7. Composition(组合)
- Composition: construct new object with existing objects.
- It is the relationship of "has-a".
- Ways of inclusion:
- Fully
- By reference
- 示例:
class Person { ... };
// 货币
class Currency { ... };
// 储蓄户口
class SavingsAccount {
pubilc:
SavingsAccount (const char* name, const char* address, int cents);
~SavingsAccount();
void print();
private:
// Fully inclusion
Person m_saver;
Currency m_balance;
};
// Person 和 Currency 初始化
SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount (const char* name, const char* address, int cents) : m_saver(name, address), m_balance(0, cents) {}
void SavingsAccount::print() {
m_saver.print();
m_balance.print();
}
8. Inheritance(继承)
- Inheritance: is to take the existing class, clone it, and then make additions and modifications to the clone.
- "Is-a"

- 示例1:访问父类私有变量
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A():i(0) {
cout << "A::A()" << endl;
}
~A() {
cout << "A::~A()" << endl;
}
void print() {
cout << "A::print() ---》 " << i << endl;
}
void set(int ii) {
i = ii;
}
private:
int i;
};
// 继承, 其中 public 必需
class B : public A {
public:
void f() {
set(20);
// 直接访问 i,是会报错
// 父类私有的成员变量,子类不能直接访问
i = 30;
print();
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.set(10);
b.print();
b.f();
return 0;
}
- 示例2:访问父类 protected 函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A():i(0) {
cout << "A::A()" << endl;
}
~A() {
cout << "A::~A()" << endl;
}
void print() {
cout << "A::print() ---》 " << i << endl;
}
protected:
void set(int ii) {
i = ii;
}
private:
int i;
};
// 继承, 其中 public 必需
class B : public A {
public:
void f() {
set(20);
// 直接访问 i,是会报错
// 父类私有的成员变量,子类不能直接访问
// i = 30;
print();
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
// set 调整为 protected
// 子类可以使用,但是,main 函数中不能调用
b.set(10);
b.print();
b.f();
return 0;
}
8.1 子类和父类关系
- 示例1:子类和父类构造顺序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A {
public:
A(int ii):i(ii) {
cout << "A::A()" << endl;
}
~A() {
cout << "A::~A()" << endl;
}
void print() {
cout << "A::print()" << i << endl;
}
void set(int ii) {
i = ii;
}
private:
int i;
};
class B : public A {
public:
B() : A(15) {
cout << "B::B()" << endl;
}
~B() {
cout << "B::~B()" << endl;
}
void f() {
set(20);
print();
}
};
int main()
{
// 父类先初始化,然后才会初始化子类
B b;
b.print();
b.f();
return 0;
}
-
父类和子类构造和析构顺序:

-
示例:子类和父类关系
#include <iostream>
class Employee {
public:
Employee(const std::string& name, const std::string& ssn);
const std::string& get_name() const;
void print(std::ostream& out) const;
void print(std::ostream& out, const std::string& msg) const;
protected:
std::string m_name;
std::string m_ssn;
};
Employee::Employee (const std::string& name, const std::string& ssn) :m_name(name), m_ssn(ssn)
{
// initializer list sets up the values!
}
inline const std::string& Employee::get_name() const
{
return m_name;
}
inline void Employee::print(std::ostream& out) const
{
out << m_name << std::endl;
out << m_ssn << std::endl;
}
inline void Employee::print(std::ostream& out, const std::string& msg) const
{
out << msg << std::endl;
print(out);
}
// Manager 类
class Manager : public Employee {
public:
Manager(const std::string& name, const std::string& ssn, const std::string& title);
const std::string title_name() const;
const std::string& get_title() const;
void print(std::ostream& out) const;
private:
std::string m_title;
};
// 子类的构造,直接调用父类的构造函数
// 父类的构造过程,也必须放在 initializer list 里面
Manager::Manager(const std::string& name, const std::string& ssn, const std::string& title = "") :Employee(name, ssn), m_title(title) {
}
inline void Manager::print(std::ostream& out) const {
Employee::print(out); // call the base class print
out << m_title << std::endl;
}
inline const std::string& Manager::get_title() const
{
return m_title;
}
inline const std::string Manager::title_name() const
{
return std::string(m_title + ": " + m_name);
}
int main() {
Employee bob("Bob Jones", "555-44-0000");
Manager bill("Bill Smith", "666-55-1234", "Important Person");
std::string name = bill.get_name();
std::cout << bill.title_name() << "\n" << std::endl;
bill.print(std::cout);
bob.print(std::cout);
bob.print(std::cout, "Employee:");
// Error:
// Manager::print(std::ostream& out) 函数
// 如果父类当中有 overload 函数,子类中出现同名函数时,子类仅保留子类自己的函数
// bill.print(std::cout, "Manager: ");
// 修正:
bill.Employee::print(std::cout, "Manager: ");
}
8.2 Function overloading
- Same functions with different arguments list.
// 示例
void print(char *str, int width); // #1
void print(double d, int width); // #2
void print(long l, int width); // #3
void print(int i, int width); // #4
void print(char *str); // #5
8.2.1 Default arguments
- A default argument is a value given in the declaration that the compiler automatically inserts if you don't provide a value in the function call.
- To define a function with an argument list, defaults must be added from right to left.
8.3 内联函数(inline)
-
the processing time required by a device prior to the execution of a command.
- Push parameters
- Push return address
- Prepare return values
- Pop all pushed
-
An inline function is expanded in place, like a preprocessor macro, so the overhead of the function call is eliminated.
-
示例:
-
a.h
inline void f(int i, int j);
a.cpp
#include "a.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline void f(int i, int j) {
cout << i << " " << j << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "a.h"
int main()
{
f(10, 10);
return 0;
}
- 编译异常:
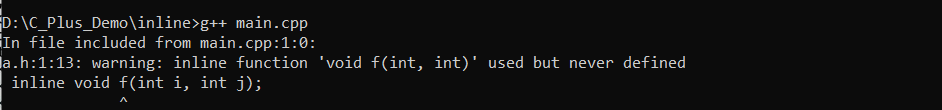
8.3.1 修正
a.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline void f(int i, int j) {
cout << i << " " << j << endl;
}
main.cpp
#include "a.h"
int main()
{
f(10, 10);
return 0;
}
8.3.2 Inline functions in header file
- So you can put inline functions' bodies in header file. Then #include it where the function is needed.
- Never be afraid of multi-definition of inline functions, since they have no body at all.
- Definitions of inline functions are just declarations.
8.3.3 内联函数优缺点
- Body of the called function is to be inserted into the caller.
- This may expand the code size.
- but deduces the overhead of calling time.
- So it gains speed at the expenses of space.
- In most cases, it is worth.
- It is much better than macro in C. It checks the types of the parameters.
- Any function you define inside a class declaration is automatically an inline.
参考资料: