在JavaScript中,字符串String 和 数组Array在其原型对象上都有一些常用的操作方法,那么今天就来整理总结下,一些容易被搞混的方法
1、字符串操作中的match、search 和 replace
String.prototype.match() 用途: 在字符串内检索指定的值,或找到一个或多个正则表达式的匹配
举例说明:
const reg = /an/ const str = 'a banana two banana' const b = str.match(reg) console.log(b)
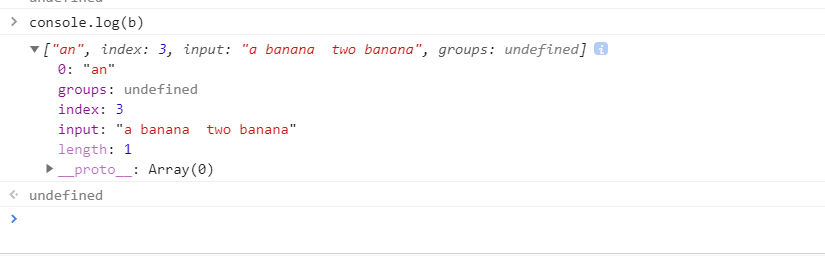
由上图可以看出match()方法返回的是一个类数组结构的对象,有length属性,用下标表示值,那么
const reg = /an/g const str = 'a banana two banana' const b = str.match(reg) console.log(b) // 得到一个数组 ['an', 'an', 'an', 'an']
String.prototype.search() 用途: 检索字符串中指定的子字符串,或检索与正则表达式相匹配的子字符串。如果没有找到任何匹配的子串,则返回 -1。
实际上字符串的indexOf() 方法也能够返回相同的值,只是search()方法支持使用正则表达式作为参数,而indexOf方法必须使用字符串
const string = 'abcdefghijk' const reg = /DEF/i const str = 'cde' console.log(string.search(str)) // 2 console.log(string.search(reg)) // 3
String.prototype.replace() 用途: 在字符串中用一些字符替换另一些字符,或替换一个与正则表达式匹配的子串。
const string='abcdefgabcdefgabcdefg' const reg = /abc/g string.replace(reg, 'ABC') // "ABCdefgABCdefgABCdefg"
2、字符串中的substr() 和 substring()
String.prototype.substr() 用途: 可在字符串中抽取从 开始 下标开始的指定数目的字符
const string = 'abcdefg' string.substr(1, 5) // 'bcdef'
String.prototype.substring() 用途:方法用于提取字符串中介于两个指定下标之间的字符。返回的子串包括 开始 处的字符,但不包括 结束 处的字符
需要注意的是两个参数都必须大于0 ,如果省略第二个参数,则一直截取到字符串的最后一位
const string = 'abcdefghijk' string.substring(1,5) // 'bcde'
3、字符串的slice() 和 split()
String.prototype.slice() 用途:slice(start, end) 方法可提取字符串的某个部分,并以新的字符串返回被提取的部分。与substr()方法不同的是,slice方法,允许参数值为负数,如果是负数,则该参数规定的是从字符串的尾部开始算起的位置。也就是说,-1 指字符串的最后一个字符,-2 指倒数第二个字符,以此类推。
const string = 'abcdefghijklmnopq' string.slice( 1, 2) // 'b' string.slice( 1, 5) // 'bcde' string.slice( -5, -1) // 'mnop'
String.prototype.split() 用途:用于把一个字符串分割成字符串数组。split支持两个参数,分别是分隔符和长度值,用来对生成的数组做限制
const string = 'How are you doing today?' string.split(' ') // ['How', 'are', 'you', 'doing', 'today'] string.split(' ', 3) // ['How', 'are', 'you'] string.split('o') // ["H", "w are y", "u d", "ing t", "day?"]
