go test命令,相信大家都不陌生,常见的情况会使用这个命令做单测试、基准测试和http测试。go test还是有很多flag 可以帮助我们做更多的分析,比如测试覆盖率,cpu分析,内存分析,也有很多第三方的库支持test,cpu和内存分析输出结果要配合pprof和go-torch来进行可视化显示,可以看一下之前的这篇帖子 golang 使用pprof和go-torch做性能分析,这篇帖子总结一下go test的一些常用方式和推荐一些很棒的第三方库。
go test文件命名是以_test.go为缀。例如userInfo_test.go。在github上写了一个小的项目,包含常见的测试方法: https://github.com/lpxxn/gotest 。app1里是基本的测试方法。app2里包含了一些第三方的库辅助我们更方便的测试。 大家可以下载来来 go test一下试试
测试函数以Test或者Bench为前缀开始,如:
func TestXXXXXXX(t *testing.T) func BenchXXXXXX(b *testing.B) func TestMain(m *testing.M)
看一下testing.T和testing.B者有组合 common
type T struct { common isParallel bool context *testContext // For running tests and subtests. }
type B struct { common importPath string // import path of the package containing the benchmark context *benchContext N int previousN int // number of iterations in the previous run previousDuration time.Duration // total duration of the previous run benchFunc func(b *B) benchTime time.Duration bytes int64 missingBytes bool // one of the subbenchmarks does not have bytes set. timerOn bool showAllocResult bool result BenchmarkResult parallelism int // RunParallel creates parallelism*GOMAXPROCS goroutines // The initial states of memStats.Mallocs and memStats.TotalAlloc. startAllocs uint64 startBytes uint64 // The net total of this test after being run. netAllocs uint64 netBytes uint64 }
common包含了T和B的所有公共方法,常见的比如Log()日志信息,Error() 错误信息,Fail()致命错误等方法,
TestMain(*testing.M)方法有些特殊,在一个包内只能有一个TestMain方法。这个方法会在测试方法运行前调用,相当于main()方法。我们可以在这个方法内做一些初始化数据操作等。看一下testing.M结构体
// M is a type passed to a TestMain function to run the actual tests. type M struct { deps testDeps tests []InternalTest benchmarks []InternalBenchmark examples []InternalExample timer *time.Timer afterOnce sync.Once numRun int }
专为TestMain准备
先以app1来对基本的test进行解说,app1的项目结构为。

具体的代码大家看一下就好,都是一些特别简单的方法。
测试指定函数
简单的测试方法
func TestNewUserInfo(t *testing.T) { u := NewUserInfo() if len(u.Name) == 0 { t.Error("name is empty") } }
得到新创建的user信息,检查name是否为空,如果为空则错误。
-run 后面的参数是正则,所有匹配这正则的方法都会被运行,比如测试所有包含user(不区分大小写)的测试方法:
go test -v -run="(?i)user"
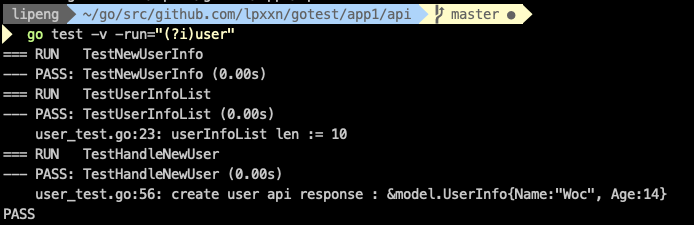
-v 是用于输出所有Log的信息
也可以指写具体的方法名,只要包含这些名称的测试方法就会运行,如果要测试多个方法,名称用"|"分开
go test -v -run=TestGetOrderList go test -v -run="TestGetOrderList|TestNewUserInfo"
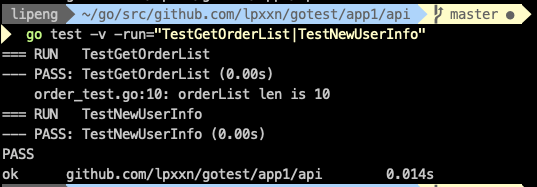
执行的结果不用我多说,运行是否通过,最后还有运行的时长,方法实在在简单了,执行的太快只精确到2位,所以0.00。
测试指定文件
测试指定的_test.go文件,需要注意的是在同一个包下,需要把测试文件和源文件都写出来:
go test -v user_test.go user.go
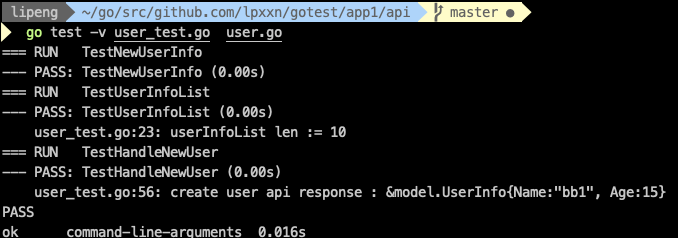
测试文件夹内所有的test文件
直接在某个目录运行go test命令就会运行这个文件夹下所有的_test.go文件内的测试方法。
go test -v

如果文件夹里还包含文件夹,可以添加 "./..."来递归测试。
go test -v ./...

