1 Scope of Document
This document describes SPI F-RAM hardware design
2 Requiremen
2.1 Function Requirement
support spi f-ram fm25l16b in linux
2.2 Performance Requirement
NA
3 Hardware Overview
standard spi interface, four line cs sck mosi miso;
4 Functional Description
4.1 Functional Block Diagram
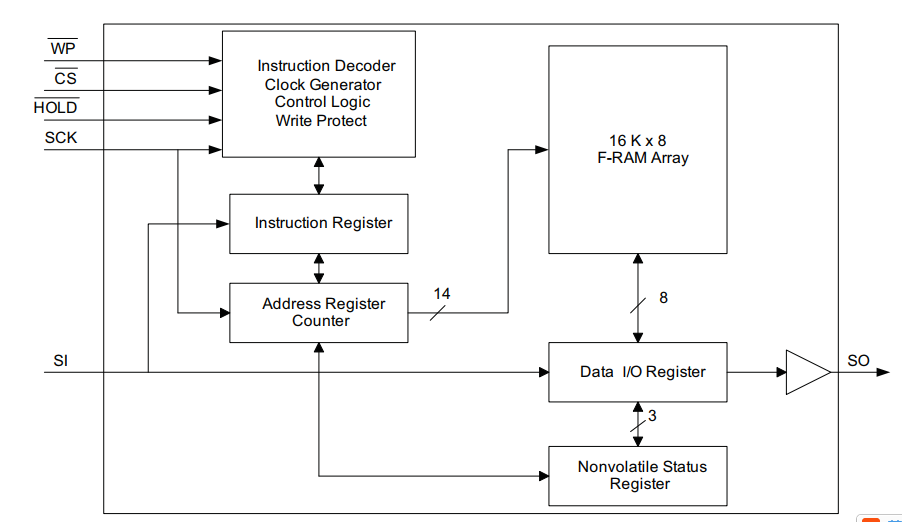
4.2 SPI F-RAM
4.2.1 Overview
advantage:
1) High-endurance 100 trillion (1014) read/writes.
2) Very fast serial peripheral interface
5 Porting
5.1 3.2.0 Kernel porting
Device Drivers --->
[*] Misc devices --->
EEPROM support --->
<*> SPI EEPROMs from most vendors
Register platform source:
static struct spi_eeprom fram = {
.byte_len = SZ_16K / 8,
.name = "fm25l16b",
.page_size = 256,
.flags = EE_ADDR2,
};
static struct spi_board_info am335x_spi0_slave_info[] = {
{
.modalias = "at25",
.platform_data = &fram,
.max_speed_hz = 2 * 1000 * 1000,
.bus_num = 1,
.chip_select = 0,
.irq = -1,
.mode = SPI_MODE_0,
},
};
/* setup spi0 */
static void spi0_init(int evm_id, int profile)
{
setup_pin_mux(spi0_pin_mux);
spi_register_board_info(am335x_spi0_slave_info,
ARRAY_SIZE(am335x_spi0_slave_info));
return;
}
Kernel log:
at25_proble
at25 spi1.0: 2 KByte fm25l16b eeprom, pagesize 256
Device access interface:
/sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/eeprom
5.2 4.14.40 Kernel porting
Add in kernel configure option
Device Drivers --->
[*] Misc devices --->
EEPROM support --->
<*> SPI EEPROMs from most vendors
Change the dts file for support F-RAM
spi0_pins: pinmux_spi0 {
pinctrl-single,pins = <
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x950, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE0) /* spi0_sclk.spi0_sclk */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x95C, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE0) /* spi0_cs0.spi0_cs0 */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x954, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE0) /* spi0_d0.spi0_d0 */
AM33XX_IOPAD(0x958, PIN_INPUT_PULLUP | MUX_MODE0) /* spi0_d1.spi0_d1 */
>;
};
};
&spi0 {
status = "okay";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&spi0_pins>;
fram@0 {
reg = <0x0>;
compatible = "atmel,at25", "cypress,fm25l16b";
spi-max-frequency = <2000000>;
pagesize = <256>;
size = <2048>;
address-width = <16>;
};
};
Kernel log:
[ 1.107399] at25 spi0.0: 2 KByte at25 eeprom, pagesize 256
Device access interface:
/sys/bus/nvmem/devices/spi0.00/nvmem
Note: in kernel 4.14.40 spi eeprom driver was register under nvmem framwork, so the device access interface different from 3.2.0 device interface.
6 Test Method
read/write test code in 3.2.0
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
int ret, fd, i, j;
char read_data[256];
char write_data[256];
char offset;
fd = open ( "/sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/eeprom", O_RDWR );
if ( fd < 0 ) {
perror ( "Open at24c08 fail " );
return -1;
}
for ( i = 0; i < 256; i++ )
write_data[i] = i;
lseek ( fd, 0 , SEEK_SET );
ret = write ( fd, write_data, 256 );
if ( ret < 0 ) {
printf ( "Write error " );
return -1;
}
lseek ( fd, 0 , SEEK_SET );
ret = read ( fd, read_data, 256 );
if ( ret < 0 ) {
printf ( "Read error " );
return -1;
} else if ( ret < 256 ) {
perror ( "Incomplete read " );
printf ( "%d ", ret );
return -1;
}
for ( i = 0; i < 256; i++ ) {
if ( i % 16 == 0 )
printf ( " " );
printf ( " %03d ", read_data[i] );
}
printf ( " " );
}
Using hexdump tool, read spi f-ram data
# hexdump -C /sys/bus/spi/devices/spi1.0/eeprom
00000000 08 74 65 73 74 5f 70 70 70 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.test_ppp.......|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
*
00000800
read/write test methon in 4.14.40
root@IoTP:/sys/bus/nvmem/devices/spi0.00# echo "./test_123" > nvmem
root@IoTP:/sys/bus/nvmem/devices/spi0.00# hexdump -C nvmem
00000000 2e 2f 74 65 73 74 5f 31 32 33 0a 00 00 00 00 00 |./test_123......|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
*
00000800