我的github iSAM2016
目录
中途有一段时间去隔壁家的php玩了一遭,回头看来,vuex、vue-router有了改变,一开始就对vue-route的细节不是很了解,今天总结一下。
官网的例子:
自己的一句话:
-
定义路由组件(汽车)
const Foo = { template: '
foo' }
const Bar = { template: 'bar' -
定义路由(公路或导航)
cost ruter = {
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
} -
创建实例(红路灯)
cosnt app = new Vue({
router}).$mount('#app')
动态的路由匹配
一个页面是经常重复使用的,传递一个参数就可以了,比如传递一个ID号baidu.com?userId=123,这样
就需要一个动态的路由来解决。
cost ruter = {
{ path: '/user:12', component: user }
}当一个路由使用是后面有动态的参数,会映射到this.$router.param 中,这是函数体内调用路由的方法
响应路由参数的变化
因为没有仔细看官网的实例,这点没有看待,我遇到一次坑。这次教训并不是粗心,是因为没有仔细看文档的好习惯,这个不好的习惯必须的改。就像数学老师说的回归到基本理论
这也是一个常见的问题,我问需要监听hash值的改变,来查询参数如:
- book/search?cat=1
- book/search?cat=2
可是只有参数发生了改变,vue-router 认为组件式可以重用的,参数变化是不能引起从新向服务器获取数据
const user = {
wacth: {
'$route' (to, from) {
// 对路由变化作出响应...
}
}
}嵌套路由
像这样的的嵌套 /user/foo/profile
<div id="root">
<router-view> </router-view>
</div><router-view>是最顶层的出口,渲染最高级路由匹配到的组件。同样地,一个被渲染
组件同样可以包含自己的嵌套
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{ path: '/user/:id', component: User,
children: [
// UserHome will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id is matched
{ path: '', component: UserHome },
// UserProfile will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id/profile is matched
{ path: 'profile', component: UserProfile },
// UserPosts will be rendered inside User's <router-view>
// when /user/:id/posts is matched
{ path: 'posts', component: UserPosts }
]
}
]
})函数式导航
注意 this.$route 和 this.router在使用上是有区别的
this.$router.push()
调用的方法
// 字符串
this.$router.push('home')
// 对象
this.$router.push({ path: 'home' })
// 命名的路由
this.$router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: 123 }})
// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=private
this.$router.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})
this.$router.go(n)
意思是在 history 记录中向前或者后退多少步
路由的命名
可以为路由设置,别名方便使用。如设置name, isshow
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/user/:userId',
name: 'user',
isShow: false
component: User
}
]
})路由的命名:示例
切换路由的时候可以修改页面的标题
router.afterEach(transition => {
document.title = transition.name
})导航钩子
导航钩子
全局钩子
const router = new VueRouter({ ... })
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// ...