BenchMark 测试
benchMark通过一系列的性能指标来对我们的方法进行测试,比如cpu,内存。循环测试次数据等。
基本的命令是
go test -bench="."
-bench 类似于-run 可以跟正则表达式来控制执行的方法
测试方法
func BenchmarkUserInfoList(b *testing.B) { b.StopTimer() // do something b.StartTimer() for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ { // pretend delay //time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500) userInfoList := UserInfoList() if len(userInfoList) != 10 { b.Error("userInfoList is empty") } } }
返回的结果
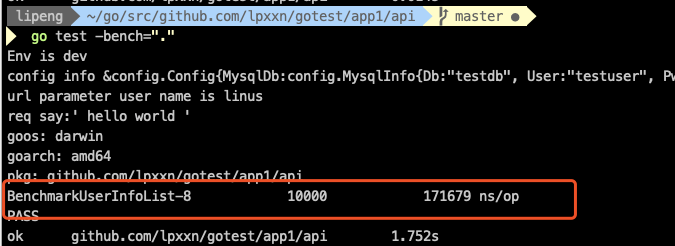
benchmark方法名加当前测试cpu内核的数量,这个可以通过-cpu 来设置数量,10000是执行的次数,就是代码中的b.N 171679 ns/op 每次操作的耗时。
可以通过flag benchtime来控制执行时长
go test -bench="." -cpu=3 -benchtime=5s
-benchmem 用于显示内存的分配情况
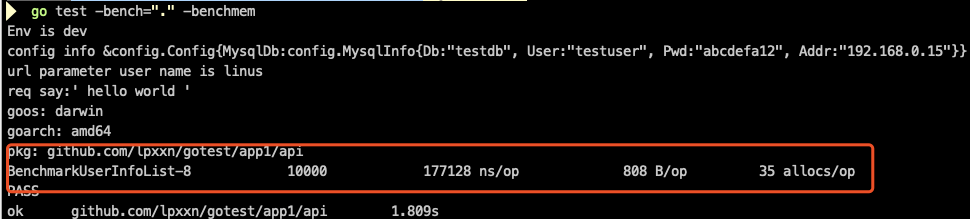
808 B/op 表示每一调用需要808个字节, 35 allocs/op表示每一次调用有35次内存分配
当然还有很多flag 大家可以通过下面的命令查看官方文档
go help testflag
TestMain
一个包下面只能有一个TestMain方法。这个方法就和main()方法差不太多。他会在其他的Test方法之前执行,我们可以利用他做一些初始化数据操作,执行完后释放资源等操作。
例如我在TestMain里把当前的环境变量设置为dev。 然后加载配置,当然都是模拟的。
func TestMain(m *testing.M) { os.Setenv(config.ENV_STR, config.ENV_DEV) config.LoadConfig() fmt.Printf("Env is %s ", os.Getenv(config.ENV_STR)) fmt.Printf("config info %#v ", config.ConfigInfo) // do something... eg: init data // ... os.Exit(m.Run()) }
在执行所有的go test时会先执行TestMain

测试代码覆盖率
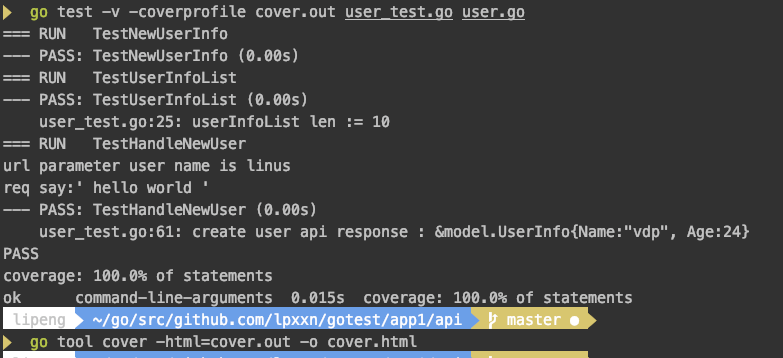
测试覆盖率就是运行我们的测试方法所有跑过的代码占全部代码的比例,比如我们跑一下user_test.go的所有测试方法,然后看一下覆盖率:
两个命令:
go test -v -coverprofile cover.out user_test.go user.go go tool cover -html=cover.out -o cover.html
一个是执行测试,另一个是把输出的文件转换成html
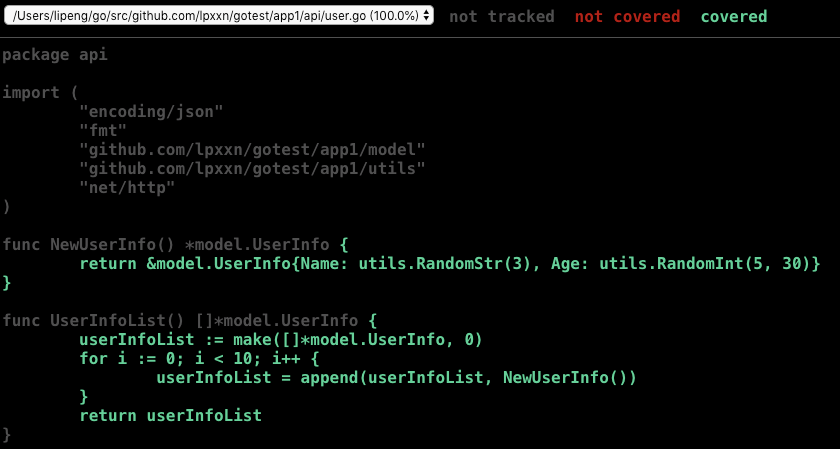
用浏览器打开生成的html,绿颜色表示运行到的代码,红颜色表示没有运行到的代码,我的代码是全部都运行到了。
测试http
先来一个原生的http handler方法
func HandleNewUser(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { name := r.URL.Query().Get("name") fmt.Printf("url parameter user name is %s ", name) say := r.FormValue("say") fmt.Printf("req say:' %s ' ", say) newUser := NewUserInfo() jData, _ := json.Marshal(newUser) w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") w.Write(jData) }
这个方法没有什么逻辑,在url中获取name参数,然后在post的form中获取say参数,再返回一个user的json。
再看一下测试方法
