我的以Netty Socket编程的代码为例,
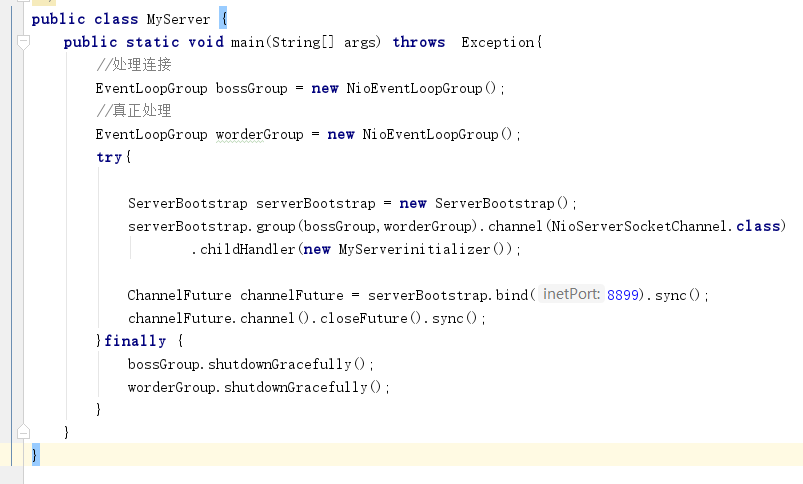
1、EventLoopGroup
进入EventLoopGroup,这是一个特殊的EventExecutorGroup,在事件循环中,在selection选择的时候,可以注册Channel。(Channel可以理解为跟客户端的连接)
/**
* Special {@link EventExecutorGroup} which allows registering {@link Channel}s that get
* processed for later selection during the event loop.
*
*/
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* Return the next {@link EventLoop} to use
*/
@Override
EventLoop next();
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}. The returned {@link ChannelFuture}
* will get notified once the registration was complete.
*/
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop} using a {@link ChannelFuture}. The passed
* {@link ChannelFuture} will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
*/
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}. The passed {@link ChannelFuture}
* will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
*
* @deprecated Use {@link #register(ChannelPromise)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}
2、EventExecutorGroup
/**
* The {@link EventExecutorGroup} is responsible for providing the {@link EventExecutor}'s to use
* via its {@link #next()} method. Besides this, it is also responsible for handling their
* life-cycle and allows shutting them down in a global fashion.
*
*/
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable<EventExecutor> {
/**
* Returns {@code true} if and only if all {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup}
* are being {@linkplain #shutdownGracefully() shut down gracefully} or was {@linkplain #isShutdown() shut down}.
*/
boolean isShuttingDown();
/**
* Shortcut method for {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} with sensible default values.
*
* @return the {@link #terminationFuture()}
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully();
/**
* Signals this executor that the caller wants the executor to be shut down. Once this method is called,
* {@link #isShuttingDown()} starts to return {@code true}, and the executor prepares to shut itself down.
* Unlike {@link #shutdown()}, graceful shutdown ensures that no tasks are submitted for <i>'the quiet period'</i>
* (usually a couple seconds) before it shuts itself down. If a task is submitted during the quiet period,
* it is guaranteed to be accepted and the quiet period will start over.
*
* @param quietPeriod the quiet period as described in the documentation
* @param timeout the maximum amount of time to wait until the executor is {@linkplain #shutdown()}
* regardless if a task was submitted during the quiet period
* @param unit the unit of {@code quietPeriod} and {@code timeout}
*
* @return the {@link #terminationFuture()}
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Returns the {@link Future} which is notified when all {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this
* {@link EventExecutorGroup} have been terminated.
*/
Future<?> terminationFuture();
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
void shutdown();
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
/**
* Returns one of the {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup}.
*/
EventExecutor next();
@Override
Iterator<EventExecutor> iterator();
@Override
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit);
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
}
3、NioEventLoopGroup ,继承自MultithreadEventLoopGroup
/**
* {@link MultithreadEventLoopGroup} implementations which is used for NIO {@link Selector} based {@link Channel}s.
*/
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
/**
* Create a new instance using the default number of threads, the default {@link ThreadFactory} and
* the {@link SelectorProvider} which is returned by {@link SelectorProvider#provider()}.
