四种语句
PHP中有四个加载文件的语句:include、require、include_once、require_once。
基本语法
require:require函数一般放在PHP脚本的最前面,PHP执行前就会先读入require指定引入的文件,包含并尝试执行引入的脚本文件。require的工作方式是提高PHP的执行效率,当它在同一个网页中解释过一次后,第二次便不会解释。但同样的,正因为它不会重复解释引入文件,所以当PHP中使用循环或条件语句来引入文件时,需要用到include。
include:可以放在PHP脚本的任意位置,一般放在流程控制的处理部分中。当PHP脚本执行到include指定引入的文件时,才将它包含并尝试执行。这种方式可以把程序执行时的流程进行简单化。当第二次遇到相同文件时,PHP还是会重新解释一次,include相对于require的执行效率下降很多,同时在引入文件中包含用户自定义函数时,PHP在解释过程中会发生函数重复定义问题。
require_once / include_once:分别与require / include作用相同,不同的是他们在执行到时会先检查目标内容是不是在之前已经导入过,如果导入过了,那么便不会再次重复引入其同样的内容。
相互区别
include和require:
include有返回值,而require没有返回值
include在加载文件失败时,会生成一个警告(E_WARNING),在错误发生后脚本继续执行。所以include用在希望继续执行并向用户输出结果时。
require在加载失败时会生成一个致命错误(E_COMPILE_ERROR),在错误发生后脚本停止执行。一般用在后续代码依赖于载入的文件的时候。
结果:
include和include_once:
include载入的文件不会判断是否重复,只要有include语句,就会载入一次(即使可能出现重复载入)。而include_once载入文件时会有内部判断机制判断前面代码是否已经载入过。这里需要注意的是include_once是根据前面有无引入相同路径的文件为判断的,而不是根据文件中的内容(即两个待引入的文件内容相同,使用include_once还是会引入两个)。
require和require_once:同include和include_once的区别相同。
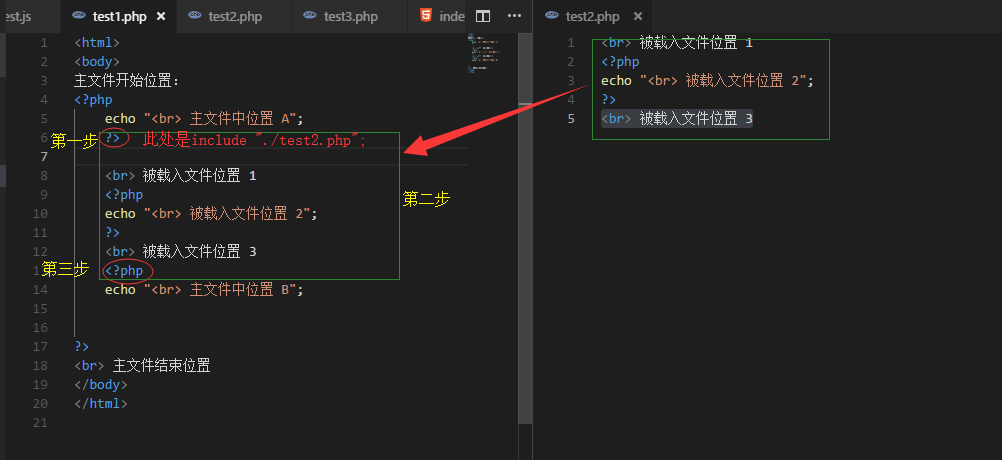
载入时执行过程
1. 从include(require)语句退出php脚本模式(进入html代码模式)
2. 载入include语句所设定的文件中的代码,并尝试执行
3. 退出html模式,重新进入php脚本模式,继续后面脚本程序的执行
结果:
分析:
加载时的路径问题
相对路径:
相对于当前网页文件所在位置来定位某个被加载的文件位置。
绝对路径:
分为本地绝对路径和网络绝对路径
本地绝对路径:
从本地的根目录逐层递归向下找,直到找到对应目录下的待引入文件。
我们都知道,绝对路径不利于项目的移植和可维护性,所以一般很少在代码中直接这样写绝对路径,但是如果我们需要用到绝对路径,应该怎么办??PHP中有魔术常量__DIR__和全局数组$_SERVER,用法如下:
网络绝对路径:
通过网址链接到文件下,服务器会将网址指向的文件执行后返回回来
无路径:
只给出文件名而没有给出路径信息,此时PHP会在当前网页目录下找该文件,如果找到相同名字的文件,执行并引入。
需要注意:无论采用哪种路径,必须要加上文件后缀名,这四种文件载入方式不能识别无后缀的文件。
返回值的比较
上文说道include有返回值,而require无返回值
对于include,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,则返回false.
对于require,如果载入成功,有返回值,返回值为1;如果载入失败,无返回值。
输出:
当文件中有return:
当被载入文件中有return语句时,会有另外的机制,此时return语句的作用是终止载入过程,即被载入文件中return语句的后续代码不再载入。return语句也可以用于被载入文件载入时返回一个数据。
结果: