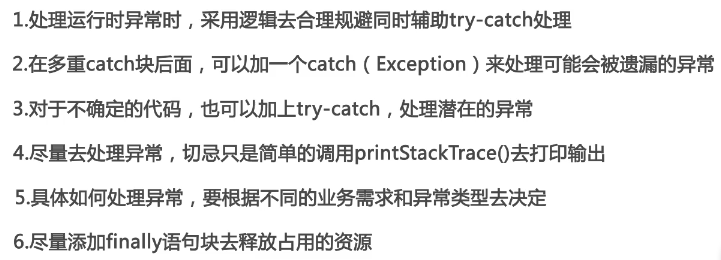
1、异常:异常就是意外。java当中将所有异常、错误都抽象同一个类,这个最上层父类Throwable。Throwable是异常和错误父类:java中异常就是程序中所有意外的结果,java中错误就是程序或者jdk本身就存在问题(解决不了)。
2、Error:java中错误的父类
Exception:异常的父类
Exception和Error都是Throwable子类
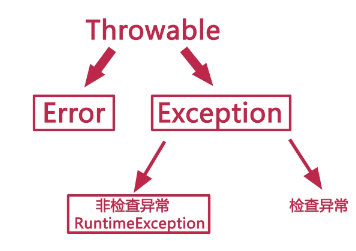
3、java是很健壮的语言,Error较少
4、Exception:RuntimeException和一般性异常
RuntimeException:不需要检查异常,运行的时候才出现的异常。eg:NullPointerException。运行时异常,全部都是RuntimeException子类
一般性异常:没有继承RuntimeException,需要进行检查,必须处理(如果出现异常,必须处理)
5、处理异常(一)
1. try…catch
格式:try{
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(Exception1 e){
处理方案:出现异常以后,程序该如何执行,没说一定要解决异常
}catch(Exception2 e){
处理方案2
}…
try出现哪种catch参数中异常,程序就执行那段catch语句
异常一旦出现,则终止try当中的代码
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ String str="liu"; // String str=null; System.out.println(str.length());//结果:3 int i=100/0; }catch(NullPointerException e){ //如果try当中代码,出现NullPointerException的异常,catch会根据参数,截获该异常,程序会执行catch中的代码 //如果没有出现异常,或者出现的异常不是catch中参数异常,不执行该catch语句 System.out.println("字符串str不能为null"); }catch(ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("除数不能为0"); } } }
系统打印异常的堆栈信息:e.printStackTrace()
public class Test1 { //如何在catch中打印异常堆栈信息 public static void main(String[] args) { try{ int i=100/0; }catch(ArithmeticException e){ //e.printStackTrace():系统来打印该异常的信息 e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2. try…catch…finally
finally:最终的,最后的,不管try当中是否有异常出现,都会去执行finally中的内容
try{
可能出现异常的代码
}catch(Exception1 e){
处理异常1
}catch(Exception2 e){
处理异常2
}…
finally{
不管try当中是否有异常,都必须要执行的代码
}
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ int i=10/0; String str=null; System.out.println(str.charAt(10)); }catch(NullPointerException e){ e.printStackTrace();; }catch(ArithmeticException e){ e.printStackTrace();; }finally{ System.out.println("不管发生什么,生活都得继续。。。"); } } }
首先,执行try当中代码,如果try中出现异常,try当中异常以后代码都不执行,跳转catch与之对应的处理方案,最后执行finally中语句
6) 自定义异常:程序员自己根据项目的需要,编写自己的异常类
eg:登录模块:需要输入用户名和密码,正确正常登录成功,如果输入错误,可以用一个自己定义的异常表示,登录失败。
1. 继承Exception
2. 重写Exception中4个构造方法
import java.util.Scanner; public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws NameOrPwdErrorException{ //从控制台输入用户名和密码,用户名是liu,密码是123 //如果用户输入正确,正常登录,如果输入错误执行异常 Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("用户名:"); String name=scanner.nextLine(); System.out.println("密码:"); String pwd=scanner.nextLine(); if("liu".equals(name) && "123".equals(pwd)){ System.out.println("欢迎您登录!"); }else{ throw new NameOrPwdErrorException("用户名或密码错误!"); } } } class NameOrPwdErrorException extends Exception{ //右击,source-->Generate Constructors from Superclass... public NameOrPwdErrorException() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public NameOrPwdErrorException(String arg0, Throwable arg1) { super(arg0, arg1); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public NameOrPwdErrorException(String arg0) { super(arg0); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public NameOrPwdErrorException(Throwable arg0) { super(arg0); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } }
7) 处理异常(二)
抛出异常对象
throws:声明可能抛出的异常
格式:返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) throws 可能抛出异常类
{
throw new 异常对象
}
可以抛出多个异常对象,但是必须在throws后面声明(确定该方法会抛出每个异常的类)