})主要用来拦截导航,让他完成跳转或取消。
参数:
to :Route: 标识即将进入的目标路由对象
from: Route 当前导航正要离开的路由
next: function 调用该方法来resolve 钩子,它的参数:
- next(): 进行管道中的下一个钩子
- next(false): 中断当前的导航
- next('/') 或者 next({ path: '/' }): 跳转到一个不同的地址。当前的导航被中断,然后进行一个新的导航。
实例:检测用户登录
全局的钩子主要用来是,判断用户是否登录
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
//页面滚动到顶部
window.scroll(0, 0);
//用户没有登录了,并且还想访问别的页面,强制跳转login页
if (!auth.login() && to.path !== '/login') {
next('login');
} else {
//用户已经登录了,不在让用户访问login页
if (auth.login() && to.path === '/login') {
next({
path: '/demo/user/list'
});
} else {
next();
}
}
})某个路由独享的钩子(VIP组件)
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeEach: (to, from, next) => {
}
]
})路由元信息
较难理解
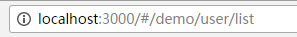
我们称呼routers 配置中的每个路由对象为路由记录。路由记录可以是嵌套的。比如http://localhost:3000/#/demo/user/list
这个地址中可以说明路由记录有三个,分别是:
- /demo
- /demo/use
- /demo/use/list
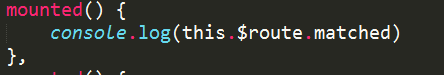
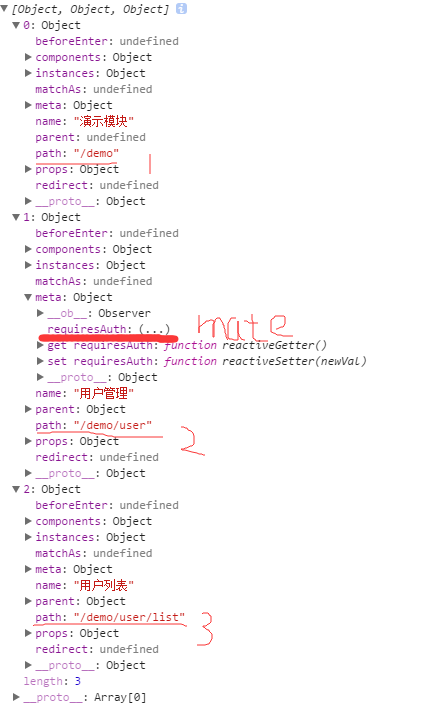
一个路由匹配到的多有路由记录暴露在$route对象当中的$route.matched 数组当中,我们需要遍历 $route.matched 来检查路由记录中的 meta 字段。
示例
路由对象信息
对象出现的地方,注意是route 没有r结尾
| route Object出现的地方 |
|---|
| router.match(location) |
| this.$route |
| 全局钩子 |
对象的属性就不书写了见路由信息对象的属性
Router 实例
Router注意是 有r结尾
Router 实例属性
$router.options
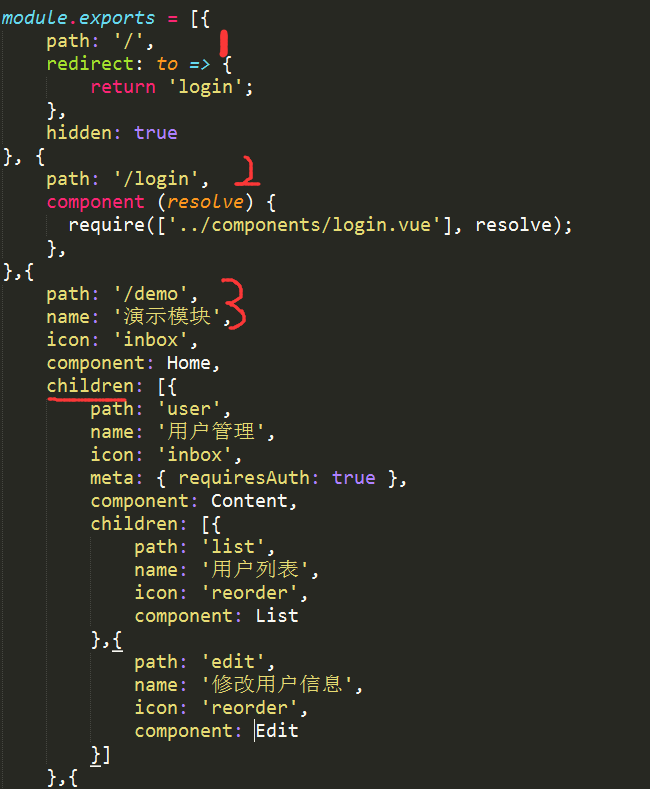
在$router 中有个鬼是$router.options 官网没有找到,说明。
这个属性包含了路由的树形结构,可以借助这个来实现menu层级的划分


上机作业5.14
android 计算器
安卓第四周作业
课后作业
5.28上机作业
5.22作业
5.21 作业
5.20作业
上机作业5.14