4、数组操作中的find 、 indexOf、includes
Array.prototype.find() 用途:用于查找通过测试(函数内判断)的数组的第一个元素的值。
- 当数组中的元素在测试条件时返回 true 时, find() 返回符合条件的元素,之后的值不会再调用执行函数。
- 如果没有符合条件的元素返回 undefined
var ages = [3, 10, 18, 20]; function checkAdult(age) { return age >= 18; } ages.find(checkAdult); // 18
Array.prototype.indexOf() 用途:可返回数组中某个指定的元素位置。如果没有则返回-1
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] array.indexOf(3) // 2 array.indexOf(6) // -1
Array.prototype.includes() 用途: 判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,如果是返回 true,否则false。
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] array.includes(1) // true array.includes(6) // false
5、数组操作中的slice() 和 splice()
Array.prototype.slice() 用途: 方法可从已有的数组中返回选定的元素。可提取数组的某个部分,并以新的数组返回被提取的部分。
const array = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] array.slice() // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] array.slice(0,1) // [1] array.slice(0) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] array.slice(-5, -1) // [4,5,6,7]
Array.prototype.splice() 用途:splice() 方法用于添加或删除数组中的元素。注意:这种方法会改变原始数组。
语法: array.splice(index,howmany,item1,.....,itemX)
index: 必须,从哪个位置开始插入或者删除元素
howmany: 可选,可以是0,如果没有,则删除所有的元素
item1...itemX: 可选,删除后要添加的元素
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] array.splice(0,0, 'a') // [] console.log(array) // ['a', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] array.splice(0, 1) // ['a'] console.log(array) // [1,2,3,4,5] array.splice(3, 3, 'abcd') // [4, 5] console.log(array) // [1,2,3,'abcd']
6、数组操作中的some、every、filter
Array.prototype.some 用途:
方法用于检测数组中的元素是否满足指定条件(函数提供)。
some() 方法会依次执行数组的每个元素:
- 如果有一个元素满足条件,则表达式返回true , 剩余的元素不会再执行检测。
- 如果没有满足条件的元素,则返回false
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const big = function(x) { return x > 4 } array.some(big) // true const bbig = function(x) { return x > 6 } array.some(bbig) // false
Array.prototype.every 用途:用来检验数组中的每一个元素是否都符合筛选的函数
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const big = function(x) { return x > 0 } array.every(big) // true const bbig = function(x) { return x > 3 } array.every(bbig) // false
Array.prototype.filter() 用途:
filter() 方法创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素。
注意: filter() 不会对空数组进行检测。
注意: filter() 不会改变原始数组。
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const big = function(x) { return x > 3 } array.filter(big) // [4,5]
7、数组操作中的map、forEach、reduce
Array.prototype.map() 用途:
map() 方法返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值。map() 方法按照原始数组元素顺序依次处理元素。
注意: map() 不会对空数组进行检测。
注意: map() 不会改变原始数组。
注意map的参数有两个 分别是function(currentValue, index , arr) {} , 还有thisValue,对象作为该执行回调时使用,传递给函数,用作 "this" 的值。
如果省略了 thisValue,或者传入 null、undefined,那么回调函数的 this 为全局对象。所以执行array.map(parseInt)时,由于parseIn需要两个参数,一个是数字或字符串,另一个是需要转换的进制数,那么就变成了parseInt(1, 0, arr), parseInt(2, 1, arr), parseInt(3, 2, arr), parseInt(4, 3, arr), parseInt(5, 4, arr), 由于parseInt只有两个参数,那么会忽略arr, 只有parseInt(1, 0)返回二进制的的1, parseInt(2, 1) 1第二个参数不能为1,返回NaN, parseInt(3, 2) 返回 2进制的3 ,2进制没有3,那么返回NaN,其他同理
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const cub = function(x) { return x*x } array.map(cub) // [1, 4, 9 ,16, 25] array.map(parseInt) // [1, NaN ,NaN, NaN, NaN]
Array.prototype.forEach() 用途: forEach() 方法用于调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数。注意: forEach() 对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
注意:该方法没有返回值,除非在传入的函数中改变原数组,否则不改变原数组
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4 ,5] const cub = function(item, index, arr) { arr[index] = item * item } array.forEach(cub) console.log(array) // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Array.prototype.reduce() 用途:reduce() 方法接收一个函数作为累进器,数组中的每个值(从左到右)开始缩减,最终计算为一个值。可以作为一个高阶函数,用于函数的 compose。语法: array.reduce(function(total, currentValue, currentIndex, arr), initialValue)
- total 必需。初始值, 或者计算结束后的返回值。
- currentValue 必需。当前元素。
- currentIndex 可选。当前元素的索引。
- arr 可选。当前元素所属的数组对象。
- initialValue: 可选。传递给函数的初始值。
// 数组求和 const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] const sum = function(x, y) { return x + y } array.reduce(sum, 0) // 15
reduce方法的高级应用,统计数组中元素出现的次数,假设所有元素都不是null、''和undefined
const array = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' , 'd', 'c', 'b', 'a'] array.reduce(function(total, currentValue, index) { if(total[currentValue]) { total[currentValue] += 1 } else { total[currentValue] = 1 } return total }, {}) // {a: 2, b: 2, c: 2, d: 2, e: 1}