周三要考试,可是根本就踏实不下来复习,毕设也静不下心弄了。于是就玩玩比赛了,晚上12点还有一场CF,到时候再玩个1个多小时去睡觉。
说说我周赛做的两道题吧:
一个四位数变成另一个四位数,要求的操作有三种:
1. 对任意一位加1,如果大于9,回到1
2. 对任意一位减1,如果小于1,回到9
3. 交换相邻两位的数字,最左边和最右边不算相邻
可以知道状态空间为9*9*9*9<10^4,直接BFS搞就可以了,因为我大量使用STL,导致TLE了,后来改成int,就AC了,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 2005;
//string a, b;
int a, b;
int hash[100 * 100];
int ten[4] = {1, 10, 100, 1000};
int GetHash(int x)
{
return x;
}
int Add(int x, int i)
{
int t = (x / ten[i]) % 10;
if(t < 9) return x + ten[i];
else return x - t * ten[i] + ten[i];
}
int Sub(int x, int i)
{
int t = (x / ten[i]) % 10;
if(t > 1) return x - ten[i];
else return x - t * ten[i] + 9 * ten[i];
}
int Swp(int x, int i)
{
int t1 = (x / ten[i]) % 10;
int t2 = (x / ten[i + 1]) % 10;
return x - t1 * ten[i] - t2 * ten[i + 1] +
t2 * ten[i] + t1 * ten[i + 1];
}
int go()
{
vector<int> ans;
vector<int> Q;
//set<string> one;
Q.push_back(a);
ans.push_back(0);
//one.insert(a);
memset(hash, 0, sizeof(hash));
hash[GetHash(a)] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < Q.size(); i++)
{
//printf("$%d\n", Q[i]);
if(Q[i] == b)
{
//printf("%d %d\n", Q[i], b);
return ans[i];
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
int strAdd = Add(Q[i], j);
int strSub = Sub(Q[i], j);
//if(one.find(strAdd) == one.end())
if(hash[GetHash(strAdd)] == 0)
{
//one.insert(strAdd);
Q.push_back(strAdd);
ans.push_back(ans[i] + 1);
hash[GetHash(strAdd)] = 1;
}
//else return ans[i] + 1;
//if(one.find(strSub) == one.end())
if(hash[GetHash(strSub)] == 0)
{
//one.insert(strSub);
Q.push_back(strSub);
ans.push_back(ans[i] + 1);
hash[GetHash(strSub)] = 1;
}
//else return ans[i] + 1;
if(j < 3)
{
int strSwp = Swp(Q[i], j);
//if(one.find(strSwp) == one.end())
if(hash[GetHash(strSwp)] == 0)
{
//one.insert(strSwp);
Q.push_back(strSwp);
ans.push_back(ans[i] + 1);
hash[GetHash(strSwp)] = 1;
}
// else return ans[i] + 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
{
//cin >> a >> b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("%d\n", go());
}
}
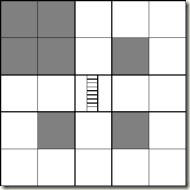
一张20*20的地图,上满有障碍点,非障碍点,楼梯三种格子,起点、终点落在非障碍点上,梯子每分钟改变一个朝向(横着,竖着),从起点到终点,四个方向,问说最少的步数,走楼梯的话,就一下子跨两格。
设置一个这样的状态(x,y,step),花费的空间也就20*20*400左右,然后去BFS,这样是可以AC的,有趣的是,我觉得只要存step的奇偶性就行了,也就是这样的状态(x,y,step%2),我觉得这样是对的,但一时不知道怎么严谨说明,大概就是,如果先扩展到一个奇数步的节点的话,那么这个就是奇数所能到达的最小的走法了,看着代码虽然100+行,但是自己看了看,发现其实也没啥东西,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 25;
int m, n, sx, sy, ex, ey;
char mm[MAX][MAX];
int hash[405 * 410];
class CNODE
{
public:
int x, y, t;
public:
CNODE() {}
CNODE(int _x, int _y, int _t)
: x(_x), y(_y), t(_t) {}
int GetHash()
{
int res = 0;
res += (x * 20 + y);
res = res * 410 + (t % 2);
//res = res * 410 + t;
return res;
}
};
int go()
{
memset(hash, 0, sizeof(hash));
vector<CNODE> Q;
Q.push_back(CNODE(sx, sy, 0));
hash[Q[0].GetHash()] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < Q.size(); i++)
{
int x = Q[i].x;
int y = Q[i].y;
int t = Q[i].t;
if(x == ex && y == ey) return t;
CNODE dd = CNODE(x, y, t + 1);
if(hash[dd.GetHash()] == 0)
{
hash[dd.GetHash()] = 1;
Q.push_back(dd);
}
for(int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) for(int k = -1; k <= 1; k++)
if(j * j + k * k == 1)
{
int dx = x + j;
int dy = y + k;
if(dx < 0 || dx >= m || dy < 0 || dy >= n)
continue;
if(mm[dx][dy] == '*') continue;
CNODE dq;
if(mm[dx][dy] == '.' || mm[dx][dy] == 'T' || mm[dx][dy] == 'S')
{
dq = CNODE(dx, dy, t + 1);
if(hash[dq.GetHash()] == 0)
{
hash[dq.GetHash()] = 1;
Q.push_back(dq);
}
if(dx == ex && dy == ey) return t + 1;
}
else
{
if((mm[dx][dy] == '|' && k == 0 && t % 2 == 0) ||
(mm[dx][dy] == '-' && k == 0 && t % 2 == 1))
{
if(dx + j >= 0 && dx + j < m)
{
dq = CNODE(dx + j, dy, t + 1);
if(hash[dq.GetHash()] == 0)
{
hash[dq.GetHash()] = 1;
Q.push_back(dq);
}
if(dx == ex && dy == ey) return t + 1;
}
}
if((mm[dx][dy] == '-' && j == 0 && t % 2 == 0) ||
(mm[dx][dy] == '|' && j == 0 && t % 2 == 1))
{
if(dy + k >= 0 && dy + k < n)
{
dq = CNODE(dx, dy + k, t + 1);
if(hash[dq.GetHash()] == 0)
{
hash[dq.GetHash()] = 1;
Q.push_back(dq);
}
if(dx == ex && dy == ey) return t + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
printf("no\n");
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d", &m, &n) != EOF)
{
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%s", mm[i]);
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(mm[i][j] == 'S') sx = i, sy = j;
if(mm[i][j] == 'T') ex = i, ey = j;
}
}
printf("%d\n", go());
}
}