。
Spring支持两种方法,那么我们在使用spring进行动态代理时究竟使用的哪一种方法呢?spring优先支持实现接口的方式,如果没有接口则使用cglib方式
代理
通过代理可以隐藏目标类的具体实现;在不修改目标类代码的情况下能够对其功能进行增强。
l 委托类和代理类有相同的接口或者共同的父类
l 代理类为委托类负责处理消息,并将消息转发给委托类
l 委托类和代理类对象通常存在关联关系
l 一个代理类对象与一个委托类对象关联
l 代理类本身并不是真正的实现者!而是通过调用委托类的方法来实现功能!
静态代理
使用硬编码的方式增强原有方法
l 优点:可以做到不对目标对象进行修改的前提下,对目标对象进行功能的扩展和拦截。
l 缺点:因为代理对象,需要实现与目标对象一样的接口,会导致代理类十分繁多,不易维护,同时一旦接口增加方法,则目标对象和代理类都需要维护。
Girl -> 目标对象 -> 被包装/增强的对象
public class Girl implements Human{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Em mmm.. mm.."); } }
抽象接口
interface Human { public void eat(); }
ProxyGirl 代理对象,包含对原对象方法的增强,通过构造方法传入原对象,并实现和原对象相同的接口,实现接口方法,便可以利用Java多态的特性,通过访问代理方法同时能够调起原对象的实现,并对其增强。
public class ProxyGirl implements Human { private Human human; public ProxyGirl() { super(); } public ProxyGirl(Human human) { super(); this.human = human; } public void eat() { System.out.println("chiqian"); human.eat(); System.out.println("chihou"); } }
测试类
Girl girl = new Girl(); Human proxyGirl = new ProxyGirl(girl); proxyGirl.eat();
动态代理
动态代理是指动态的在内存中构建代理对象(需要我们制定要代理的目标对象实现的接口类型),即利用JDK的API生成指定接口的对象,也称之为JDK代理或者接口代理。
l 目标对象实现了接口 JDK动态代理
l 目标对象没有实现口CGLib