一、题目:
二、思路:
我认为这道题出的很好,不仅考验了选手的数学素养,也考验了选手的计算机功底。(反正我没做出来。)
我们稍加思考就会发现,如果对于每个点(不论是正视图还是左视图),我们都在对应的竖坐标将这个几何体“拦腰斩断”,那么最终一定会得到一堆层,每层都是若干个“梯形体”。
上、下面平行且为长方形,四个侧面都是梯形,由此围成的立体图形叫梯形体。
注意梯形体和台体是有区别的。台体要求侧棱必须交于一点,但是梯形体没有这个要求。所以,梯形体当然也就不能用台体体积的计算公式了。
那梯形体的体积怎样计算呢?两种方法,一种是分割法,参见下面这张图;另一种是对梯形体的高积分。
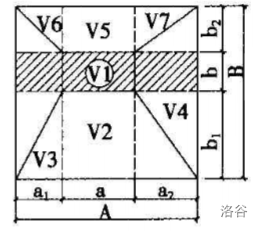
[V = dfrac{H}{3} imes left(AB + ab + dfrac{Ab + aB}{2}
ight)
]
其中,(A) 和 (B) 是梯形体下底面的长和宽,(a) 和 (b) 是梯形体上底面的长和宽。(H) 是梯形体的高。
我们还有一个性质,如果一堆等高梯形体的上底面和下底面分别能拼成一个大的矩形,那么我们就可以把最终拼成的两个大矩形当做一个新梯形体的上下底面,从而能算出这堆梯形体的总体积。
所以这道题就简单了!我们只需要维护当前层的上下底面的长和宽进行累加即可。长和宽的更新可以用斜率的倒数进行计算。
对了这道题还有一个非常蛋疼的地方,就是竖坐标可能会相同。我本来使用随机抖动法来避免这个问题,但是以失败告终;只能老老实实特殊处理。具体过程见代码。
三、代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define FILEIN(s) freopen(s, "r", stdin);
#define FILEOUT(s) freopen(s, "w", stdout)
#define mem(s, v) memset(s, v, sizeof s)
#define eps 1e-8
inline int read(void) {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return f * x;
}
const int MAXN = 100005;
int tot, n[2];
int changex[2][MAXN], maxx[2];
double delta[2][MAXN];
struct Point {
int x, y;
}p[2][MAXN];
struct Node {
int t, h, id;
inline friend bool operator <(const Node&a, const Node&b) {
return a.h > b.h;
}
}height[MAXN << 1];
inline void input(int t) {
n[t] = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n[t]; ++ i) {
p[t][i].x = read();
p[t][i].y = read();
maxx[t] = max(maxx[t], p[t][i].y);
height[++ tot] = { t, p[t][i].y, i };
}
}
inline void get_changex(int t) { // 处理竖坐标相同的情况。
for (int i = 2; i <= n[t]; ++ i)
if (p[t][i].y == p[t][i - 1].y)
changex[t][i] = p[t][i].x - p[t][i - 1].x;
}
inline void get_delta(int t) {
for (int i = 2; i < n[t]; ++ i) {
if (p[t][i].y != p[t][i - 1].y) {
delta[t][i] += 1.0 * (p[t][i].x - p[t][i - 1].x) / (p[t][i].y - p[t][i - 1].y);
}
if (p[t][i].y != p[t][i + 1].y) {
delta[t][i] += -1.0 * (p[t][i].x - p[t][i + 1].x) / (p[t][i].y - p[t][i + 1].y);
}
}
}
inline double get_volume(double a, double b, double A, double B, double H) {
return H / 3 * (A * B + a * b + 0.5 * (A * b + B * a));
}
int main() {
input(0);
get_changex(0);
get_delta(0);
input(1);
get_changex(1);
get_delta(1);
if (maxx[0] != maxx[1]) { puts("Invalid plan"); return 0; }
sort(height + 1, height + tot + 1);
double L[2] = {0, 0}, k[2] = {0, 0}, nowh = height[1].h, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= tot; ++ i) {
if (nowh != height[i].h) {
double l[2];
l[0] = L[0] + k[0] * (nowh - height[i].h);
l[1] = L[1] + k[1] * (nowh - height[i].h);
ans += get_volume(L[0], L[1], l[0], l[1], nowh - height[i].h);
L[0] = l[0]; L[1] = l[1];
nowh = height[i].h;
}
L[height[i].t] += changex[height[i].t][height[i].id];
k[height[i].t] += delta[height[i].t][height[i].id];
}
printf("%.8lf
", ans);
return 0;
}