摘要:在实际开发过程中,免不了涉及到混合编程,比如,对于python这种脚本语言,性能还是有限的,在一些对性能要求高的情景下面,还是需要使用c/c++来完成。
本文分享自华为云社区《混合编程:如何用pybind11调用C++》,作者:SNHer。
在实际开发过程中,免不了涉及到混合编程,比如,对于python这种脚本语言,性能还是有限的,在一些对性能要求高的情景下面,还是需要使用c/c++来完成。那怎样做呢?我们能使用pybind11作为桥梁,pybind11的优点是对C++ 11支持很好,API比较简单,现在我们就简单记下Pybind11的入门操作。
1.pybind11简介与环境安装
Pybind11 是一个轻量级只包含头文件的库,用于 Python 和 C++ 之间接口转换,可以为现有的 C++ 代码创建 Python 接口绑定。Pybind11 通过 C++ 编译时的自省来推断类型信息,来最大程度地减少传统拓展 Python 模块时繁杂的样板代码, 已经实现了 STL 数据结构、智能指针、类、函数重载、实例方法等到Python的转换,其中函数可以接收和返回自定义数据类型的值、指针或引用。
直接使用pip安装 pip3 install pybind11 由于pybind11依赖于pytest,所以在安装前需要先把pytest给安装上 pip3 install pytest
2. 求和函数
首先,我们编写一个C++源文件,命名为example.cpp。
// pybind11 头文件和命名空间
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>
namespace py = pybind11;
int add(int i, int j)
{
return i + j;
}
PYBIND11_MODULE(example, m)
{
// 可选,说明这个模块是做什么的
m.doc() = "pybind11 example plugin";
//def( "给python调用方法名", &实际操作的函数, "函数功能说明" ). 其中函数功能说明为可选
m.def("add", &add, "A function which adds two numbers", py::arg("i")=1, py::arg("j")=2);
}
PYBIND11_MODULE()宏函数将会创建一个函数,在由Python发起import语句时该函数将会被调用。模块名字“example”,由宏的第一个参数指定(千万不能出现引号)。第二个参数"m",定义了一个py::module的变量。函数py::module::def()生成绑定代码,将add()函数暴露给Python。
我们使用CMake进行编译。首先写一个CMakeLists.txt。
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8.12) project(example) add_subdirectory(pybind11) pybind11_add_module(example example.cpp)
就是CMakeList.txt和example.cpp放在一个目录下面。
cmake . make
会生成example.cpython-36m-x86_64-linux-gnu.so文件。
这个文件就是python可以调用的文件。还是在相同目录下运行python,进入python命令行
import example example.add(3, 4) [out]: 7
3. STL和python内建数据类型的对应关系
在使用python编程时,常使用内建容器作为函数的参数和返回值,python语言的这种特性使我们的程序变得非常灵活和易于理解。那么在使用pybind11封装C++实现的函数的时候,如何保留这一特性呢?本文介绍pybind11实现list和dict作为参数及返回值的方法。
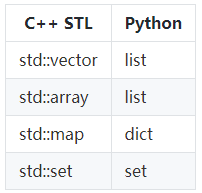
返回vector
//文件名:func.cpp
#include "func.h"
vector<long> list_square(vector<long> &in_list, vector<long>& out_list){
vector<long>::iterator iter;
for(iter = in_list.begin(); iter != in_list.end(); iter++){
out_list.push_back(*iter * *iter);
}
return out_list;
}
map<string, long> dict_square(map<string, long>& in_dict, map<string, long>& out_dict){
map<string, long>::iterator iter;
iter = in_dict.begin();
while(iter != in_dict.end()){
out_dict.insert({iter->first, iter->second * iter->second});
iter++;
}
return out_dict;
}
- 写pybind11封装函数
//文件名:func_wrapper.cpp
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>
#include<pybind11/stl.h>
#include "func.h"
PYBIND11_MODULE(square, m){
m.doc() = "Square the members of the container";
m.def("list_square", &list_square);
m.def("dict_square", &dict_square);
}
返回struct
#include <pybind11/pybind11.h>
#include <iostream>
struct Foo {
std::string a;
};
void show(Foo f) {
std::cout << f.a << std::endl;
}
namespace py = pybind11;
PYBIND11_PLUGIN(example) {
py::module m("example", "pybind11 example plugin");
m.def("show", &show, "Prints a");
py::class_<Foo>(m, "Foo")
.def_readwrite("a", &Foo::a);
return m.ptr();
}
- 写pybind11封装函数
import sys
sys.path.append(".")
import example
b = example.Foo
b.a = "Hello"
example.show(b)