*/
public NioEventLoopGroup() {
this(0);
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the specified number of threads, {@link ThreadFactory} and the
* {@link SelectorProvider} which is returned by {@link SelectorProvider#provider()}.
*/
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads) {
this(nThreads, (Executor) null);
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the specified number of threads, the given {@link ThreadFactory} and the
* {@link SelectorProvider} which is returned by {@link SelectorProvider#provider()}.
*/
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) {
this(nThreads, executor, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
/**
* Create a new instance using the specified number of threads, the given {@link ThreadFactory} and the given
* {@link SelectorProvider}.
*/
public NioEventLoopGroup(
int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory, selectorProvider, DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final SelectorProvider selectorProvider, final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
super(nThreads, threadFactory, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(
int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider) {
this(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
super(nThreads, executor, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory) {
super(nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject());
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory,
final RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
super(nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler);
}
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory,
final RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
final EventLoopTaskQueueFactory taskQueueFactory) {
super(nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory,
rejectedExecutionHandler, taskQueueFactory);
}
/**
* Sets the percentage of the desired amount of time spent for I/O in the child event loops. The default value is
* {@code 50}, which means the event loop will try to spend the same amount of time for I/O as for non-I/O tasks.
*/
public void setIoRatio(int ioRatio) {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).setIoRatio(ioRatio);
}
}
/**
* Replaces the current {@link Selector}s of the child event loops with newly created {@link Selector}s to work
* around the infamous epoll 100% CPU bug.
*/
public void rebuildSelectors() {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).rebuildSelector();
}
}
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory = args.length == 4 ? (EventLoopTaskQueueFactory) args[3] : null;
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2], queueFactory);
}
}
进入构造函数NioEventLoopGroup函数,
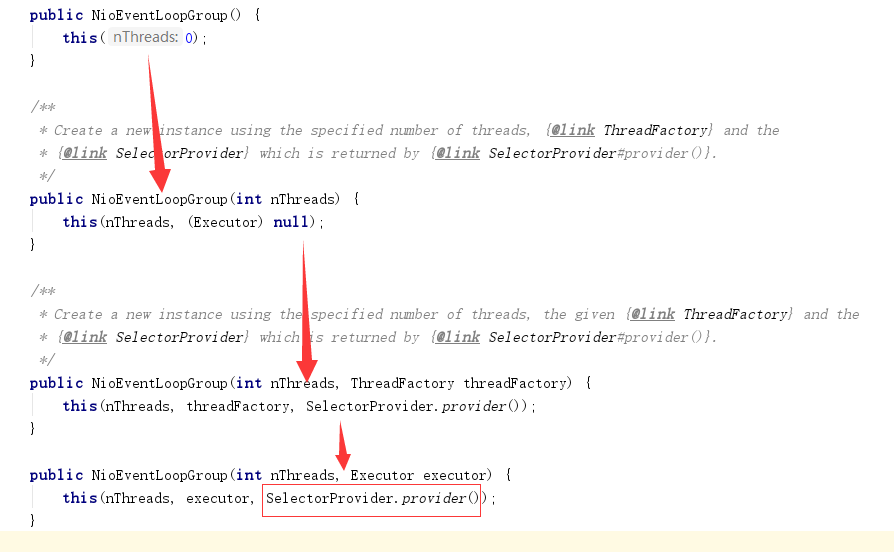
然后进入下面这个构造函数,调用了父类的方法

进入父类的方法 MultithreadEventLoopGroup,继承自 MultithreadEventExecutorGroup
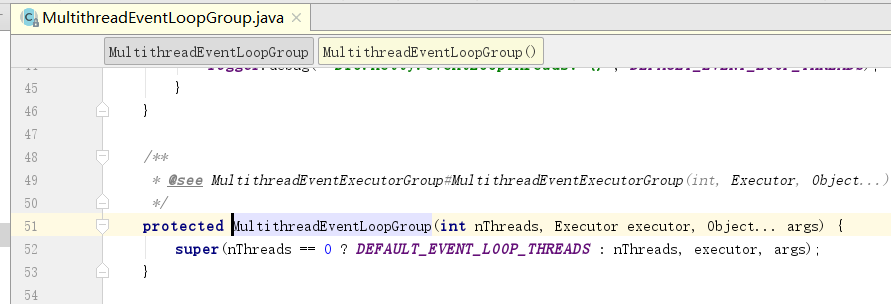
如果nThrads==0,则使用 DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS
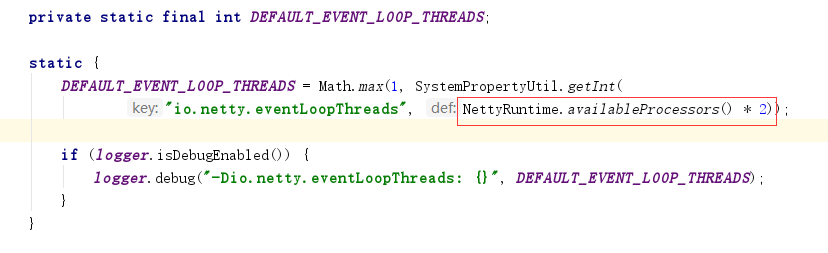
如果io.netty.eventLoopThreads没有定义,则使用NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2 作为默认线程数
进入父类MultithreadEventExecutorGroup构造函数
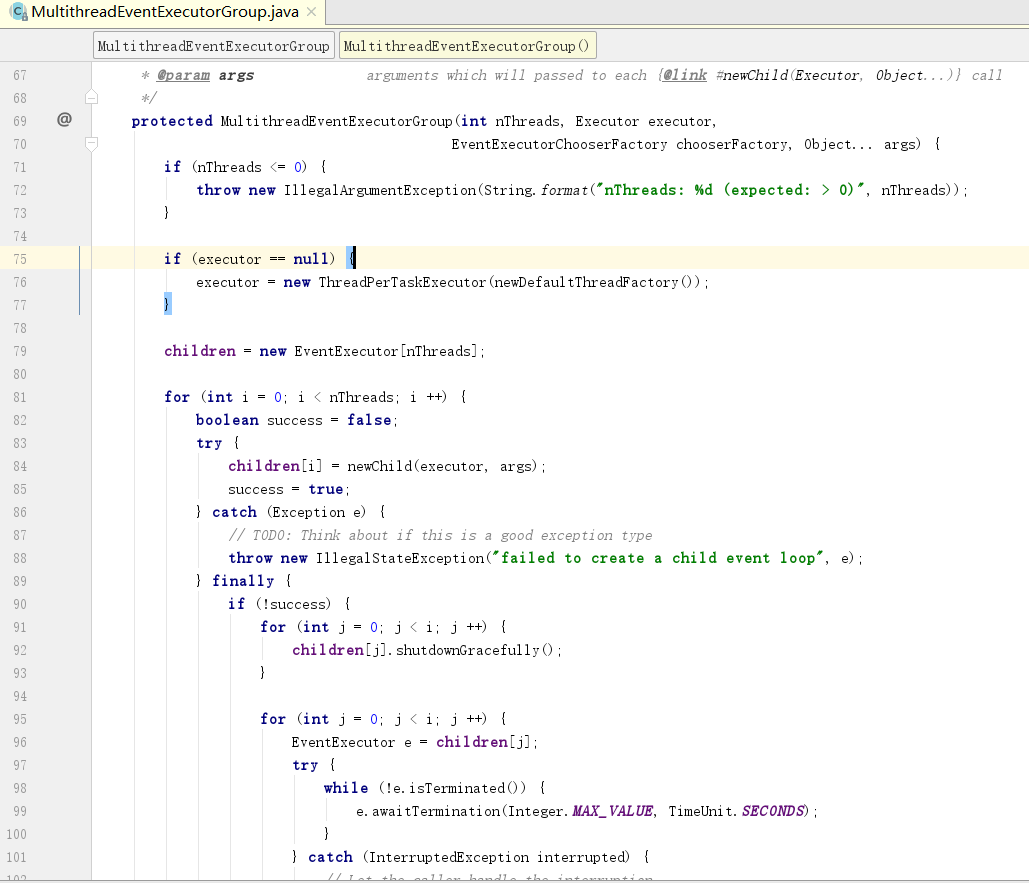
newChild是一个抽象方法

进入NioEventLoopGroup中newChild的实现