func TestHandleNewUser(t *testing.T) { postBody := url.Values{} postBody.Add("say", "hello world") req := httptest.NewRequest(http.MethodPost, "http://localhost/createuser?name=linus", strings.NewReader(postBody.Encode())) req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded") w := httptest.NewRecorder() HandleNewUser(w, req) if w.Code != http.StatusOK { t.Error("new user api error") } if w.Body.Len() == 0 { t.Error(" response is empty") } user := &model.UserInfo{} err := json.Unmarshal(w.Body.Bytes(), user) if err != nil { t.Error("response data error") } t.Logf("create user api response : %#v", user) }
使用的是httptest包,先是创建了一个请求,url包含了name参数,body里有say参数。然后再通过NewRecorder创建一个responseWriter,把这两个参数传递给我们的handler,再测试有没有返回我们想要的执行结果。
如果你使用的web服务框架是gin。测试gin handler的代码我写在了app2里。有时间你可以看一下,大致的代码:
func TestNewUserInfo(t *testing.T) { a := assert.New(t) router := gin.New() const path = "/newUserInfo" router.POST(path, NewUserInfo) body := url.Values{} body.Set("say", "hello world") rr, err := testutils.PostFormRequst(path + "?name=lp", router, body) a.Nil(err) user := &model.UserInfo{} err = json.Unmarshal(rr.Body.Bytes(), user) a.Nil(err) a.NotEqual(user.Name, "") a.NotEqual(user.Age, 0) t.Logf("%#v ", user) }
推荐几个第三方的库
有几个我常用的第三方库给大家推荐一下,相关的测试代码都写到 app2_thirdlib里了
github.com/stretchr/testify
github.com/jarcoal/httpmock
testify里有assert相信有其他语言基础的同学一定知道他是做什么的,断言处理比如
a.Nil(err) a.NotEqual(user.Name, "") a.NotEqual(user.Age, 0)
如果判断的结果为false则测试失败。
httpmock这个好玩,假如我们的项目有请求其他项目的api调用,但是我们没有源码,只知道返回结果。但是我们进行test测试时,要请求这个api。httpmock就是做这个用的,他们拦住我们的http请求,然后返回我们预置的response。
func TestUserRoleList(t *testing.T) { a := assert.New(t) // mock http testutils.HttpMockActivateNonDefault() httpmock.RegisterNoResponder( httpmock.NewStringResponder(http.StatusOK, fmt.Sprintf(` [ { "id": 1, "name": "a" }, { "id": 2, "name": "b" }, { "id": 3, "name": "c" } ] `))) defer httpmock.DeactivateAndReset() router := gin.New() const path = "/userRoleList" router.GET(path, UserRoleList) rr, err := testutils.GetRequst(path, router) a.Nil(err) a.Equal(rr.Result().StatusCode, http.StatusOK) roles := make([]model.UserRole, 0) err = json.Unmarshal(rr.Body.Bytes(), &roles) a.Nil(err) a.NotEqual(len(roles), 0) t.Logf("len of roles: %d ", len(roles)) }
我的UserRoleList方法调用了其他项目的api。httpmock会把这个http请求拦住,上面我们提前写好的数组。
大家可以下载我的源码,然后 go test ./... 一下试试